Ecg Sine Wave Pattern
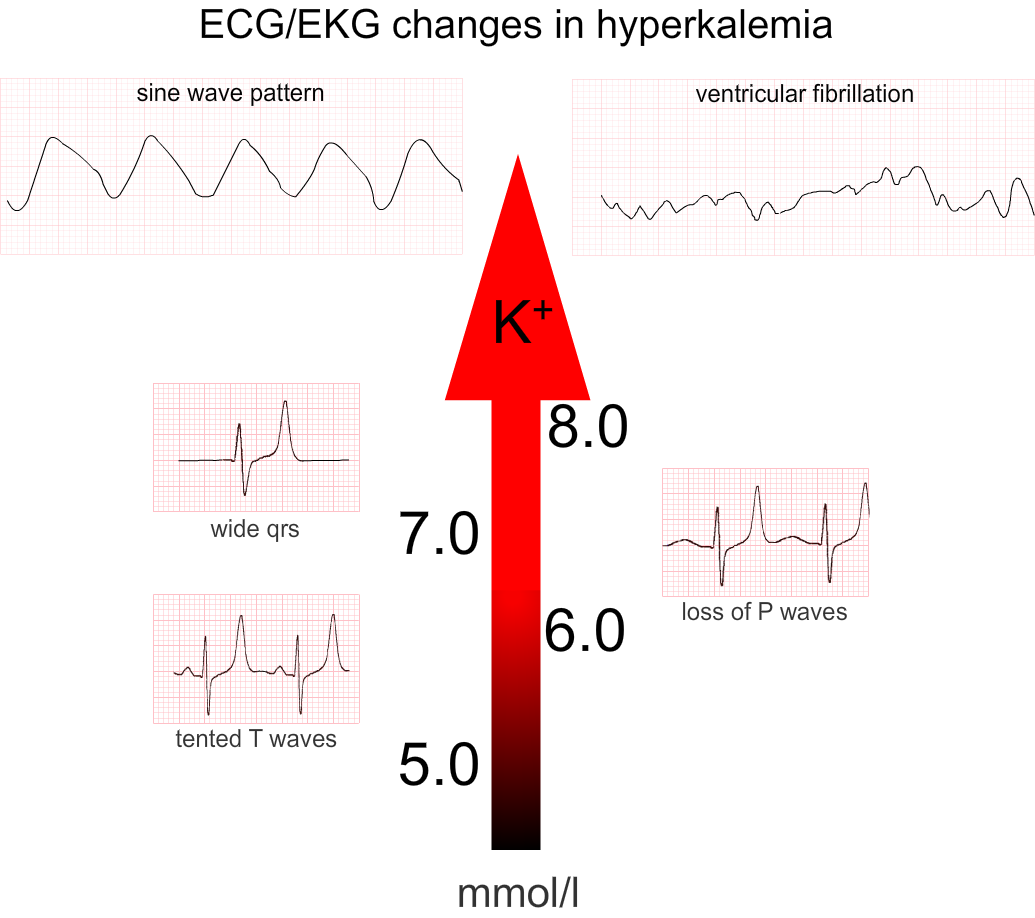
Ecg Sine Wave Pattern - The qt/qtc intervals are prolonged (520/670 msec) but they are normal when the widened qrs complex duration is considered (360/460 msec). The similarity of the waveforms indicates that the origin of the impulse is the same. Web the sine wave pattern is one of the manifestations of severe hyperkalemia. Web potassium is 1 of 3 critical electrolytes involved in the function of the action potential of cardiac muscle cells (the others are calcium and sodium). Web killer ecg patterns: The morphology of this sinusoidal pattern on ecg results from the fusion of wide qrs complexes with t waves. We aimed to assess this phenomenon, with potential associations with arrhythmogenesis. Litfl ecg library is a free educational resource covering over 100 ecg topics relevant to emergency medicine and critical care. There are a number of intervals on an ecg that are important: The word ecg derives from the german language. Web the ecg changes reflecting this usually follow a progressive pattern of symmetrical t wave peaking, pr interval prolongation, reduced p wave amplitude, qrs complex widening, sine wave formation, fine ventricular fibrillation and asystole. Web in normal sinus rhythm with 1:1 atrioventricular (av) conduction, a p wave with a uniform morphology precedes each qrs complex. The morphology of this sinusoidal. We describe the case of a patient who presented with hyperkalaemia and. Web killer ecg patterns: Web the ecg changes reflecting this usually follow a progressive pattern of symmetrical t wave peaking, pr interval prolongation, reduced p wave amplitude, qrs complex widening, sine wave formation, fine ventricular fibrillation and asystole. Tall tented t waves (early sign) prolonged pr interval; Had. This is the “sine wave” rhythm of extreme hyperkalemia. Web ecg case 174: Web it is difficult to tell where the p wave ends and the qrs begins. There is frequently a background progressive bradycardia. The sine wave pattern depicts worsening cardiac conduction delay caused by the elevated level of extracellular potassium. The similarity of the waveforms indicates that the origin of the impulse is the same. Web this article (10.1056/nejmicm1113009) was updated on october 4, 2012, at nejm.org. This is the “sine wave” rhythm of extreme hyperkalemia. This article is an answer to the ecg case 174. This pattern usually appears when the serum potassium levels are well over 8.0 meq/l. The most significant role for potassium occurs in phase 3 of the action potential, when potassium moves out of the cell to return the resting membrane potential (rmp) to a negative state. The qt/qtc intervals are prolonged (520/670 msec) but they are normal when the widened qrs complex duration is considered (360/460 msec). Had we seen the earlier ecgs, we. Prompt recognition and treatment of The rate is between 50 and 100 beats per minute, though some use 60 beats per minute as the lower end of normal, and the cycle length is fairly uniform between sequential p waves and qrs complexes. T wave flattening, prominent u waves, sagging st depressions. There are a number of intervals on an ecg. There is frequently a background progressive bradycardia. Web ecg waves and hyperkalaemia. The qrs complex is very wide (0.24 sec), best established by measuring the qrs. In 1902, the dutch physician einthovan invented ecg, and his tremendous input in clinical. The pr interval is assessed in order to determine whether impulse conduction from the. This pattern usually appears when the serum potassium levels are well over 8.0 meq/l. Also, there are occasional pacer spikes, which are not capturing. The sinoatrial (sa) node is the heart’s pacemaker under normal circumstances and the rhythm is referred to as sinus rhythm. A rhythm is defined as three consecutive heart beats with identical waveforms on the. The qrs. Severe hyperkalaemia causes idoventricular rhythms, sine wave and vf arrest. An ecg is an essential investigation in the context of hyperkalaemia. T wave flattening, prominent u waves, sagging st depressions. The earliest manifestation of hyperkalaemia is an increase in t wave amplitude. Peer reviewed with thanks by dr stephen smith of dr smith’s ecg blog. The sine wave pattern depicts worsening cardiac conduction delay caused by the elevated level of extracellular potassium. There are no p waves seen before or after any qrs complexes. Litfl ecg library is a free educational resource covering over 100 ecg topics relevant to emergency medicine and critical care. Peaked t waves qrs widening, pr prolongation sine wave pattern. This. Severe hyperkalaemia causes idoventricular rhythms, sine wave and vf arrest. Web the ecg changes reflecting this usually follow a progressive pattern of symmetrical t wave peaking, pr interval prolongation, reduced p wave amplitude, qrs complex widening, sine wave formation, fine ventricular fibrillation and asystole. We describe the case of a patient who presented with hyperkalaemia and. Most common ecg finding in. This is the “sine wave” rhythm of extreme hyperkalemia. The morphology of this sinusoidal pattern on ecg results from the fusion of wide qrs complexes with t waves. Sine wave pattern (late sign) arrhythmias Web killer ecg patterns: The similarity of the waveforms indicates that the origin of the impulse is the same. Peaked t waves qrs widening, pr prolongation sine wave pattern. Also, there are occasional pacer spikes, which are not capturing. There is frequently a background progressive bradycardia. Hyperkalaemia is an electrolyte disturbance that can have effects on myocardial conduction causing electrocardiographic changes. Web ecg case 174: The most significant role for potassium occurs in phase 3 of the action potential, when potassium moves out of the cell to return the resting membrane potential (rmp) to a negative state. There are no p waves seen in any of the leads.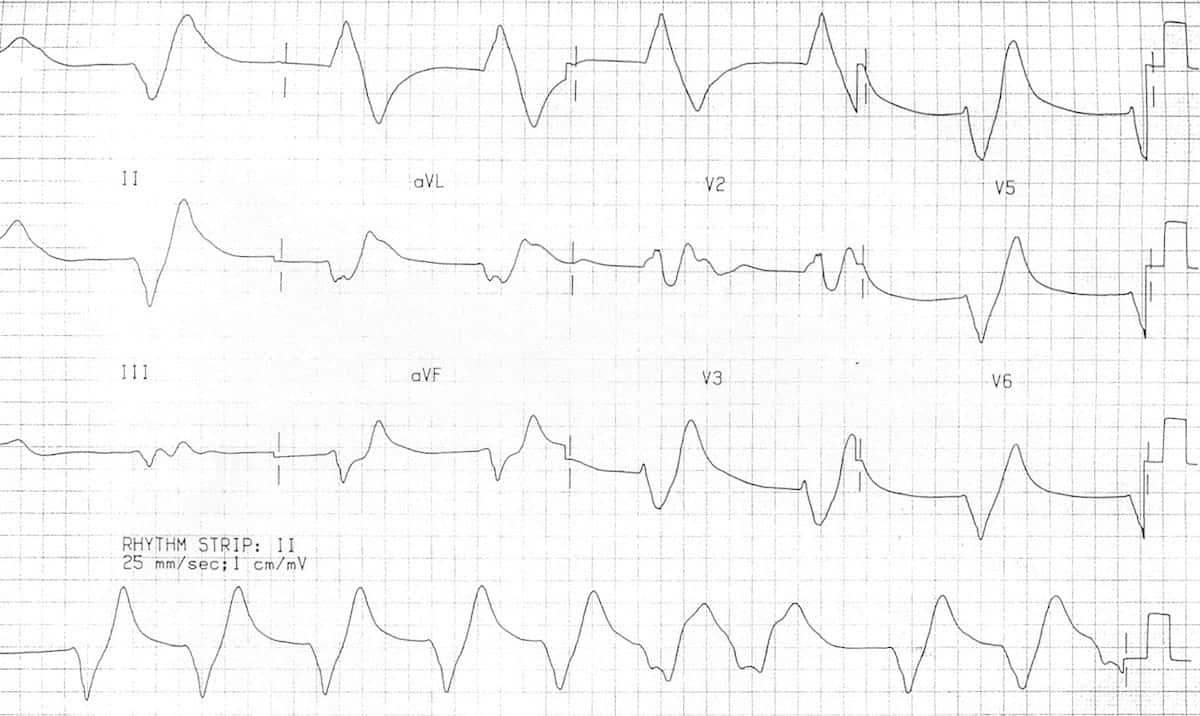
Hyperkalaemia ECG changes • LITFL • ECG Library

Ecg sinusoidal pulse lines frequency heartbeat Vector Image
Hyperkalemia ecg findings garetbetter

ECG changes due to electrolyte imbalance (disorder) ECG & ECHO

12 lead EKG showing sinewave done in the emergency room. Download
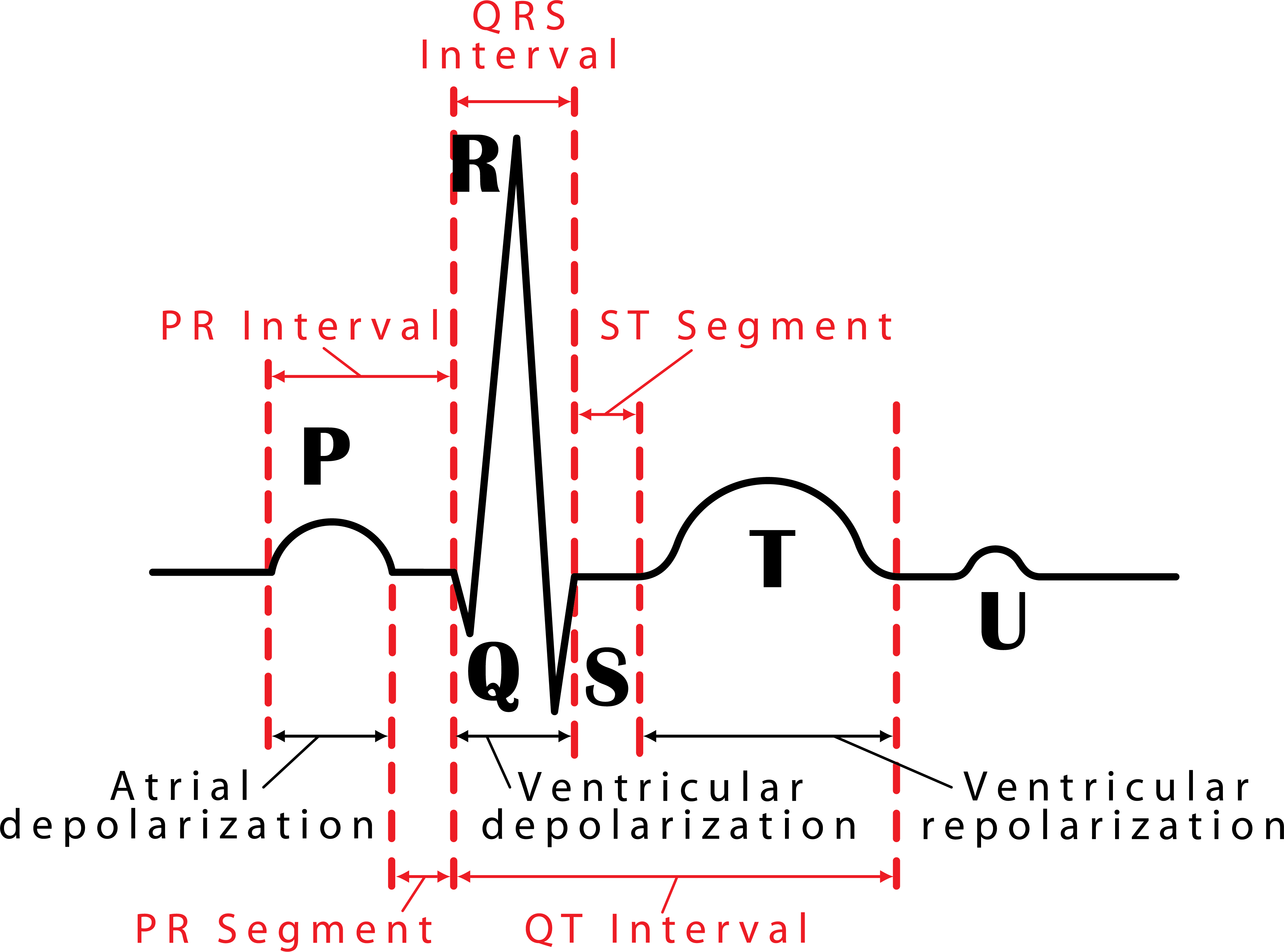
048 How to Read an Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) Interactive Biology
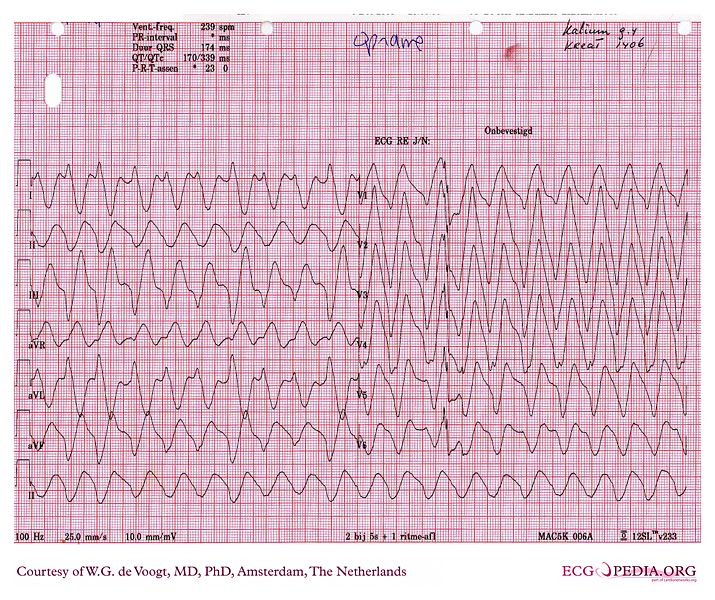
Sine wave pattern wikidoc

Sine Wave Pattern Ecg Images and Photos finder

Sine Wave Hyperkalemia Ecg Changes

An Electrocardiographic Sine Wave in Hyperkalemia — NEJM
An Ecg Is An Essential Investigation In The Context Of Hyperkalaemia.
The Normal Rhythm Of The Heart.
The Qrs Complex Is Very Wide (0.24 Sec), Best Established By Measuring The Qrs.
Tall Tented T Waves (Early Sign) Prolonged Pr Interval;
Related Post: