Facet Referral Pattern
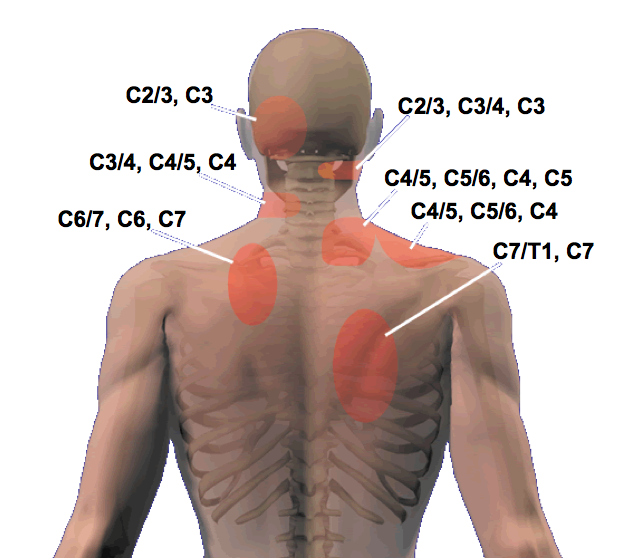
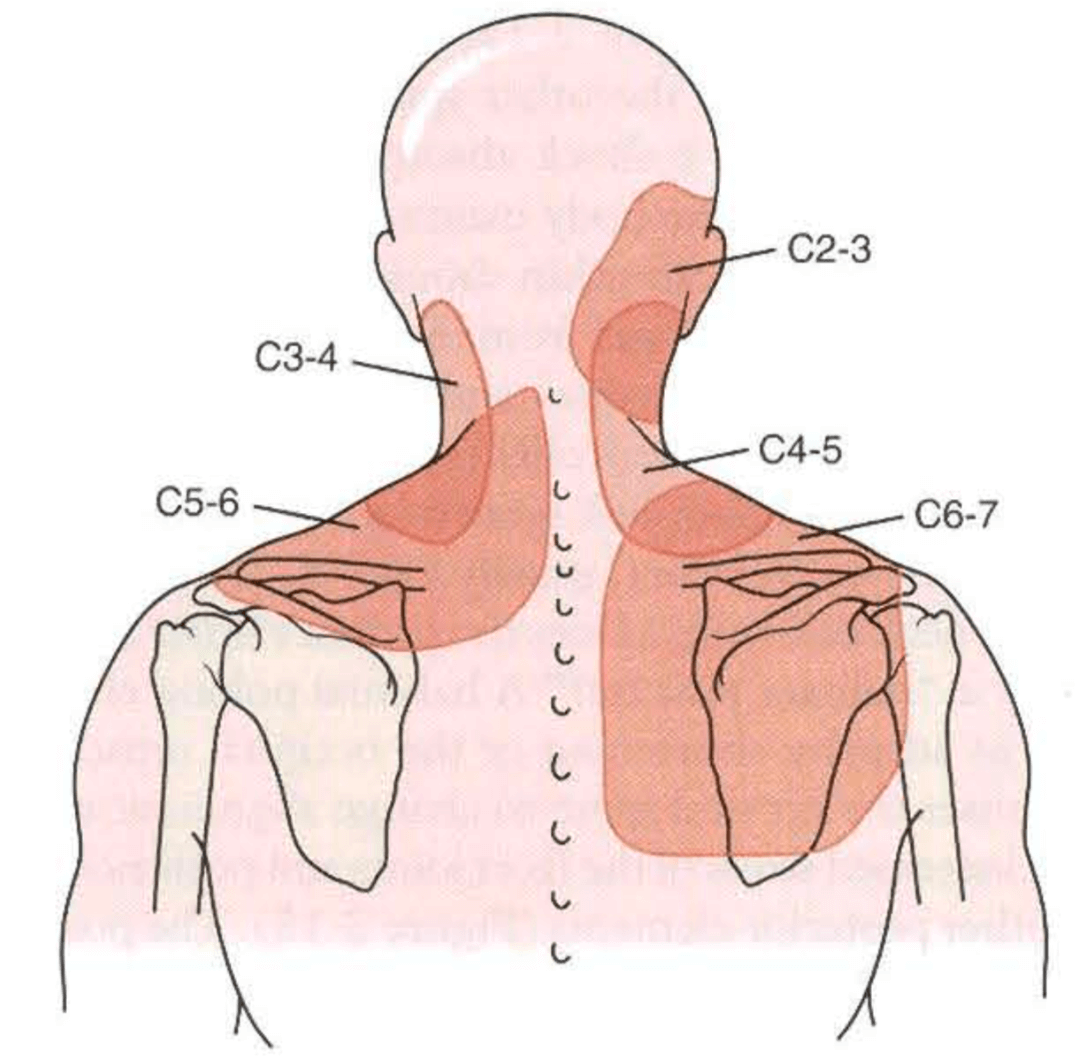
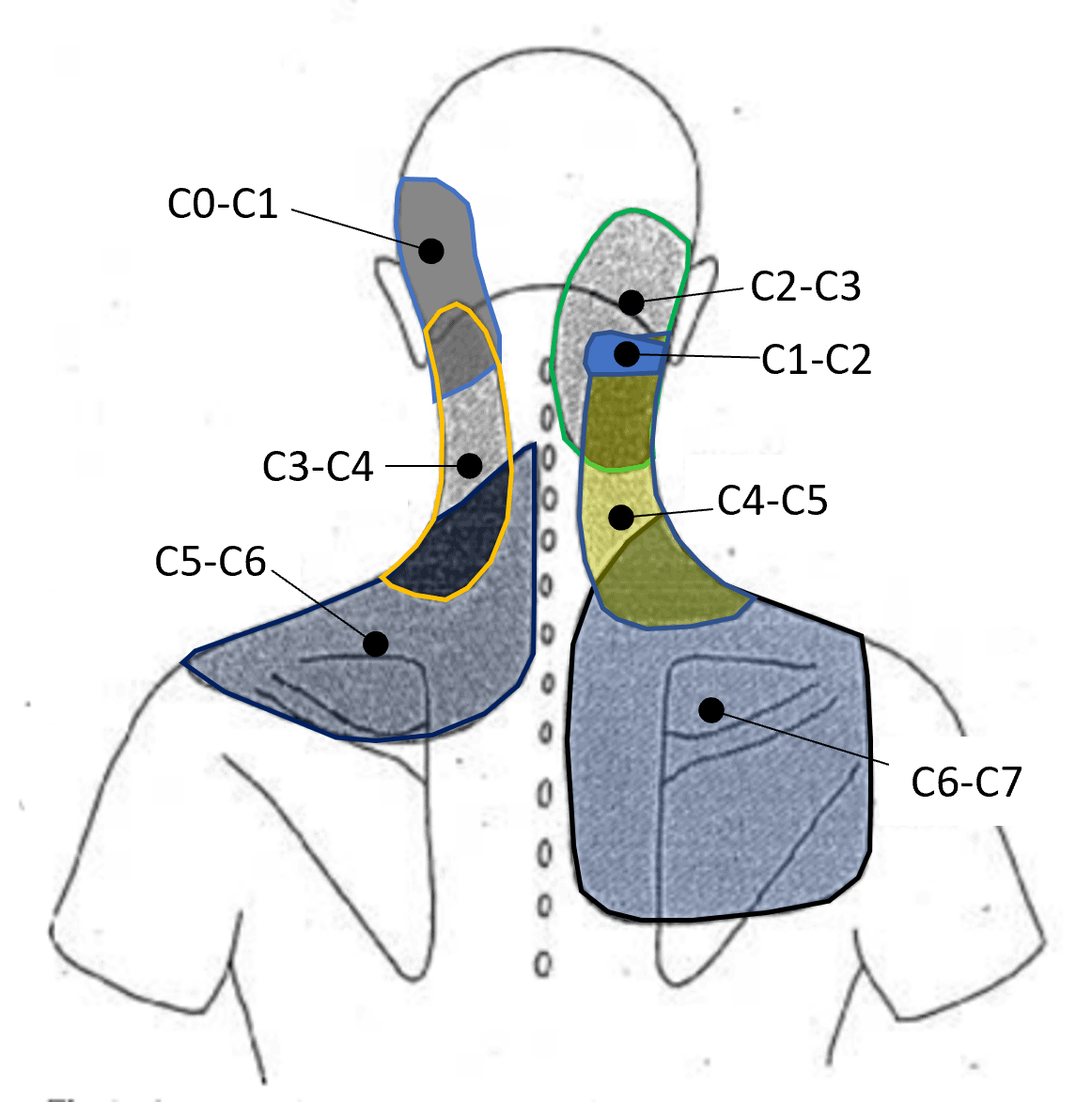
Facet Referral Pattern - Web the“pseudoradicular” referral patterns of the lumbar facet joints may mimic the pain felt from a herniated disc and may make differentiating between the two conditions difficult. Web article 16 january 2020. Medical history, referred pain patterns, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging studies (standard radiographs, mri, ct and spect) may suggest but not confirm lfj syndrome as a. In the lumbar spine, the referred pain is typically around the buttock and thigh and is rarely felt below the knee. A comprehensive recognition of referred pain is important for clinicians when dealing with it. This pain is usually worse in the morning or after periods of inactivity. Web the pain is usually unilateral and radiates in a facet joint referral pattern. Web the referral zones were found to be more localised and smaller after electrical stimulation of medial branches of l1 to l4 posterior primary rami and l5 dorsal ramus in asymptomatic volunteers. Pain usually increases with extension ('closing down' of the joint) and reduces with flexion ('opening' of the joint). The most common areas of referred pain from the lumbar facets are noted in black (low back) in descending order to the lightest regions (foot is least common). It can also be felt in the abdomen and/or pelvis. Web facet arthritis can be associated with pain and stiffness. This pain is usually worse in the morning or after periods of inactivity. Radicular symptoms may be evident in the presence of facetal hypertrophy, synovial cysts and osteophytes. Web each joint has a distinct referral pattern illustrated below. Web facet syndrome included local pain and pseudo radicular radiation with variability of the distribution of referral patterns of pain. Diagnostic procedures [edit | edit source] diagnostic medial branch blocks are considered the gold standard approach to diagnose facet joint pain. Web lumbar facet syndrome refers to a dysfunction at the level of the posterior facet joints of the spine.. A thoough understanding of the mechanism of injury is essential. Osteoarthritis (oa) of the spine involves the facet joints, otherwise known as the zygapophyseal joints. Web the referral zones were found to be more localised and smaller after electrical stimulation of medial branches of l1 to l4 posterior primary rami and l5 dorsal ramus in asymptomatic volunteers. These joints together. Web the majority of these studies have not found reliable referral patterns of fj pain. Pain usually increases with extension ('closing down' of the joint) and reduces with flexion ('opening' of the joint). These joints together with the disc form the intervertebral joint. Injury to the joint is not commonly detected by conventional radiographic studies. Web facet syndrome included local. Web the most frequent form of facet pathology is lfj oa. The key at the bottom of the figure legend is listed in. Referral patterns have been described as seen in fig. Web palpation of tender points along paravertebral regions and transverse processes as well as any pain referral patterns from trigger points adds to the formulation of a focused. Web lumbar facet pain referral patterns. For example, pain from cervical (neck) facet arthritis may radiate toward the back of the head, ear, or shoulder. Web the most frequent form of facet pathology is lfj oa. These paired diarthrodial joints in the posterior. Web referral patterns for pain arising from ao and aa joints. Web symptoms and diagnosis of facet joint disorders. Web each joint has a distinct referral pattern illustrated below. Web lumbar facet pain referral patterns. Web facet arthritis can be associated with pain and stiffness. Web the most frequent form of facet pathology is lfj oa. The pain from an arthritic facet joint is often felt in the spine near the joint, but it can also refer to other locations. Diagnostic procedures [edit | edit source] diagnostic medial branch blocks are considered the gold standard approach to diagnose facet joint pain. Web palpation of tender points along paravertebral regions and transverse processes as well as any. Web lumbar facet pain referral patterns. Web each joint has a distinct referral pattern illustrated below. The most common areas of referred pain from the lumbar facets are noted in black (low back) in descending order to the lightest regions (foot is least common). These facet joints become the common targets of neck straightening. Causes of facet joint syndrome. Web the most frequent form of facet pathology is lfj oa. A comprehensive recognition of referred pain is important for clinicians when dealing with it. Each facet joint can refer pain to a number of locations, with a great deal of overlap between the different levels. This pain is usually worse in the morning or after periods of inactivity. Referral. Web referred pain is a common but less understood symptom that originates from somatic tissues. When pain is “referred,” it means it appears in a different part of the body than the actual source of the pain. This pain is usually worse in the morning or after periods of inactivity. Web each joint has a distinct referral pattern illustrated below. Pain usually increases with extension ('closing down' of the joint) and reduces with flexion ('opening' of the joint). Web palpation of tender points along paravertebral regions and transverse processes as well as any pain referral patterns from trigger points adds to the formulation of a focused treatment plan. Web pain referral patterns from the lumbar facet joints. Referral patterns have been described as seen in fig. Striped areas (hash marks) represent overlapping cervical facet joint pain maps. Web in the cervical spine the ivd and facet joints are innervated by the same spinal segment, making it difficult to determine whether both structures are implicated as the source of nociception, or, if one structure is sensitised through means of. For example, pain from cervical (neck) facet arthritis may radiate toward the back of the head, ear, or shoulder. The most commonly affected cervical spine levels are c5, c6 and c7. Web the most frequent form of facet pathology is lfj oa. The most common areas of referred pain from the lumbar facets are noted in black (low back) in descending order to the lightest regions (foot is least common). Changes at the level of the posterior facet joints can influence the disc and vice versa. Fj pain may be referred distally into the lower limb, thereby mimicking sciatica.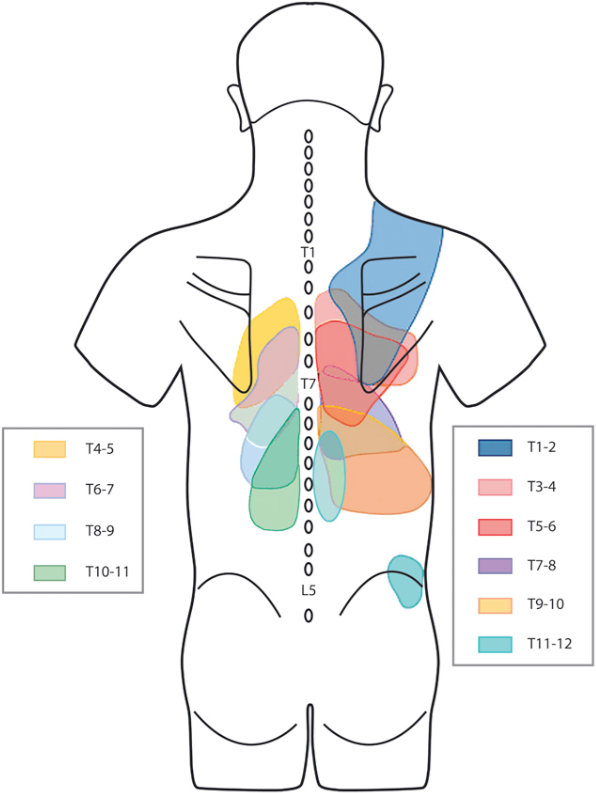
Details for Thoracic Facet Referral Pain Patterns and Related Queries

(PDF) Consensus practice guidelines on interventions for cervical spine

Illustration of distribution pattern related to facet joint pain
Cloward sign & Cervical Referral Patterns Modern Manual Therapy Blog
Neck pain treatment Manor Chiropractic

Cervical Facet Referral Patterns Bead Pattern (Free)
Cervical Facet Joint Referral Patterns Diagram Quizlet

Consensus practice guidelines on interventions for cervical spine
![Facet referral patterns of Mooney and Robertson [31]. Download](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228329346/figure/fig21/AS:667206794883077@1536085904587/Zones-of-Head-in-Jinkins-2004_Q640.jpg)
Facet referral patterns of Mooney and Robertson [31]. Download
What's the Purpose of a Neck Facet Injection? Regenexx
These Paired Diarthrodial Joints In The Posterior.
Diagnostic Procedures [Edit | Edit Source] Diagnostic Medial Branch Blocks Are Considered The Gold Standard Approach To Diagnose Facet Joint Pain.
Web Referral Patterns For Pain Arising From Ao And Aa Joints.
These Facet Joints Become The Common Targets Of Neck Straightening.
Related Post: