Eruption Pattern Permanent Teeth
Eruption Pattern Permanent Teeth - Web eruption of permanent and primary teeth follows a particular time sequence. What matters most is that you can spot any changes and communicate with your child’s dentist about what’s. Web the eruption of teeth usually occurs symmetrically in each arch, with mandibular teeth erupting before the same maxillary teeth. Your child may not follow the average regime, but with the proper monitoring and guidance, it won’t matter. Learn about permanent teeth coming in and how to care for them. Web an understanding of the normal sequence and patterns of tooth eruption is the foundation for identifying and treating children with abnormal dental development and optimizing their oral health. The primary dentition is eventually lost and replaced by the permanent dentition. Web this chapter considers the development and eruption of the teeth, specific chronologies of both the primary and permanent human dentitions, dental age, tooth formation standards, and applications to dental practice (e.g., an understanding of both the chronology of dental development so that surgical intervention does not harm normal. Most children have a full set of primary teeth by. Teeth vary in size, shape and their location in the jaws. Web as a general rule, four teeth erupt for every six months of life, mandibular teeth erupt before maxillary teeth, and teeth erupt sooner in females than males. Web the mandibular central incisors and the first molars are the first to erupt, replacing their primary predecessors while the third molar teeth are the last to erupt in the late teen. Web lower teeth usually erupt before upper teeth. Web premature or early tooth eruption refers to the eruption of teeth before their expected schedule. What matters most is that you can spot any changes and communicate with your child’s dentist about what’s. Teeth already present in the oral cavity at birth are termed natal teeth, while those that erupt within. Web the eruption of teeth usually occurs symmetrically in each arch, with mandibular teeth erupting before the same maxillary teeth. Learn more about the differences with primary and permanent teeth structures. Primary teeth are smaller in size and whiter in color than the permanent teeth that will follow. Web your child’s permanent teeth erupt in a predictable pattern. The pattern. Web this chapter considers the development and eruption of the teeth, specific chronologies of both the primary and permanent human dentitions, dental age, tooth formation standards, and applications to dental practice (e.g., an understanding of both the chronology of dental development so that surgical intervention does not harm normal. Web the first permanent molars usually erupt between ages 6 and. Web the first permanent molars usually erupt between ages 6 and 7 years. Know which children need to be referred and when and which children can be monitored. This chapter is an overview of the process of active eruption, the morphological changes, and the chronology of tooth eruption. The sequence of eruption is more important than the timing which varies. The typical anatomy and development of. Web the first permanent molars usually erupt between ages 6 and 7 years. Teeth vary in size, shape and their location in the jaws. Web the mandibular central incisors and the first molars are the first to erupt, replacing their primary predecessors while the third molar teeth are the last to erupt in the. What matters most is that you can spot any changes and communicate with your child’s dentist about what’s. Learn about permanent teeth coming in and how to care for them. The prevalence of ectopic eruption is different for individual teeth. The sequence of eruption is more important than the timing which varies greatly in both primary and permanent teeth. This. Teeth in both jaws usually erupt in pairs — one on the right and one on the left. This chapter is an overview of the process of active eruption, the morphological changes, and the chronology of tooth eruption. Primary teeth are smaller in size and whiter in color than the permanent teeth that will follow. Web the primary teeth gradually. Teeth already present in the oral cavity at birth are termed natal teeth, while those that erupt within the first month of life are called neonatal teeth. Web the primary teeth eruption timeline is a graphic depiction of the sequence in which each tooth erupts in your child’s mouth. Web this chapter considers the development and eruption of the teeth,. Teeth already present in the oral cavity at birth are termed natal teeth, while those that erupt within the first month of life are called neonatal teeth. Web premature or early tooth eruption refers to the eruption of teeth before their expected schedule. 6 the permanent dentition consists of 32 teeth including 4 central incisors (8, 9, 24, 25), 4. Teeth already present in the oral cavity at birth are termed natal teeth, while those that erupt within the first month of life are called neonatal teeth. 6 the permanent dentition consists of 32 teeth including 4 central incisors (8, 9, 24, 25), 4 lateral incisors (7, 10, 23, 26), 4 canines (6, 11. The sequence of eruption is more important than the timing which varies greatly in both primary and permanent teeth. Web the chart and photograph identify the names of the permanent teeth and provide the approximate ages at which you can expect the teeth to erupt. Learn more about the differences with primary and permanent teeth structures. Web an understanding of the normal sequence and patterns of tooth eruption is the foundation for identifying and treating children with abnormal dental development and optimizing their oral health. The aetiology behind this ectopic condition is intensively discussed. Web your child’s permanent teeth erupt in a predictable pattern. The primary dentition is eventually lost and replaced by the permanent dentition. The typical anatomy and development of. Web as a general rule, four teeth erupt for every six months of life, mandibular teeth erupt before maxillary teeth, and teeth erupt sooner in females than males. During primary dentition, the tooth buds of permanent teeth develop inferior to the primary teeth, close to the palate or tongue. Teeth in both jaws usually erupt in pairs — one on the right and one on the left. Both maxillary and mandibular arch has similar number of teeth, beginning from central incisors to molars. Web permanent teeth eruption chart. The permanent molars are referred to by their anticipated age of eruption.
Depicting the sequence of eruption of permanent te

The Stages of Tooth Eruption Maestri Family Dental
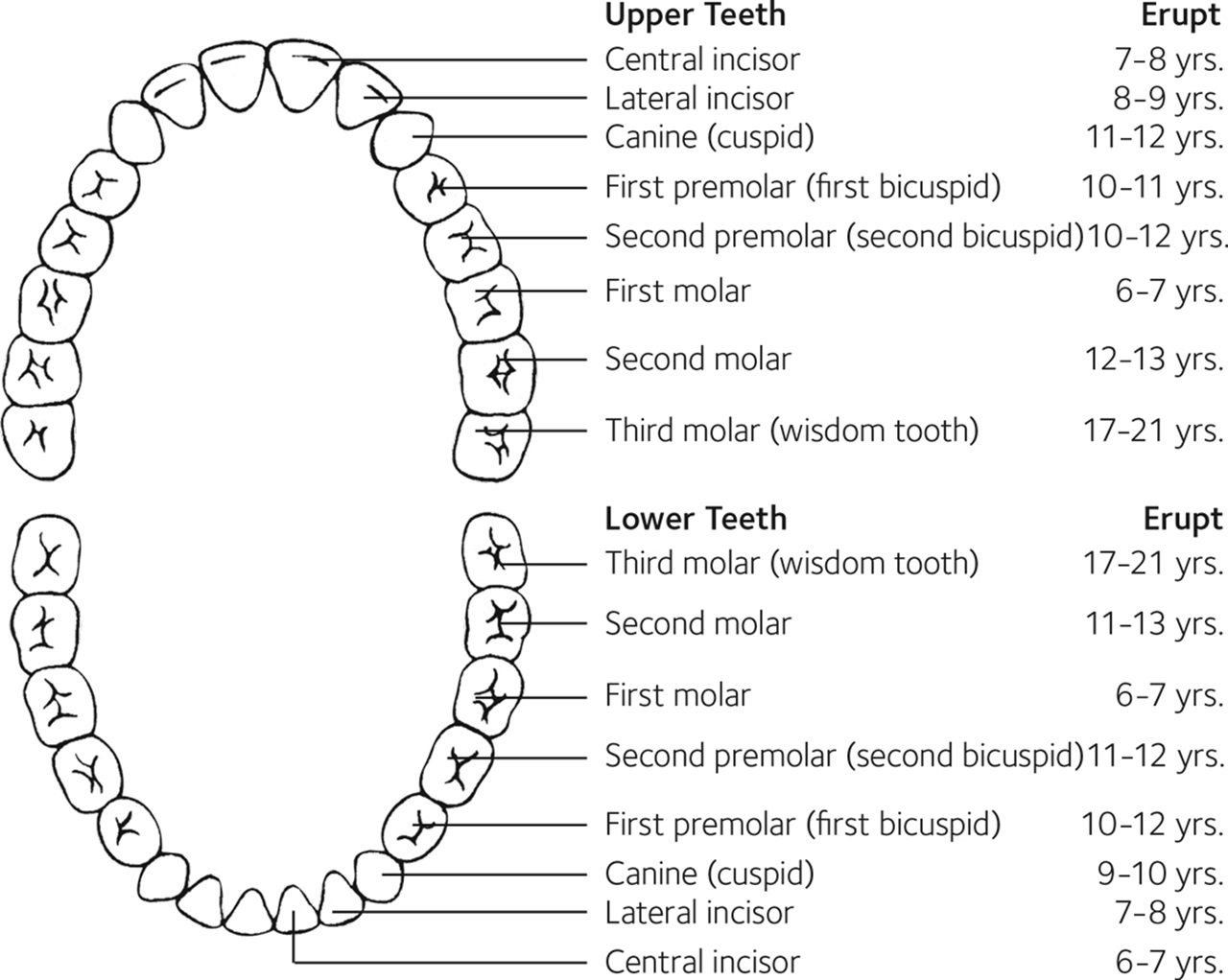
Eruption Charts MouthHealthy Oral Health Information from the ADA
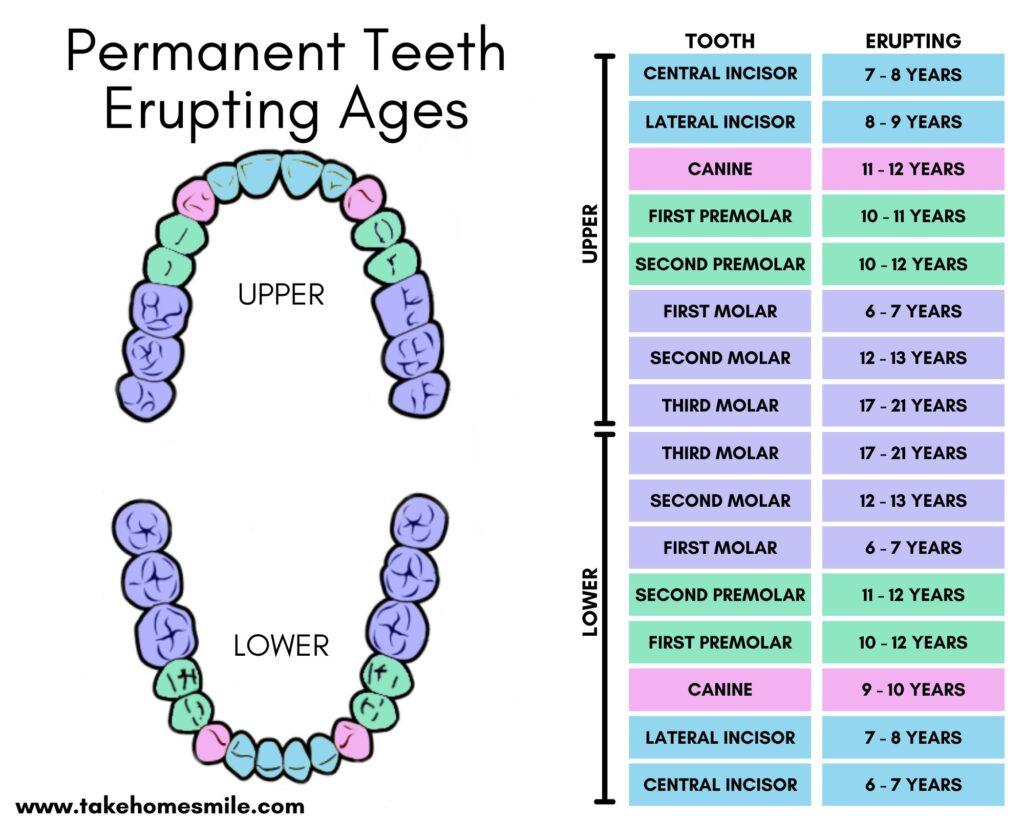
Eruption of Teeth Chart for Primary and Adult Teeth Take Home Smile
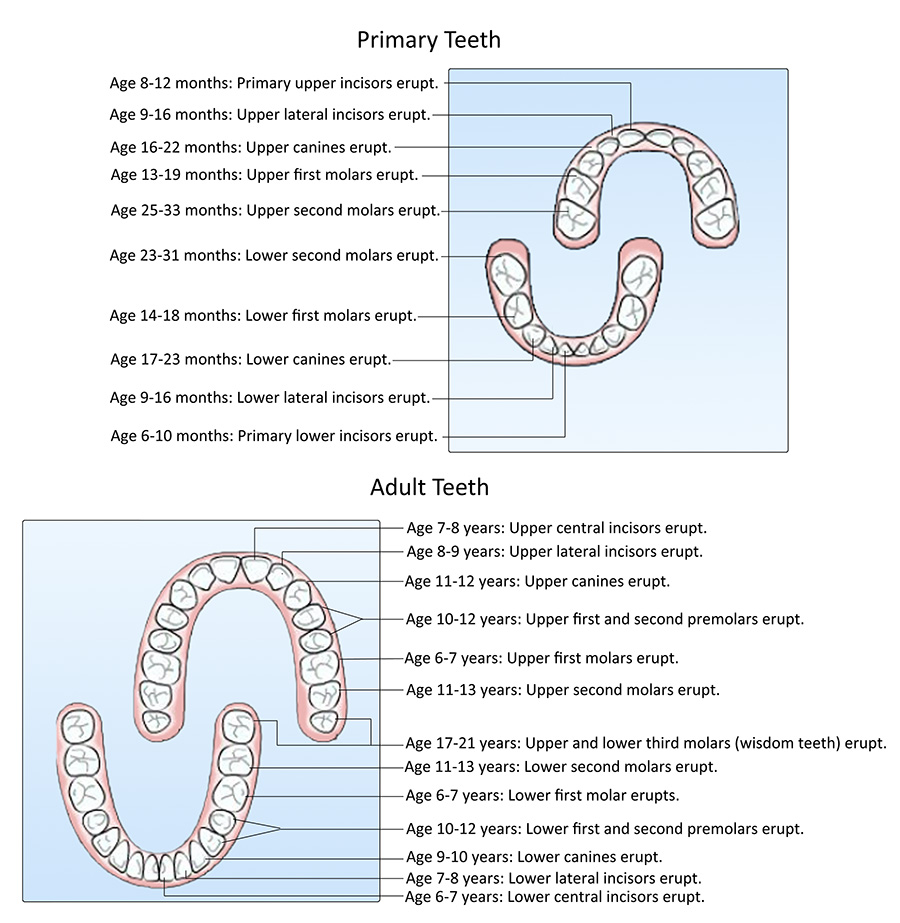
Tooth Eruption Chart Brooklawn Dental Health Center New Bedford MA
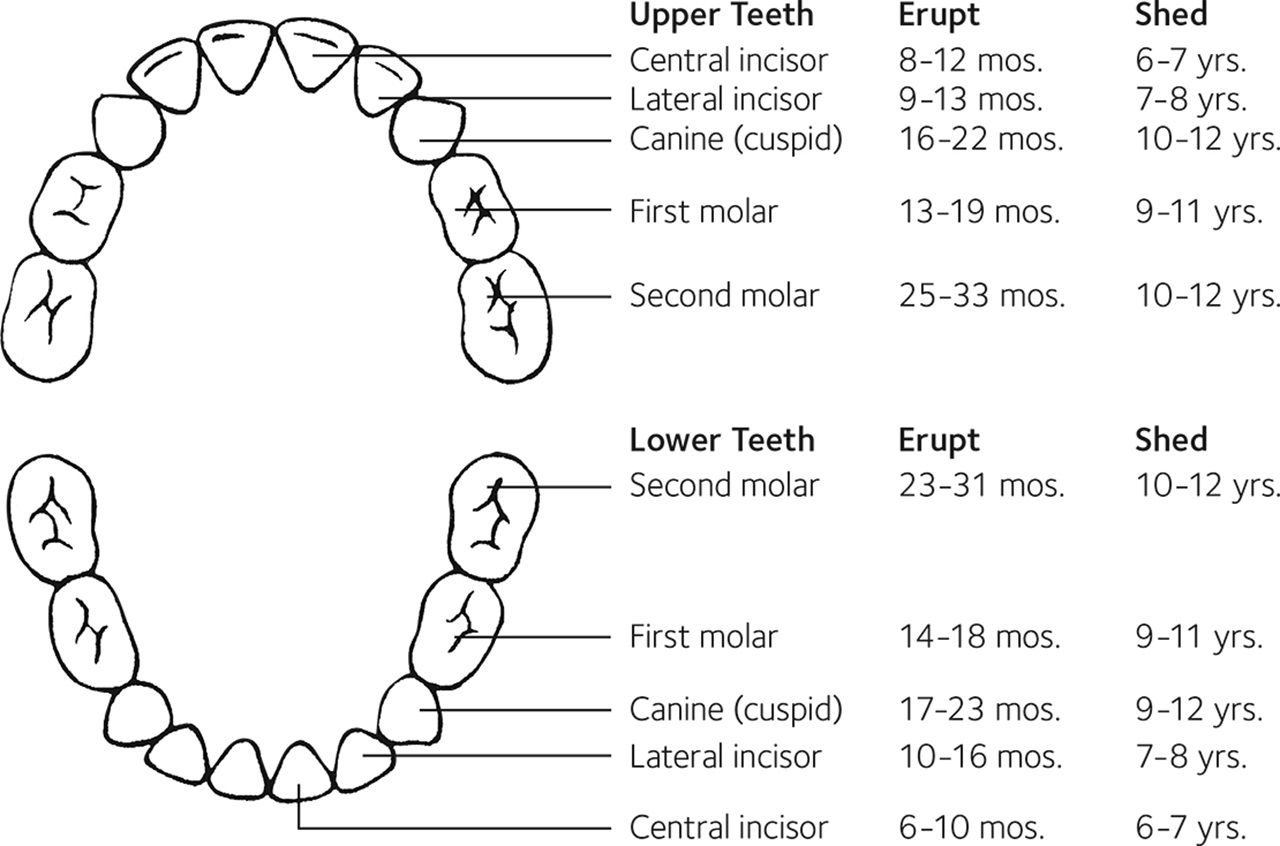
Eruption Charts MouthHealthy Oral Health Information from the ADA

Baby Primary & Permanent Tooth Eruption Chart Babymommytime Top

Permanent Teeth Eruption Timetable • SORIdent

Permanent teeth eruption and development the ortho guide

Teeth names and permanent teeth eruption chart with accurate notation
The First Permanent Teeth To Emerge Are Usually The Maxillary And Mandibular First Molars.
The Pattern Of Eruption Differs Slightly Between Maxillary And Mandibular Arch.
This Chapter Is An Overview Of The Process Of Active Eruption, The Morphological Changes, And The Chronology Of Tooth Eruption.
Every Single Permanent Tooth Can Erupt Ectopically.
Related Post: