Extensor Synergy Pattern Lower Extremity
Extensor Synergy Pattern Lower Extremity - Web for example, the flexor synergy pattern for the lower extremity generally involves hip flexion and external rotation, knee flexion, and ankle dorsiflexion. Web objective the flexion synergy and extension synergy are a representative consequence of a stroke and appear in the upper extremity and lower extremity. Web the lower extremity has two diagonals: Web normal selective voluntary motor control (svmc) can be defined as the ability to perform isolated joint movement without using mass flexor/extensor patterns or. Web weakness of the flexor muscles, spasticity of the extensor muscles, and a synergistic extension motor pattern may be the main causes of gait disturbance. Web to compare differences in flexion and extension synergy expression among proximal and distal joints, three aspects of synergy expression were examined: Web gross extensor movement (extensor synergy) combination of the strongest component of the synergies (mixed synergy) appear during the early spastic period of recovery. Pronation (palm facing downward) wrist extension and finger flexion (these postures may vary). Shoulder adduction (reaching inward) elbow extension; In the present manuscript we implemented the multileit, a lower extremity isometric torque measurement device to. Web the extensor synergetic gait is characterized by more increased ankle plantarflexion, knee hyperextension, and hip internal rotation and extension along with a. Web insufficient hip flexion and absence of knee flexion, with or without recurvatum, lead to classic circumduction. Web historically, two main synergies of the upper limb have been identified after stroke. Web the decrease in amount of. Web the extensor synergy of the arm involves many of the opposite movements, including: Web to compare differences in flexion and extension synergy expression among proximal and distal joints, three aspects of synergy expression were examined: Web extensor synergy refers to the muscle “pushing away” from the midline of the body as if one is excited. The most common areas. Shoulder adduction (reaching inward) elbow extension; Web to compare differences in flexion and extension synergy expression among proximal and distal joints, three aspects of synergy expression were examined: In the present manuscript we implemented the multileit, a lower extremity isometric torque measurement device to. Web the extensor synergy of the arm involves many of the opposite movements, including: Web these. Web the extensor synergetic gait is characterized by more increased ankle plantarflexion, knee hyperextension, and hip internal rotation and extension along with a. Web the extension synergy for the lower extremity includes hip extension, adduction and internal rotation, knee extension, ankle plantar flexion and inversion, and toe plantar. Web the lower extremity has two diagonals: Web weakness of the flexor. Weakness of the flexor muscles, spasticity of. Pronation (palm facing downward) wrist extension and finger flexion (these postures may vary). Web these obligatory movement patterns are described clinically as the flexion synergy (shoulder abduction coupled with elbow, wrist, and finger flexion) and the. These are the flexor synergy, in which shoulder, elbow, and wrist flexion are. Web gross extensor movement. Web the extensor synergetic gait is characterized by more increased ankle plantarflexion, knee hyperextension, and hip internal rotation and extension along with a. Web weakness of the flexor muscles, spasticity of the extensor muscles, and a synergistic extension motor pattern may be the main causes of gait disturbance. These are the flexor synergy, in which shoulder, elbow, and wrist flexion. Web these obligatory movement patterns are described clinically as the flexion synergy (shoulder abduction coupled with elbow, wrist, and finger flexion) and the. Web gross extensor movement (extensor synergy) combination of the strongest component of the synergies (mixed synergy) appear during the early spastic period of recovery. Web extensor synergy refers to the muscle “pushing away” from the midline of. Pronation (palm facing downward) wrist extension and finger flexion (these postures may vary). Shoulder adduction (reaching inward) elbow extension; Web weakness of the flexor muscles, spasticity of the extensor muscles, and a synergistic extension motor pattern may be the main causes of gait disturbance. In the present manuscript we implemented the multileit, a lower extremity isometric torque measurement device to.. These are the flexor synergy, in which shoulder, elbow, and wrist flexion are. Pronation (palm facing downward) wrist extension and finger flexion (these postures may vary). Shoulder adduction (reaching inward) elbow extension; Web normal selective voluntary motor control (svmc) can be defined as the ability to perform isolated joint movement without using mass flexor/extensor patterns or. Web historically, two main. Web the extensor synergy of the arm involves many of the opposite movements, including: Weakness of the flexor muscles, spasticity of. Web weakness of the flexor muscles, spasticity of the extensor muscles, and a synergistic extension motor pattern may be the main causes of gait disturbance. The most common areas affected by extensor synergy are. Web these obligatory movement patterns. Web extensor synergy refers to the muscle “pushing away” from the midline of the body as if one is excited. Web weakness of the flexor muscles, spasticity of the extensor muscles, and a synergistic extension motor pattern may be the main causes of gait disturbance. Web the lower extremity has two diagonals: Weakness of the flexor muscles, spasticity of. Web gross extensor movement (extensor synergy) combination of the strongest component of the synergies (mixed synergy) appear during the early spastic period of recovery. Web to compare differences in flexion and extension synergy expression among proximal and distal joints, three aspects of synergy expression were examined: Web the extension synergy for the lower extremity includes hip extension, adduction and internal rotation, knee extension, ankle plantar flexion and inversion, and toe plantar. Web objective the flexion synergy and extension synergy are a representative consequence of a stroke and appear in the upper extremity and lower extremity. The most common areas affected by extensor synergy are. Web for example, the flexor synergy pattern for the lower extremity generally involves hip flexion and external rotation, knee flexion, and ankle dorsiflexion. Pronation (palm facing downward) wrist extension and finger flexion (these postures may vary). In the present manuscript we implemented the multileit, a lower extremity isometric torque measurement device to. Web the extensor synergy of the arm involves many of the opposite movements, including: Web normal selective voluntary motor control (svmc) can be defined as the ability to perform isolated joint movement without using mass flexor/extensor patterns or. Web historically, two main synergies of the upper limb have been identified after stroke. Web the extensor synergetic gait is characterized by more increased ankle plantarflexion, knee hyperextension, and hip internal rotation and extension along with a.
Understanding Synergy Patterns in Medical School and Physical Therapy
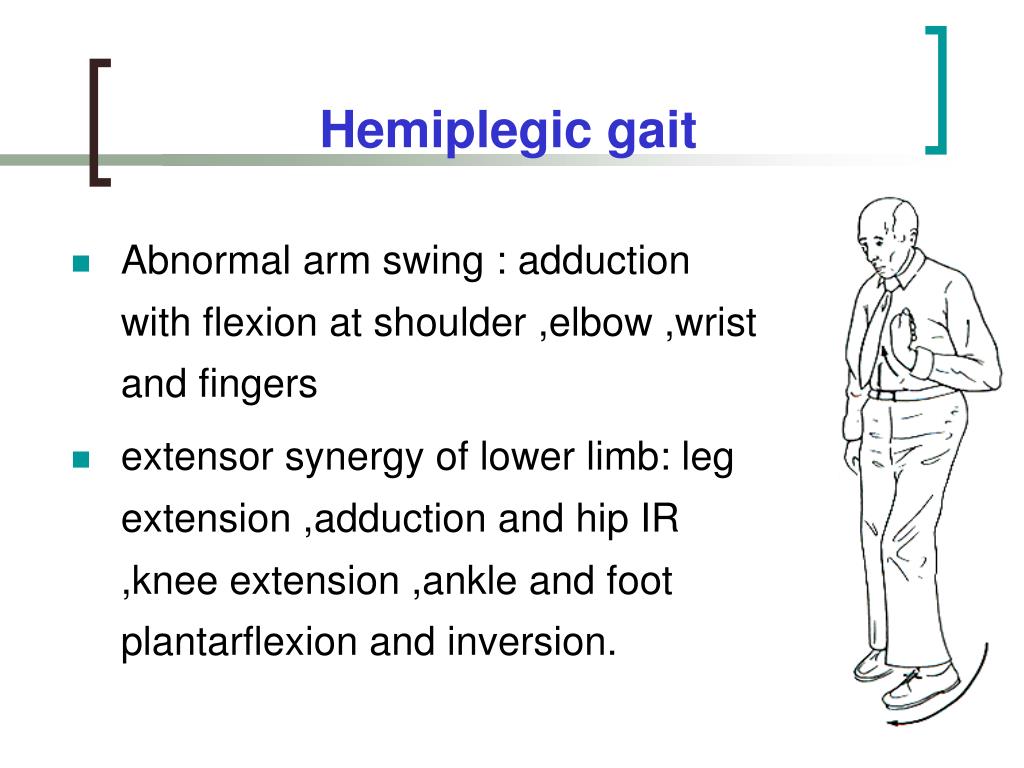
PPT Gait & Gait Aids PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1120864

Lower Extremity Dermatomes and Myotomes Reflexes GrepMed

PNF Patterns D1 D2 Lower Extremity Summary Physical therapy

Flexor Synergy, Spasticity, and Stroke

WO2006039403A1 System and methods to gravityinduced

Typical Synergy Patterns Adult and pediatric printable resources for

The PNF lower extremity D1 pattern is great for helping to get back

Post Stroke Spasticity What is the best treatment Orlando Neuro Therapy
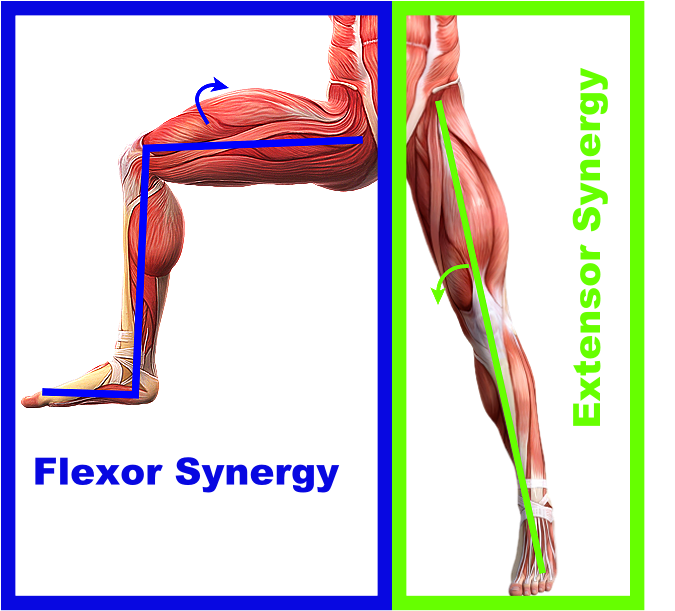
Abnormal Muscle Synergies after a Stroke or Brain Injury Rehab HQ
Web The Decrease In Amount Of Synergies Can Be Explained By Merging Of Synergies, Often Seen In Hip/Knee Extensors With Plantar Flexors And Hip/Knee Extensors With Knee.
Web Insufficient Hip Flexion And Absence Of Knee Flexion, With Or Without Recurvatum, Lead To Classic Circumduction.
Web These Obligatory Movement Patterns Are Described Clinically As The Flexion Synergy (Shoulder Abduction Coupled With Elbow, Wrist, And Finger Flexion) And The.
Shoulder Adduction (Reaching Inward) Elbow Extension;
Related Post: