Fainted After Blood Draw
Fainted After Blood Draw - Effects, risks and recovery — stanford blood center. Warning signs that occur before. May 24, 2023 at 1:35 am. However, if you stand up too soon after fainting — within about 15 to 30 minutes —. However, if you stand up too soon after fainting — within about 15 to 30. Passing out from giving blood can be. Web fainting, or passing out — a temporary loss of consciousness also known as syncope — is caused by insufficient blood flow to the brain. Web if you have fainted at a blood draw before, you should ask to do your next blood draw lying down. Web most people who faint during blood draws are likely to present some signs and symptoms before they lose consciousness. Fainting after vaccines or blood tests is usually a result of pain or anxiety. Web when drawing blood or starting an i.v., ask the patient and anyone with them if he or she has a history of becoming faint at the sight of blood. Someone is considered to have syncope if they become unconscious. May 24, 2023 at 1:35 am. Chan school of public health. However, if you stand up too soon after fainting. You might need a blood draw for a. Although fainting has a variety of possible causes, it. Web if you have fainted at a blood draw before, you should ask to do your next blood draw lying down. Web passing out, fainting or vasovagal syncope is a sudden, temporary loss of consciousness. There are studies that suggest that the applied. 1 passing out is common when getting blood drawn. However, if you stand up too soon after fainting — within about 15 to 30. May 24, 2023 at 1:35 am. You can also reduce your likelihood of fainting by doing the following: Web when drawing blood or starting an i.v., ask the patient and anyone with them if he or. Someone is considered to have syncope if they become unconscious. Web what really happens to your body after you donate blood: Web vasovagal syncope is a type of fainting that happens when your nervous system reacts to a painful or stressful trigger. Web it’s hard to identify which patients will faint during a blood draw and which will not. Other. Recovery after a vasovagal episode generally begins in less than a minute. Web vasovagal syncope is a type of fainting that happens when your nervous system reacts to a painful or stressful trigger. Effects, risks and recovery — stanford blood center. Chan school of public health. Web if you have fainted at a blood draw before, you should ask to. 7 tips to avoid fainting from shots or blood tests. Web some people faint in response to the sight of blood or to an emotional upset. Fainting after vaccines or blood tests is usually a result of pain or anxiety. Someone is considered to have syncope if they become unconscious. Web passing out, fainting or vasovagal syncope is a sudden,. Web vasovagal syncope is a type of fainting that happens when your nervous system reacts to a painful or stressful trigger. Passing out from giving blood can be. May 24, 2023 at 1:35 am. Web what really happens to your body after you donate blood: There are some medical conditions that will leave certain people predisposed to fainting after giving. Never turn your back on a patient, especially after you. Web most people who faint during blood draws are likely to present some signs and symptoms before they lose consciousness. It happens to healthy patients, young, old, and even those accustomed to blood draws. Warning signs that occur before. Web worried about fainting during your blood donation? Someone is considered to have syncope if they become unconscious. Passing out from giving blood can be. Fainting after vaccines or blood tests is usually a result of pain or anxiety. 7 tips to avoid fainting from shots or blood tests. Web who is most likely to faint after giving blood? Web fainting during blood draws is relatively common and is triggered by a variety of factors, including anxiety, pain sensitivity, and a sudden drop in blood. You can also reduce your likelihood of fainting by doing the following: Web if you have fainted at a blood draw before, you should ask to do your next blood draw lying down. However,. Other common causes of fainting include standing for a long period of time and exposure to. Chan school of public health. Web recovery after a vasovagal episode generally begins in less than a minute. 7 tips to avoid fainting from shots or blood tests. Web most people who faint during blood draws are likely to present some signs and symptoms before they lose consciousness. Web when drawing blood or starting an i.v., ask the patient and anyone with them if he or she has a history of becoming faint at the sight of blood. Web it’s hard to identify which patients will faint during a blood draw and which will not. May 24, 2023 at 1:35 am. Vasovagal syncope is almost always triggered by something happening to you or around you. Web if you have fainted at a blood draw before, you should ask to do your next blood draw lying down. However, if you stand up too soon after fainting — within about 15 to 30 minutes —. You can also reduce your likelihood of fainting by doing the following: However, if you stand up too soon after fainting — within about 15 to 30. There are some medical conditions that will leave certain people predisposed to fainting after giving blood. You might need a blood draw for a. Someone is considered to have syncope if they become unconscious.
Why did you pass out during the blood draw?

Fear of Needles Top Tips to Avoid Fainting During Your Next Blood Draw

Phlebotomy and Patient Fainting Be Prepared
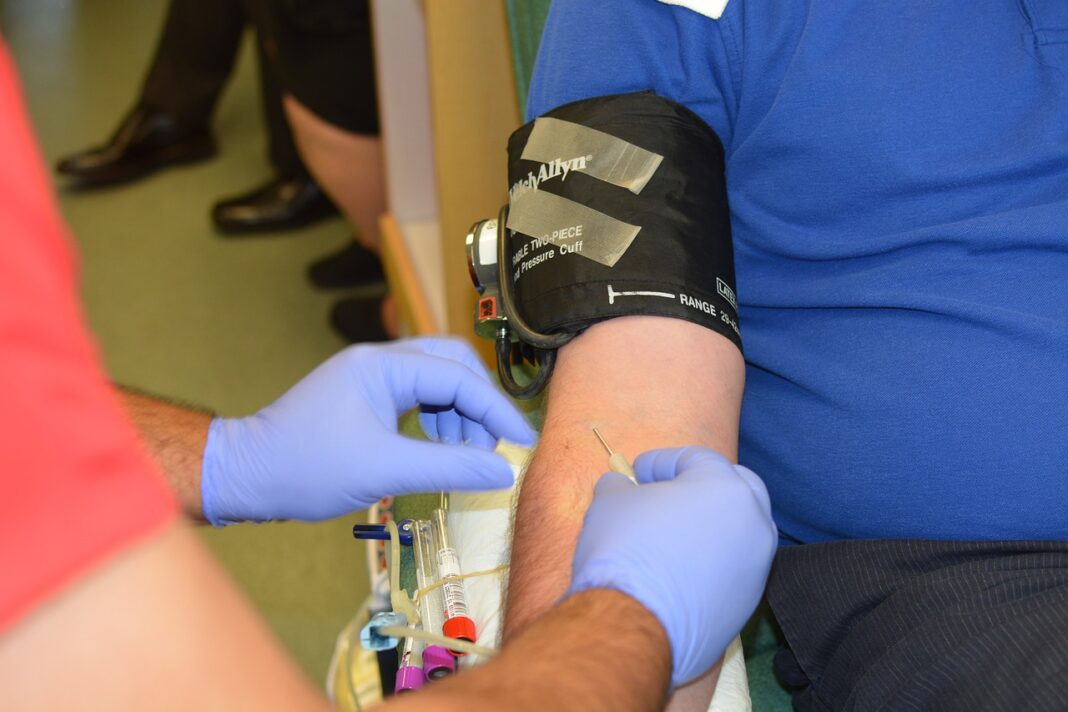
What to do if Faint after Blood Draw Healths Digest
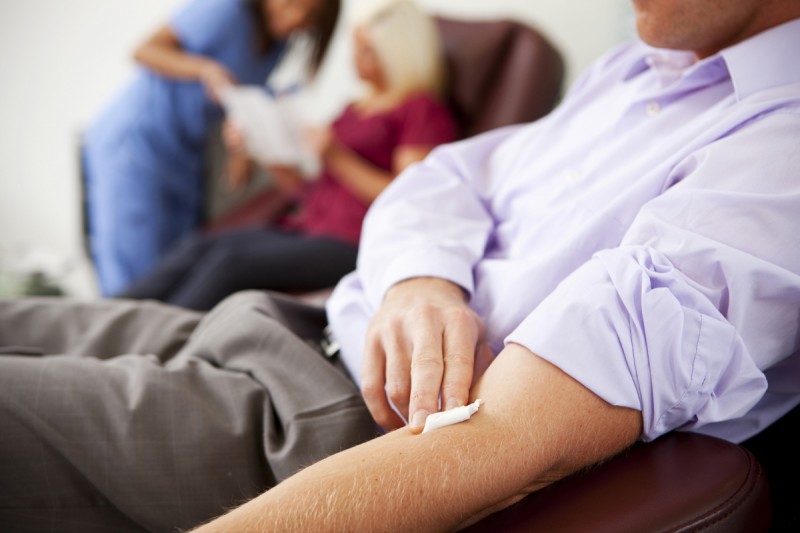
Fainting After Giving Blood Causes and Coping Methods New Health Advisor
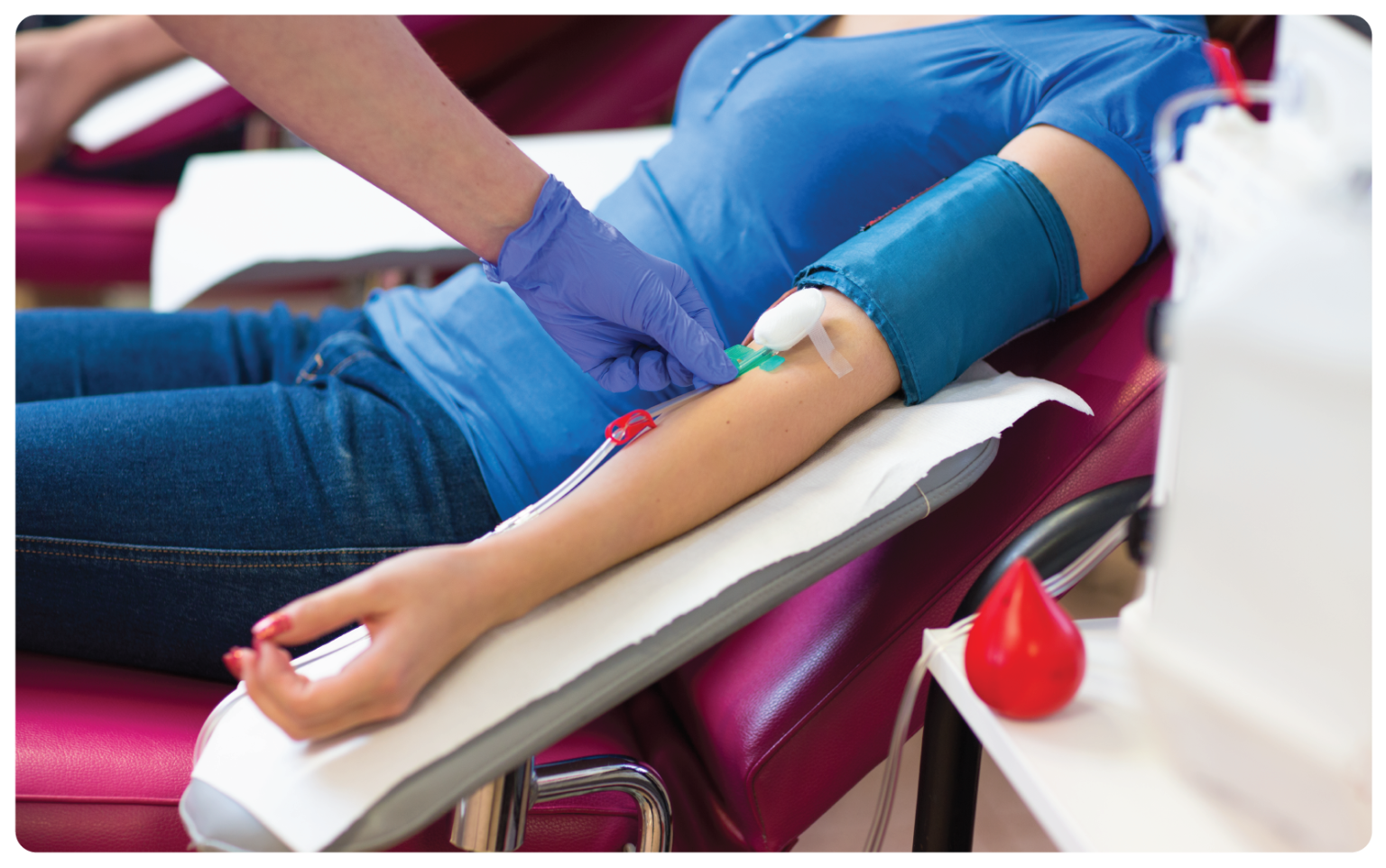
blood draw Clinical Research Glossary
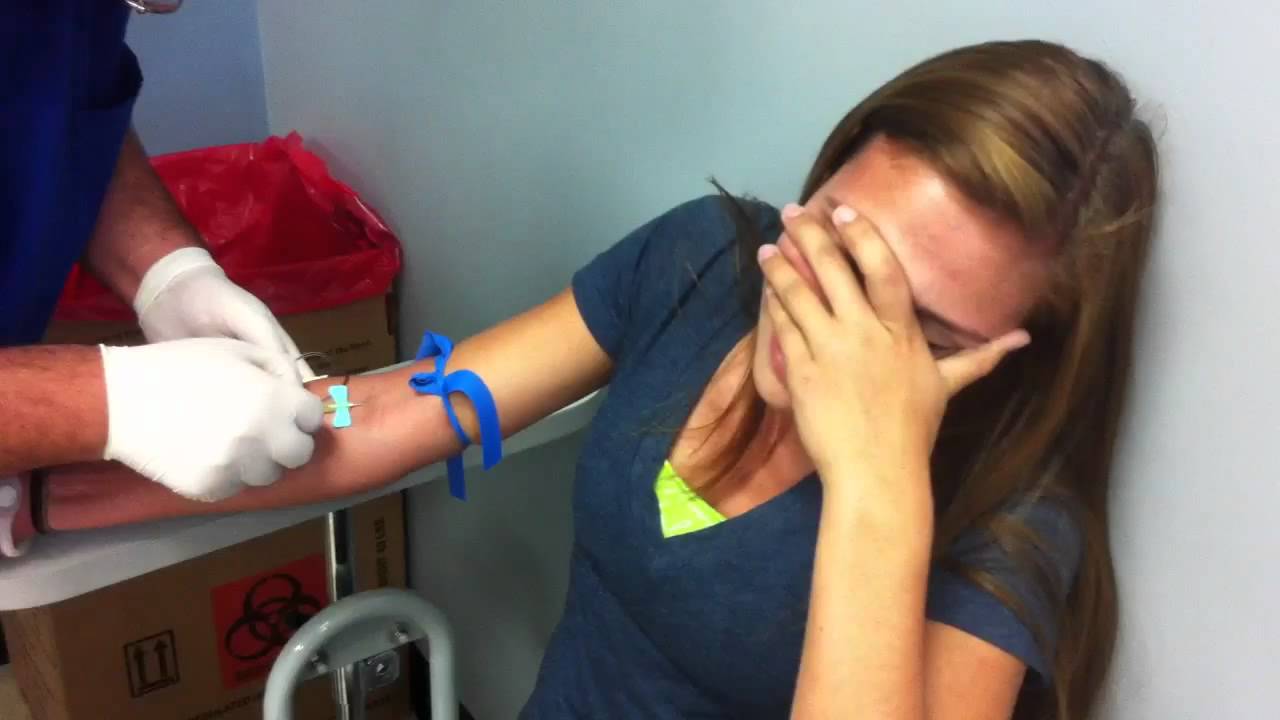
Miranda's blood test! YouTube

How To Draw Blood A StepbyStep Guide

9+ Fainting From Blood Draw TroyWessal
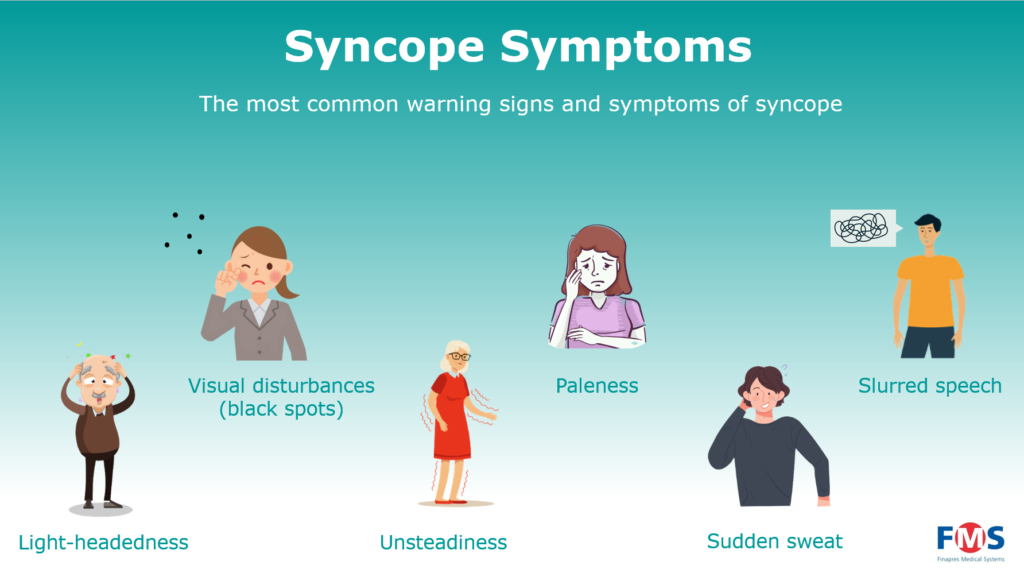
Blog post 1 "What You Need to Know About Syncope or Fainting"
Web Passing Out, Fainting Or Vasovagal Syncope Is A Sudden, Temporary Loss Of Consciousness.
Recovery After A Vasovagal Episode Generally Begins In Less Than A Minute.
Web Who Is Most Likely To Faint After Giving Blood?
Web Fainting, Or Passing Out — A Temporary Loss Of Consciousness Also Known As Syncope — Is Caused By Insufficient Blood Flow To The Brain.
Related Post: