Equinus Gait Pattern
Equinus Gait Pattern - Web this study aimed to evaluate gait outcomes and strength following the surgical correction of equinus in cerebral palsy (cp) based on different surgical procedures. Gait type description treatment / management type 1 true equinus this gait pattern is characterized by toe walking due to spasticity in the calf muscles which causes the It is caused by spasticity or contracture in the calf muscle and achilles tendon. Web equinus is a condition in which the upward bending motion of the ankle joint is limited. Within this gait type, there are two subcategories: Equinus plus recurvatum knee and extended hip. Web common gait deviations in cp can be grouped into the gait patterns of spastic hemiplegia (drop foot, equinus with different knee positions) and spastic diplegia (true equinus, jump, apparent equinus and crouch) to facilitate communication. Equinus can occur in one or both feet. (steppage gait, equine gait) seen in patients with foot drop (weakness of foot dorsiflexion), the cause of this gait is due to an attempt to lift the leg high enough during walking so that the foot does not drag on the floor. Web as with hemiplegic cerebral palsy, there are also four commonly observed types of gait patterns which impact a person’s walking ability. A significant degree of knee flexion occurred ranging from 7° to 22° ( p = 0.001). Web this study aimed to evaluate gait outcomes and strength following the surgical correction of equinus in cerebral palsy (cp) based on different surgical procedures. “drop foot”, “true equinus”, “apparent equinus” “genu recurvatum”, “jump gait”, and “crouch gait”. (steppage gait, equine gait) seen in. Web equinus deformity of the foot is a common feature of hemiplegia, which impairs the gait pattern of patients. Within this gait type, there are two subcategories: Gait type description treatment / management type 1 true equinus this gait pattern is characterized by toe walking due to spasticity in the calf muscles which causes the Several approaches have been suggested. Web this study aimed to evaluate gait outcomes and strength following the surgical correction of equinus in cerebral palsy (cp) based on different surgical procedures. Web the split second effect, described here, defines exactly how the silent equinus contracture creates incremental and significant damage and injury to the human foot and ankle resulting in a wide variety of pathological conditions.. The wgh classification system mainly focuses on pathologies of the ankle joint and. Web watch this short video simulating gait with an equinus deformity. Web equinus deformity of the foot is a common feature of hemiplegia, which impairs the gait pattern of patients. Web the split second effect, described here, defines exactly how the silent equinus contracture creates incremental and. Web one of the aims of orthotic management is to produce a more normal gait pattern by positioning joints in the proper position to reduce pathological reflex or spasticity. True equinus refers to a gait characterized by plantarflexion of the foot and ankle with respect to the leg and may be seen in stance and/or the swing phase of gait.. Web failure to recognize apparent equinus is the most common error in observational gait analysis and is of more than academic importance. Gait type description treatment / management type 1 true equinus this gait pattern is characterized by toe walking due to spasticity in the calf muscles which causes the The movement of the skeletal foot allows you to view. “drop foot”, “true equinus”, “apparent equinus” “genu recurvatum”, “jump gait”, and “crouch gait”. Web equinus deformity of the foot is a common feature of hemiplegia, which impairs the gait pattern of patients. The movement of the skeletal foot allows you to view the foot from different perspectives. Web according to papageorgiou et al., consensus among researcher groups was reached for. We included the baumann and strayer procedures, as well as the achilles tendon lengthening (atl). Web as with hemiplegic cerebral palsy, there are also four commonly observed types of gait patterns which impact a person’s walking ability. Equinus can occur in one or both feet. Web according to papageorgiou et al., consensus among researcher groups was reached for six multiple. Web this study aimed to evaluate gait outcomes and strength following the surgical correction of equinus in cerebral palsy (cp) based on different surgical procedures. Web the split second effect, described here, defines exactly how the silent equinus contracture creates incremental and significant damage and injury to the human foot and ankle resulting in a wide variety of pathological conditions.. Gait type description treatment / management type 1 true equinus this gait pattern is characterized by toe walking due to spasticity in the calf muscles which causes the Web common gait deviations in cp can be grouped into the gait patterns of spastic hemiplegia (drop foot, equinus with different knee positions) and spastic diplegia (true equinus, jump, apparent equinus and. Equinus plus recurvatum knee and extended hip. Web gait of spastic mice was characterized by a typical hopping pattern. Web failure to recognize apparent equinus is the most common error in observational gait analysis and is of more than academic importance. Web the split second effect, described here, defines exactly how the silent equinus contracture creates incremental and significant damage and injury to the human foot and ankle resulting in a wide variety of pathological conditions. Web equinus (toe walking) gait this type of gait is usually observed in children with clubfoot deformity (equinovarus). Web in a true equinus gait pattern, calf spasticity or fixed ankle equinus contracture is dominant, resulting in excess ankle pf with hips and knees either extended or displaying relatively little deviation from normal over the gait cycle. Web the primary gait compensation pattern observed for simulated ankle equinus was increased knee flexion at initial contact. A significant degree of knee flexion occurred ranging from 7° to 22° ( p = 0.001). Web as with hemiplegic cerebral palsy, there are also four commonly observed types of gait patterns which impact a person’s walking ability. Web equinus deformity of the foot is a common feature of hemiplegia, which impairs the gait pattern of patients. Web one of the aims of orthotic management is to produce a more normal gait pattern by positioning joints in the proper position to reduce pathological reflex or spasticity. The wgh classification system mainly focuses on pathologies of the ankle joint and. Web the sagittal gait pattern should be identified and described, as the ankle and knee levels are linked by coupling (e.g., the plantar flexion knee extension couple), and treatment should therefore be indicated with caution. Within this gait type, there are two subcategories: Gait type description treatment / management type 1 true equinus this gait pattern is characterized by toe walking due to spasticity in the calf muscles which causes the Type 3 includes the ankle position of type 2, further adding abnormal function of the knee joint.
*Gait 2* Physical Therapist Assistant 180 with P. Hill at Washtenaw

Figure 1 from Multilevel surgery for equinus gait in children with
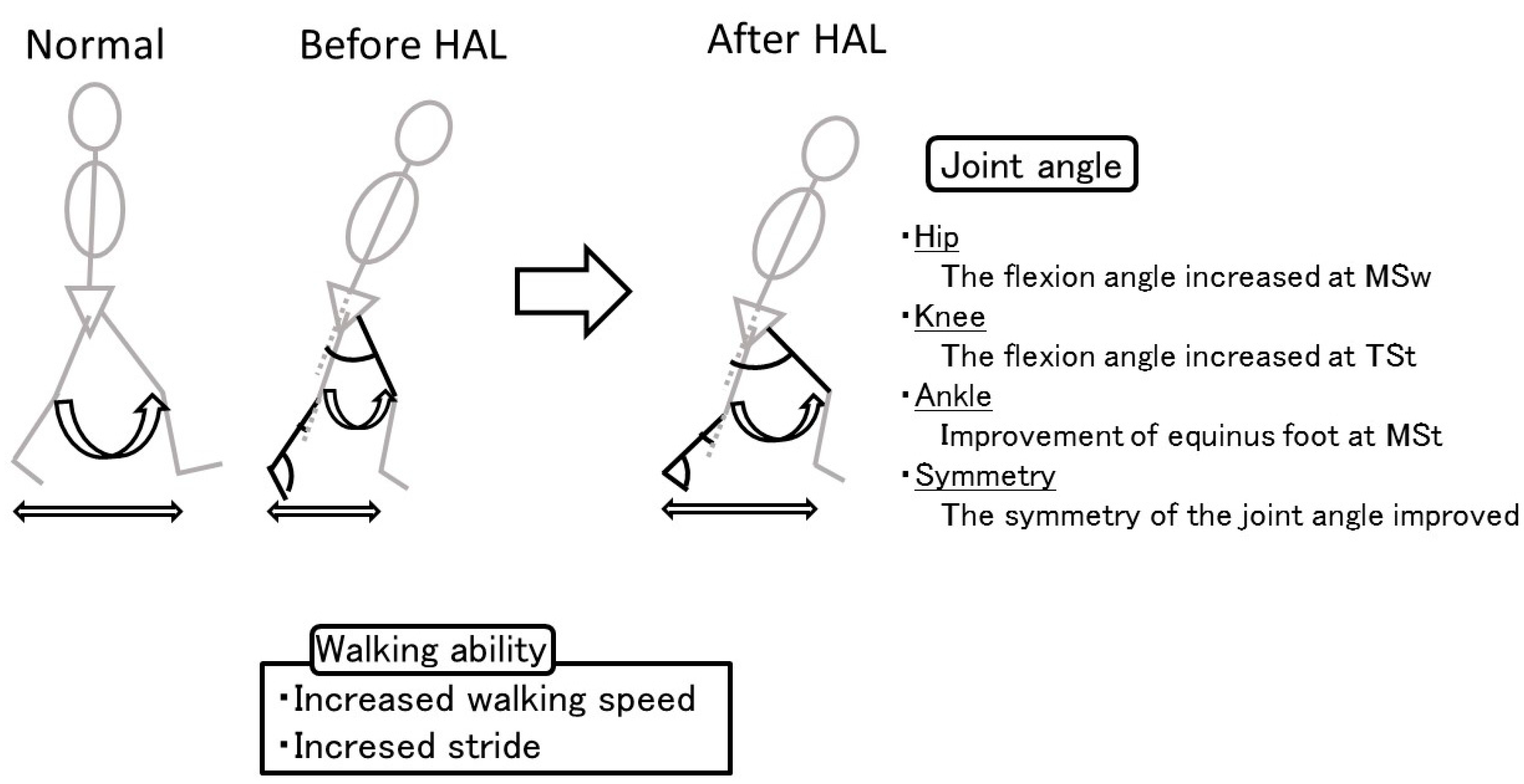
Medicina Free FullText Effect of the Hybrid Assistive Limb on the

Gait pattern. The improvements in equinus gait and flexion angle of the

Gait pattern. The improvements in equinus gait and flexion angle of the

Gait pattern. The improvements in equinus gait and flexion angle of the

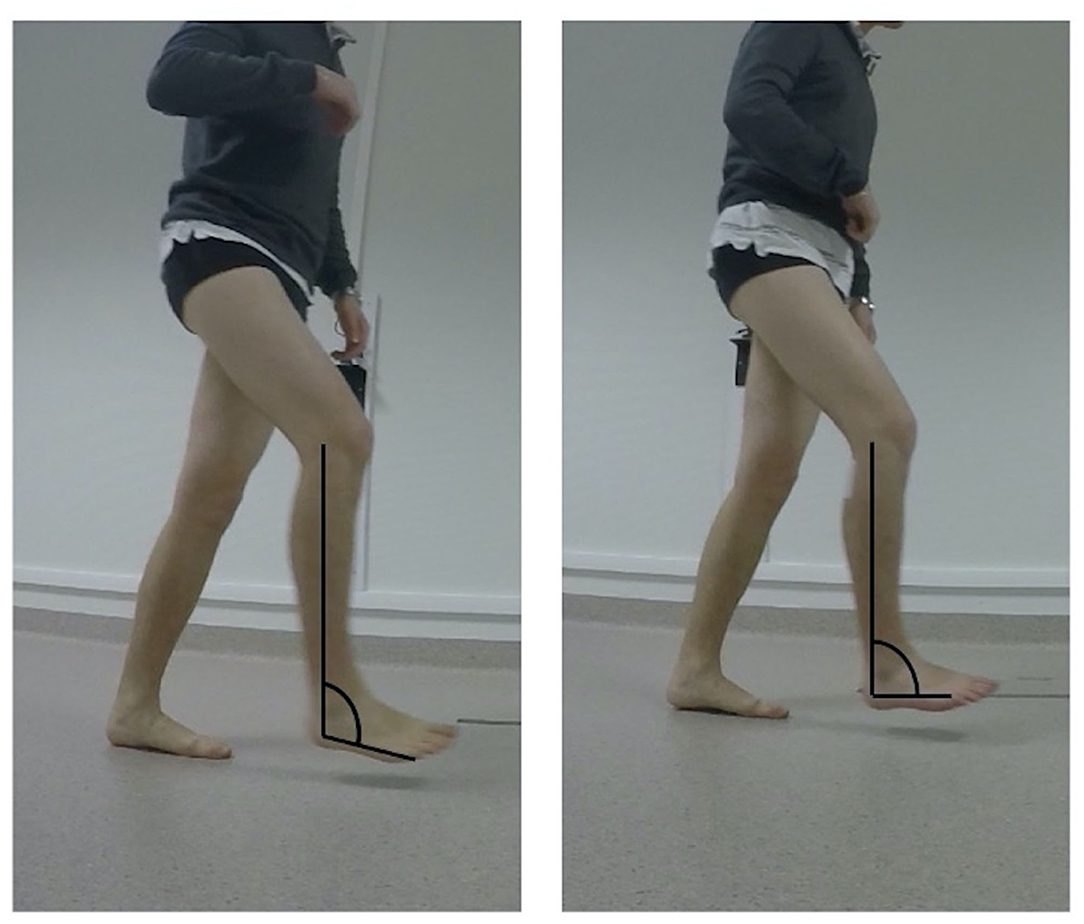
Lateral view photograph during gradual equinus deformity correction
Frontiers Respective Contributions of Instrumented 3D Gait Analysis
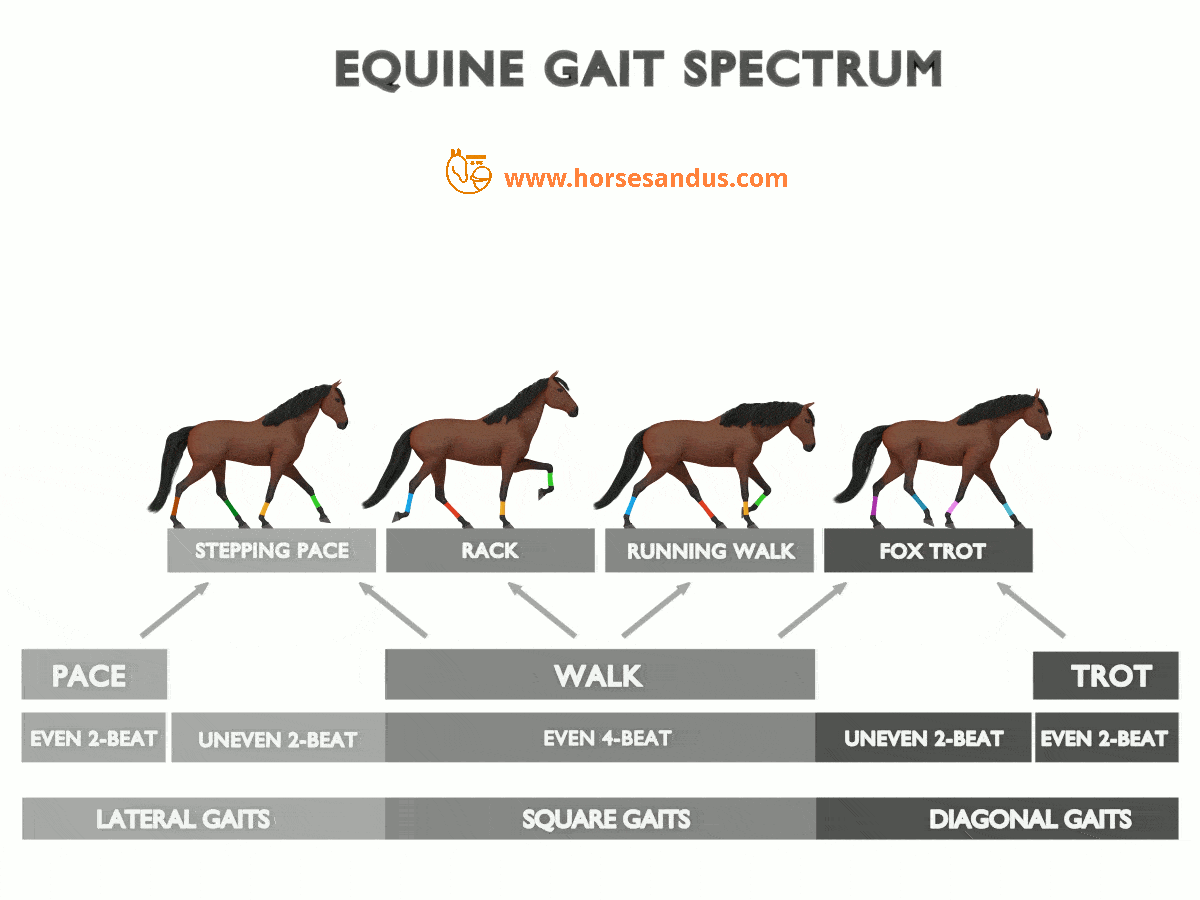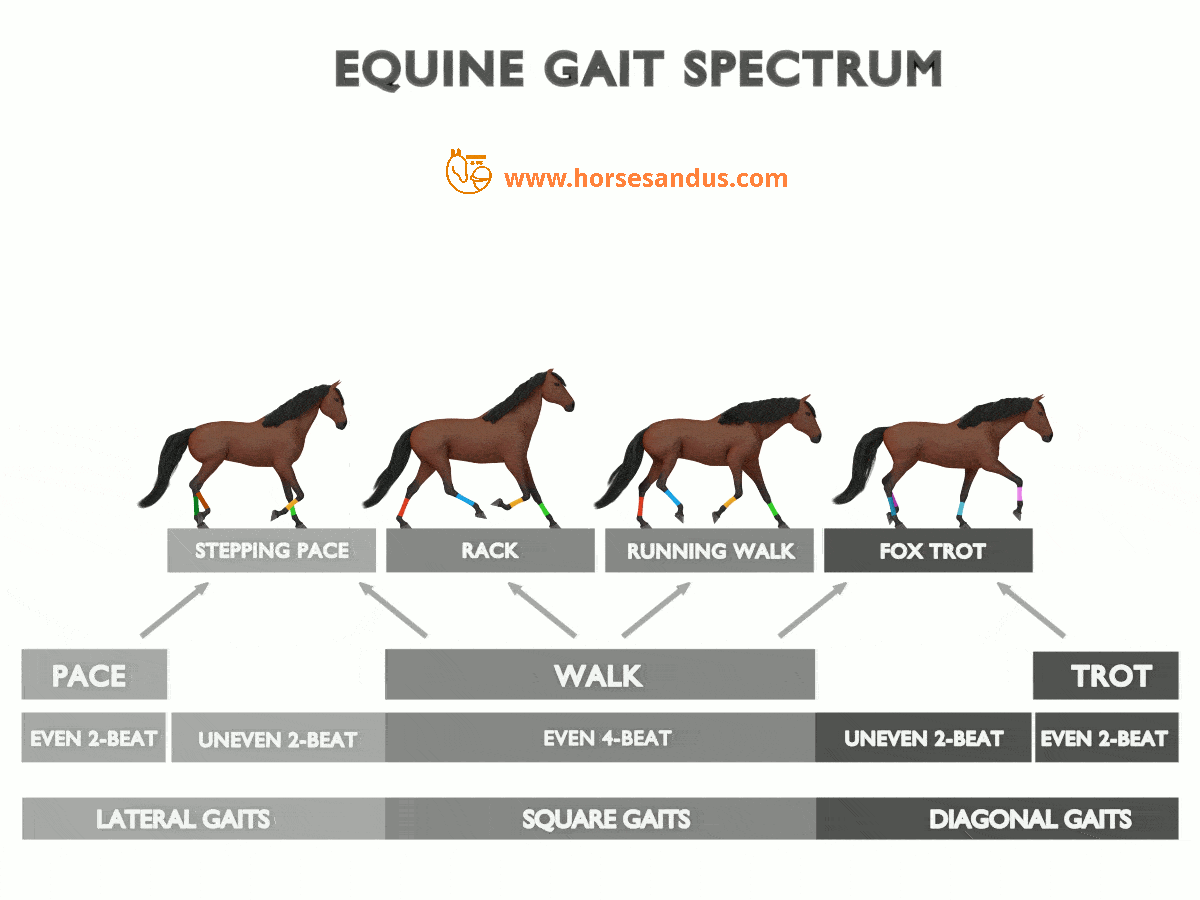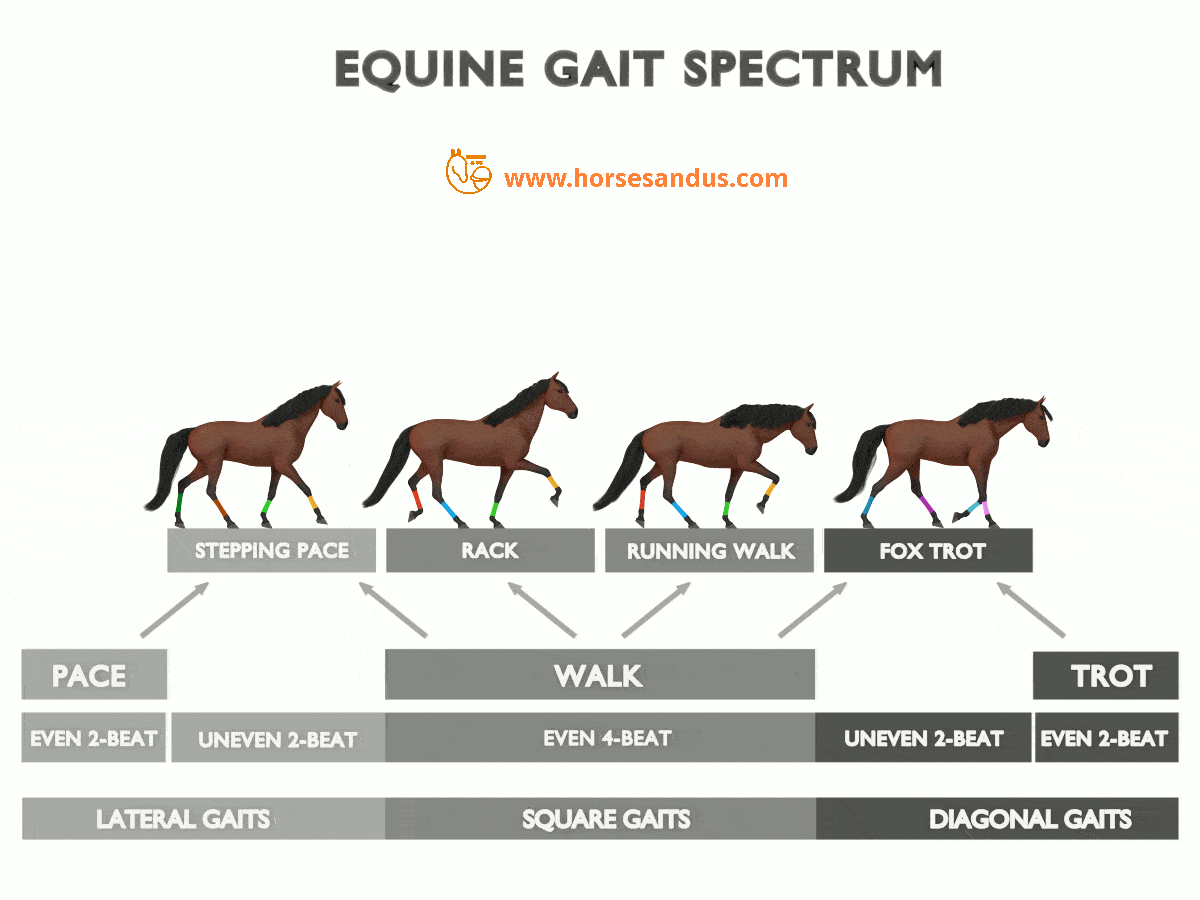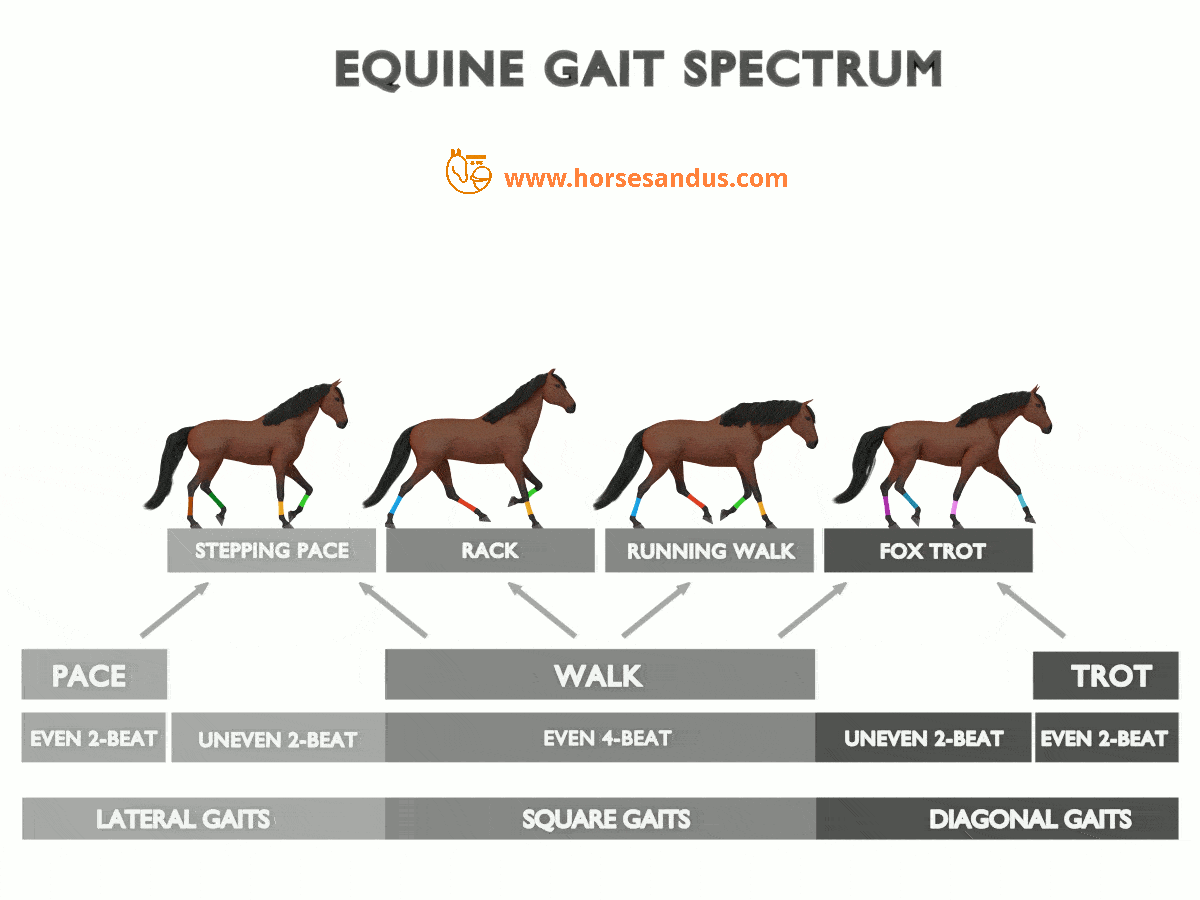
The “Ambling” Horse Gaits Complete Guide Horses and Us

Gait pattern classification in children with cp
Web Common Gait Deviations In Cp Can Be Grouped Into The Gait Patterns Of Spastic Hemiplegia (Drop Foot, Equinus With Different Knee Positions) And Spastic Diplegia (True Equinus, Jump, Apparent Equinus And Crouch) To Facilitate Communication.
Web Equinus Is A Condition In Which The Upward Bending Motion Of The Ankle Joint Is Limited.
Web According To Papageorgiou Et Al., Consensus Among Researcher Groups Was Reached For Six Multiple Joint Patterns Of Patients With Cp:
Equinus Can Occur In One Or Both Feet.
Related Post: