Ecg S1 S2 S3 Pattern
Ecg S1 S2 S3 Pattern - Web abstract = the s1 s2 s3 pattern in the electrocardiogram has been variously defined. Of these, 80 subjects (18.9%) had an associated s2 ≥ s3 pattern. The most typical ecg findings in emphysema are: Inferior leads ii, iii, avf, often most pronounced in lead iii as this is the most rightward facing. Web the ecg changes associated with acute pulmonary embolism may be seen in any condition that causes acute pulmonary hypertension, including hypoxia causing pulmonary hypoxic vasoconstriction. There are 2 main heart sounds that can be heard during auscultation: An s wave deeper than r in all 3 standard leads) is a reliable index of rvh. Some apply this term to all cases with an s wave in each standard lead, regardless of magnitude, while others use it to. S 1 and s 2, also affectionately known as ‘lub’ and ‘dub’ respectively. In some cases s waves are equal or superior to r waves in one or more limb leads.' Web in the limb leads right axis deviation develops and at times prominent q waves simulating an imi appear in leads 2,3, and avf. St depression and t wave inversion in leads corresponding to the right ventricle: Web abstract = the s1 s2 s3 pattern in the electrocardiogram has been variously defined. In children an s1 s2 s3 pattern (i.e.. Web the s1 s2 s3 pattern in the electrocardiogram has been variously defined. Table 4.2 ecg criteria for right. University of michigan murmur library. S1 heart sound corresponds to. Table 2 shows grouping of various criteria to achieve the maximal sensitivity and specificity range for our patients with copd and rvh. Note that there is a prominent s wave in leads 1, 2, and 3 and the s waves are equal in duration and magnitude to the preceding r waves. S 1 and s 2, also affectionately known as ‘lub’ and ‘dub’ respectively. The diagnosis of biatrial enlargement requires criteria for lae and rae to be met in either lead ii,. Table 4.2 ecg criteria for right. The diagnosis of biatrial enlargement requires criteria for lae and rae to be met in either lead ii, lead v1 or a combination of leads. This latter application, which we prefer, is generally associated with marked. Some apply this term to all cases with an s wave in each standard lead, regardless of magnitude,. Web the ecg changes associated with acute pulmonary embolism may be seen in any condition that causes acute pulmonary hypertension, including hypoxia causing pulmonary hypoxic vasoconstriction. An amplitude of at least 1.5 mm — was found in 423 subjects (6.7%). The diagnosis of biatrial enlargement requires criteria for lae and rae to be met in either lead ii, lead v1. In some cases s waves are equal or superior to r waves in one or more limb leads.' Other abnormalities caused by rvh 6, june, 1974 ecg diagnosis of right ventricular hypertrophy in. The most typical ecg findings in emphysema are: S1 s2 s3 pattern = far right axis deviation with dominant s waves in leads i, ii and iii. There are 2 main heart sounds that can be heard during auscultation: There is a terminal r wave in avr. Web biatrial enlargement is diagnosed when criteria for both right and left atrial enlargement are present on the same ecg. Some apply this term to all cases with an s wave in each standard lead, regardless of magnitude, while others. Web an s1, s2, s3 pattern, which may mimic a left anterior hemiblock, is frequently associated with the brugada repolarization abnormalities and most likely reflects a concomitant intraventricular conduction defect localized to the right ventricular outflow tract due to the disease involvement of the peripheral fascicles of the right bundle branch. Ecg criteria for biatrial enlargement. Some apply this term. St depression and t wave inversion in leads corresponding to the right ventricle: Inferior leads ii, iii, avf, often most pronounced in lead iii as this is the most rightward facing. S 1 and s 2, also affectionately known as ‘lub’ and ‘dub’ respectively. Web an s1, s2, s3 pattern, which may mimic a left anterior hemiblock, is frequently associated. Web the ecg changes associated with acute pulmonary embolism may be seen in any condition that causes acute pulmonary hypertension, including hypoxia causing pulmonary hypoxic vasoconstriction. Some apply this term to all cases with an s wave in each standard lead, regardless of magnitude, while others use it to indicate situations where the prominent qrs deflection is an s wave. There are 2 main heart sounds that can be heard during auscultation: Web the purpose of this chapter is to review the role of the ecg in the diagnosis of cardiac chamber enlargement. St depression and t wave inversion in leads corresponding to the right ventricle: S1 s2 s3 pattern = far right axis deviation with dominant s waves in leads i, ii and iii. Web abstract = the s1 s2 s3 pattern in the electrocardiogram has been variously defined. Web in the limb leads right axis deviation develops and at times prominent q waves simulating an imi appear in leads 2,3, and avf. S 1 and s 2, also affectionately known as ‘lub’ and ‘dub’ respectively. An s wave deeper than r in all 3 standard leads) is a reliable index of rvh. In children an s1 s2 s3 pattern (i.e. Of these, 80 subjects (18.9%) had an associated s2 ≥ s3 pattern. Deep s waves in the left precordial leads v 5 and v 6 (r:s <1); Table 2 shows grouping of various criteria to achieve the maximal sensitivity and specificity range for our patients with copd and rvh. Other abnormalities caused by rvh Web the chosen criteria have major impact on the prevalence of the s1s2s3 ecg pattern in the general population. 6, june, 1974 ecg diagnosis of right ventricular hypertrophy in. Web an s1, s2, s3 pattern, which may mimic a left anterior hemiblock, is frequently associated with the brugada repolarization abnormalities and most likely reflects a concomitant intraventricular conduction defect localized to the right ventricular outflow tract due to the disease involvement of the peripheral fascicles of the right bundle branch.
Ecg criteria of chamber enlargement

【コラム051】S1S2S3パターンを考えます。 Cardio2012のECGブログ

Standard (S1, S2, S3) and alternate (A1, A2, A3) ECG electrode
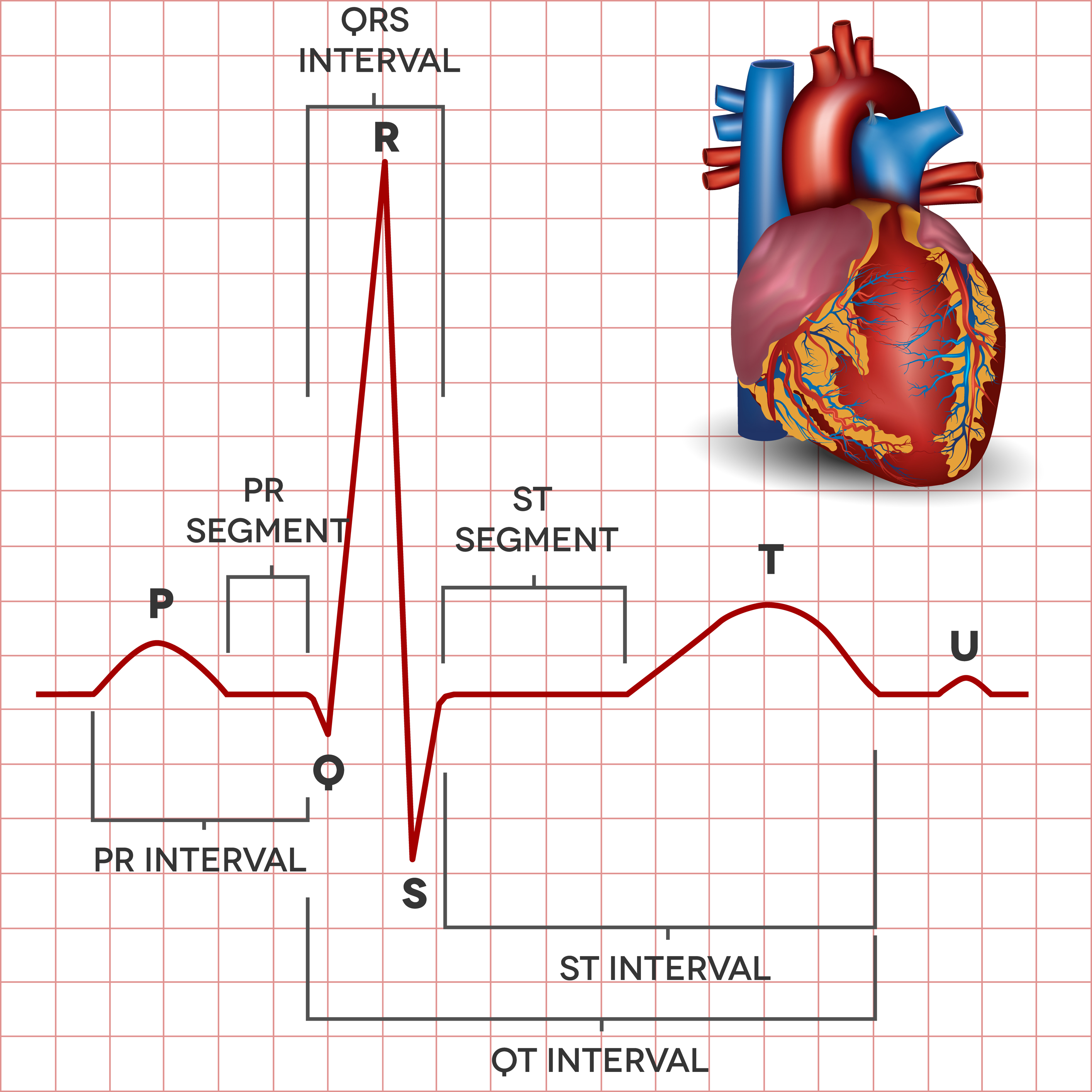
The Electrocardiogram explained What is an ECG?
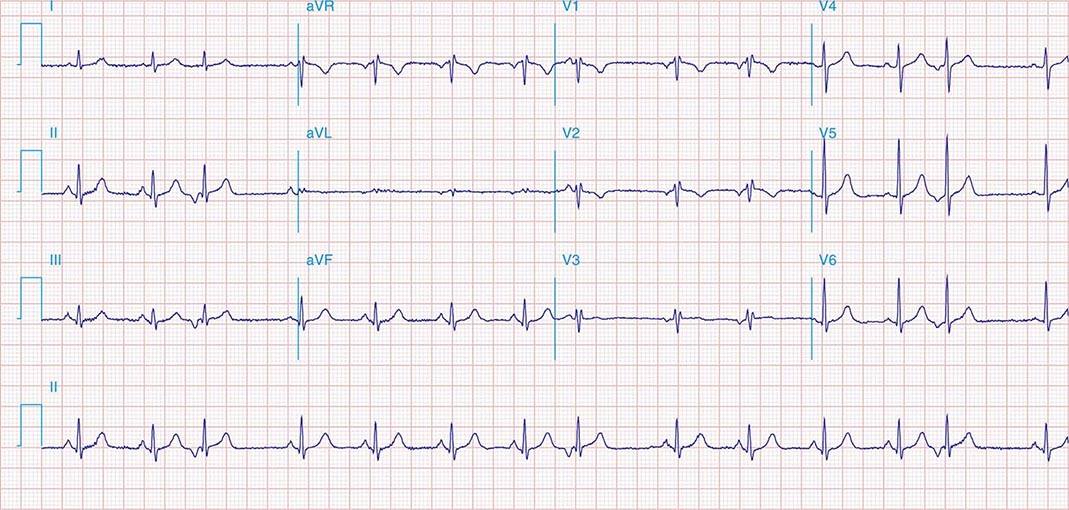
Atlas of Electrocardiography Basicmedical Key
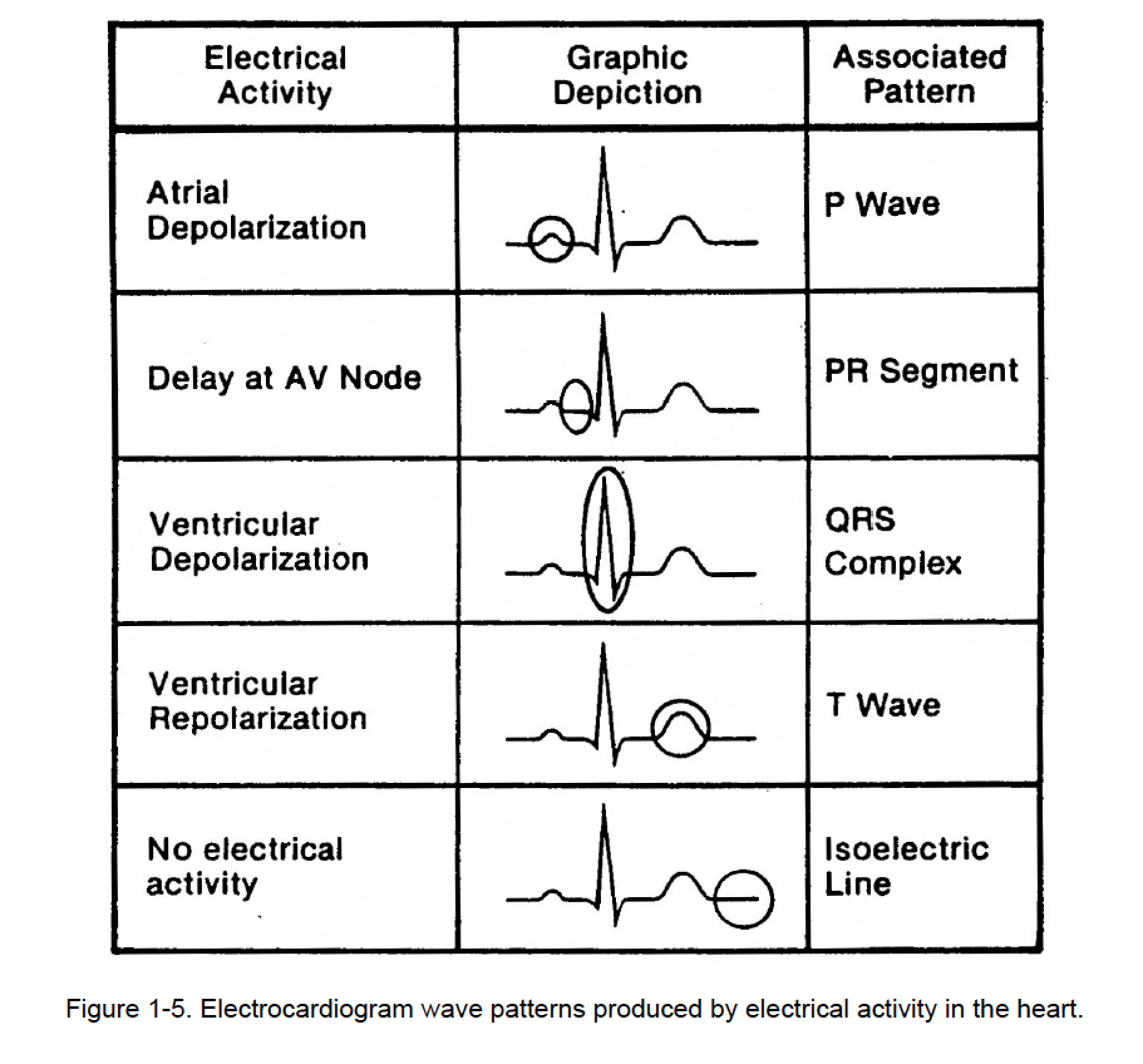
Figure 15. Cardiac Rhythm Interpretation

Description, criteria, and example of the different QRS morphologies
Standard (S1, S2, S3) and alternate (A1, A2, A3) ECG electrode
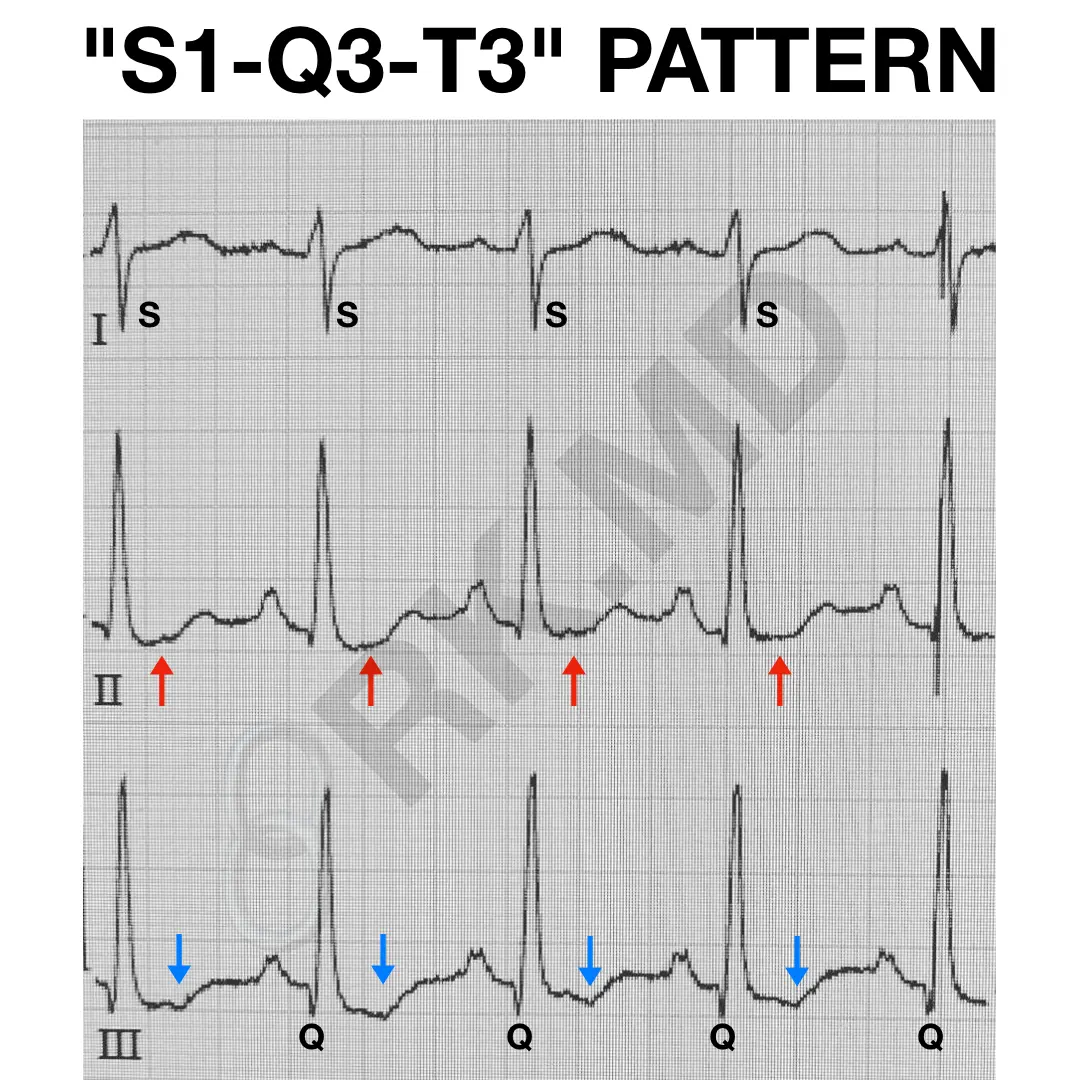
S1Q3T3 EKG Pattern RK.MD
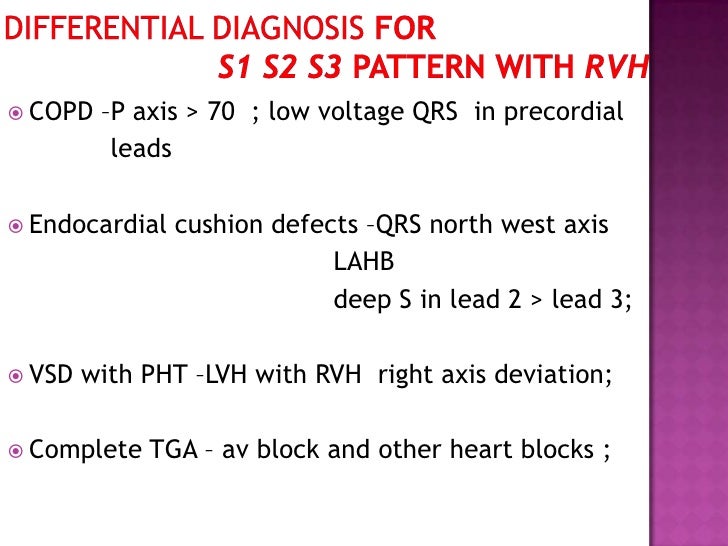
ECG Congenital Heart Disease
Note That There Is A Prominent S Wave In Leads 1, 2, And 3 And The S Waves Are Equal In Duration And Magnitude To The Preceding R Waves.
University Of Michigan Murmur Library.
Web Right Ventricular Strain Is A Repolarisation Abnormality Due To Right Ventricular Hypertrophy (Rvh) Or Dilatation.
An Amplitude Of At Least 1.5 Mm — Was Found In 423 Subjects (6.7%).
Related Post: