Drawing Of A Zygote
Drawing Of A Zygote - The egg and sperm each contain one set of chromosomes. To ensure that the offspring has only one complete diploid set of chromosomes, only one sperm must fuse with one egg. Male and female gametes are involved in sexual reproduction. Formation, development and growth stages. The cellular mechanisms present in the gametes also function in the zygote, but the newly fused dna produces a different effect in the new cell. So it will, you know, after one, so after one, and we're going to go into the details of the mechanics of mitosis, but after one round of mitosis, it is now two cells. The zygote stage development occurs in the first week of fertilization. The dna material from the two cells is combined in the resulting zygote. In mammals, the egg is protected by a layer of. Web zygote, fertilized egg cell that results from the union of a female gamete (egg, or ovum) with a male gamete ( sperm ). Web the male gametophyte develops and reaches maturity in an immature anther. This video explains the process of fertilisation in a clear and concise way, with. Understanding haploid and diploid numbers is essential in studying cell. Diploid (2n) cell that contains two sets of homologous chromosomes. Web sperm and egg cells, known as gametes, fuse during fertilization to create a. Formation, development and growth stages. In the embryonic development of humans and other animals, the zygote stage is brief and is followed by cleavage, when the single cell becomes subdivided into smaller cells. The egg and sperm each contain one set of chromosomes. The dna material from the two cells is combined in the resulting zygote. Web zygote, embryo, fetus,. This diagram represents the life cycle that generally characterizes plants. Photograph of the original illustration from a system of human anatomy by erasmus wilson published in. Understanding haploid and diploid numbers is essential in studying cell. Gametes have half the chromosomes (haploid) of a typical body cell, while zygotes have the full set (diploid). Polyspermy, or multiple sperm cells fertilizing. A zygote is the first diploid cell that is formed by the fusion of male and female gametes resulting in the formation of an embryo. To ensure that the offspring has only one complete diploid set of chromosomes, only one sperm must fuse with one egg. It is now two cells. Web a zygote is the cell formed when two. One of the two generations of a plant’s life cycle is typically dominant to the other generation. Diploid (2n) cell that contains two sets of homologous chromosomes. This diagram represents the life cycle that generally characterizes plants. The male gamete in humans is the sperm cell, while the female gamete is the ovum (also. Homologous chromosomes from each parent determine. Web zygote, embryo, fetus, baby. Understanding haploid and diploid numbers is essential in studying cell. Web the term “zygote” is used in biology, medicine, and other related professions, including psychology, to refer to a cell that arises after the union of sex cells (also called gametes). Drawing vector illustration zygote drawing stock illustrations One of the two generations of a. The male gamete in humans is the sperm cell, while the female gamete is the ovum (also. So it will, you know, after one, so after one, and we're going to go into the details of the mechanics of mitosis, but after one round of mitosis, it is now two cells. Web zygote, embryo, fetus, baby. A team of researchers. The peridium (outer covering of the sporangium) has split and haploid spores are being released. In the embryonic development of humans and other animals, the zygote stage is brief and is followed by cleavage, when the single cell becomes subdivided into smaller cells. Understanding haploid and diploid numbers is essential in studying cell. Thus the zygote now has 3 copies. The zygote represents the first stage in the. It is now two cells. Formation, development and growth stages. Photograph of the original illustration from a system of human anatomy by erasmus wilson published in. At the center of the sporangium is a swollen structure called the columella. A team of researchers labeled one of two cells in a developing embryo with gfp and used dna (blue) and actin (pink) labeling to track cell progeny to determine the contribution of each to developing structures. Drawing vector illustration zygote drawing stock illustrations So it will, you know, after one, so after one, and we're going to go into the. In mammals, the egg is protected by a layer of. Web well now, through mitosis, this zygote is going to keep replicating. Web the zygote grows and develops into a mature sporophyte, and the cycle repeats. So it will, you know, after one, so after one, and we're going to go into the details of the mechanics of mitosis, but after one round of mitosis, it is now two cells. Male and female gametes are involved in sexual reproduction. Web sperm and egg cells, known as gametes, fuse during fertilization to create a zygote. It is also a blueprint of the entire organism. Zygote body is a free online 3d anatomy atlas. Web fertilization, pictured in figure 43.6.1 43.6. The male gamete in humans is the sperm cell, while the female gamete is the ovum (also. Polyspermy, or multiple sperm cells fertilizing a single egg, will result in a zygote with several. The peridium (outer covering of the sporangium) has split and haploid spores are being released. This video explains the process of fertilisation in a clear and concise way, with. Whether it’s the sporophyte or gametophyte generation, individuals in the dominant. Web zygote, embryo, fetus, baby. Understanding haploid and diploid numbers is essential in studying cell.
Zygote Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
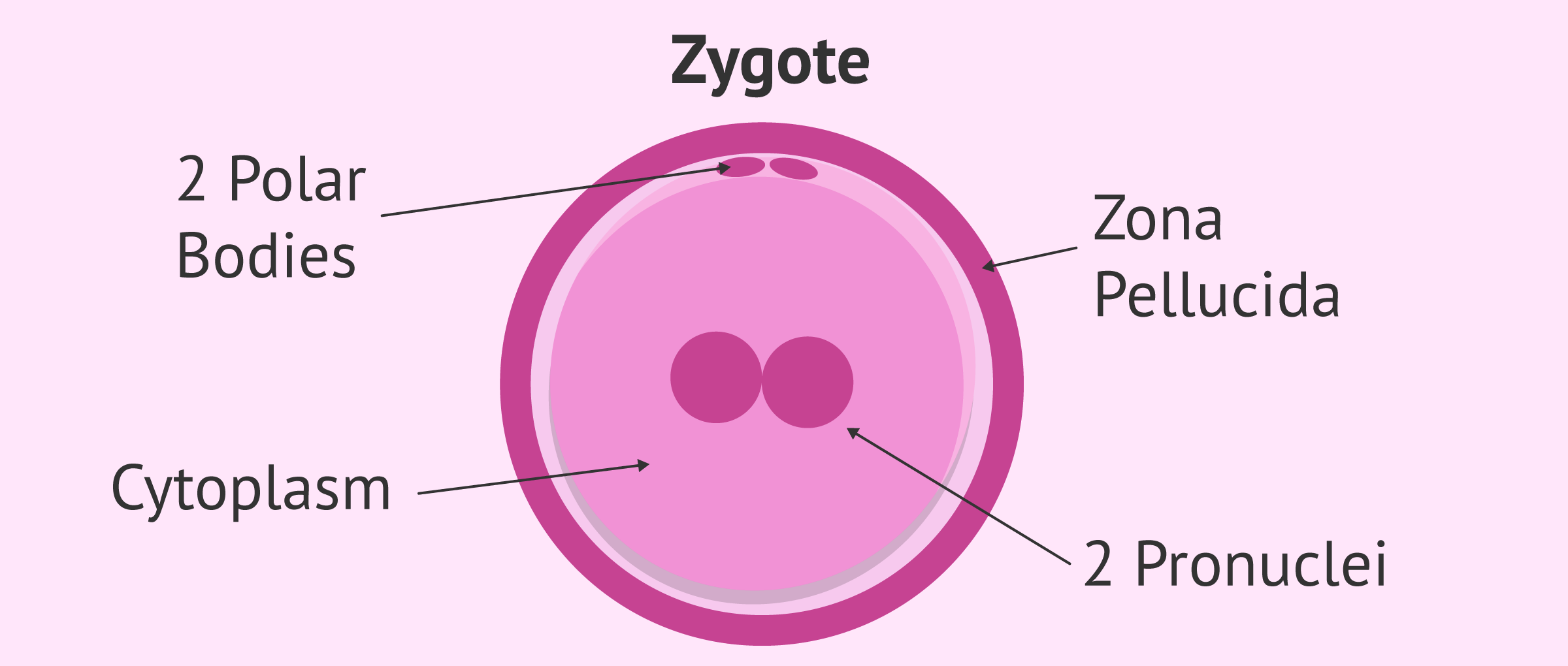
Structure of Zygote
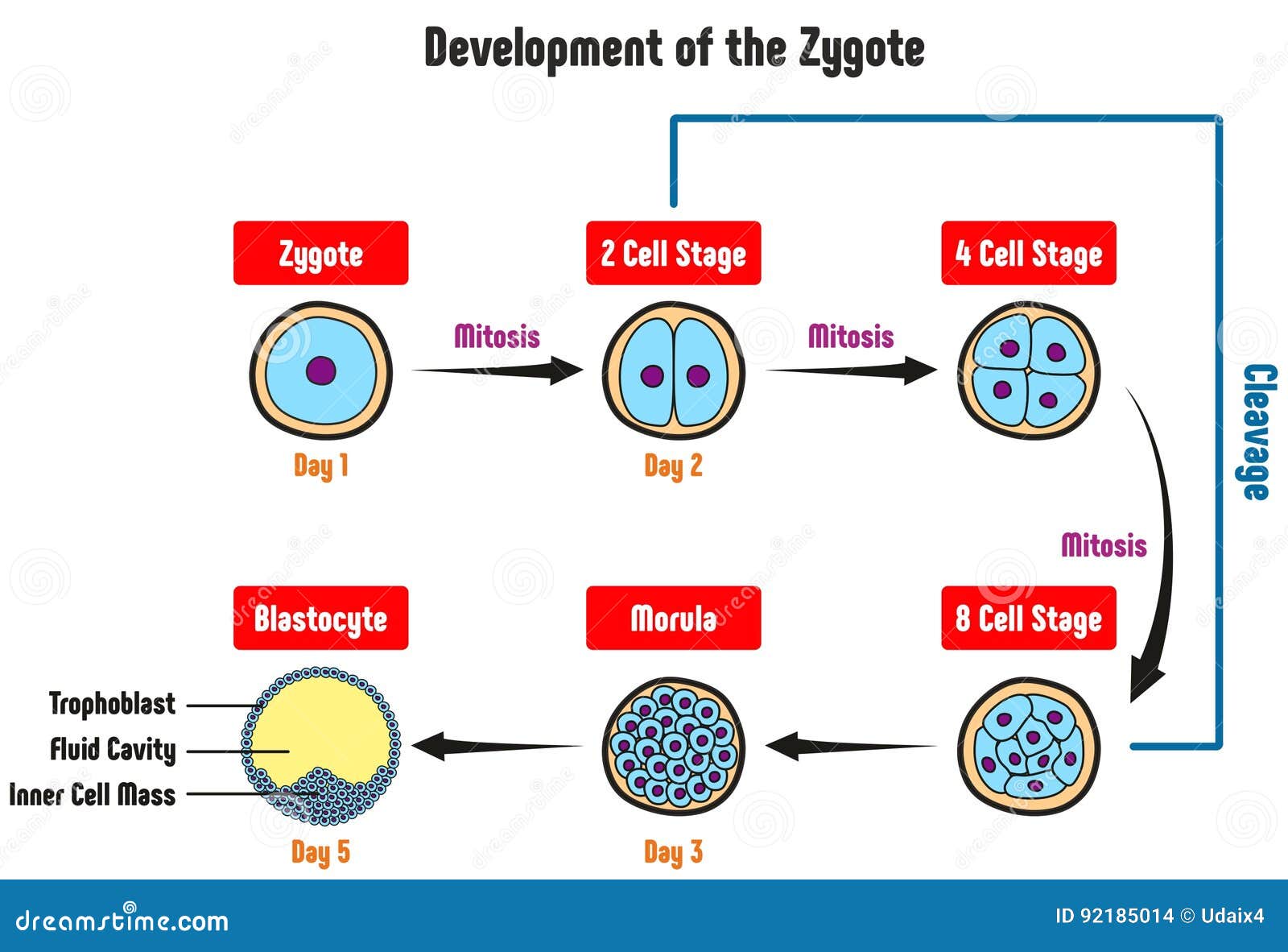
Development of the Zygote Diagram Stock Vector Illustration of

Zygote, illustration Stock Image F036/3871 Science Photo Library
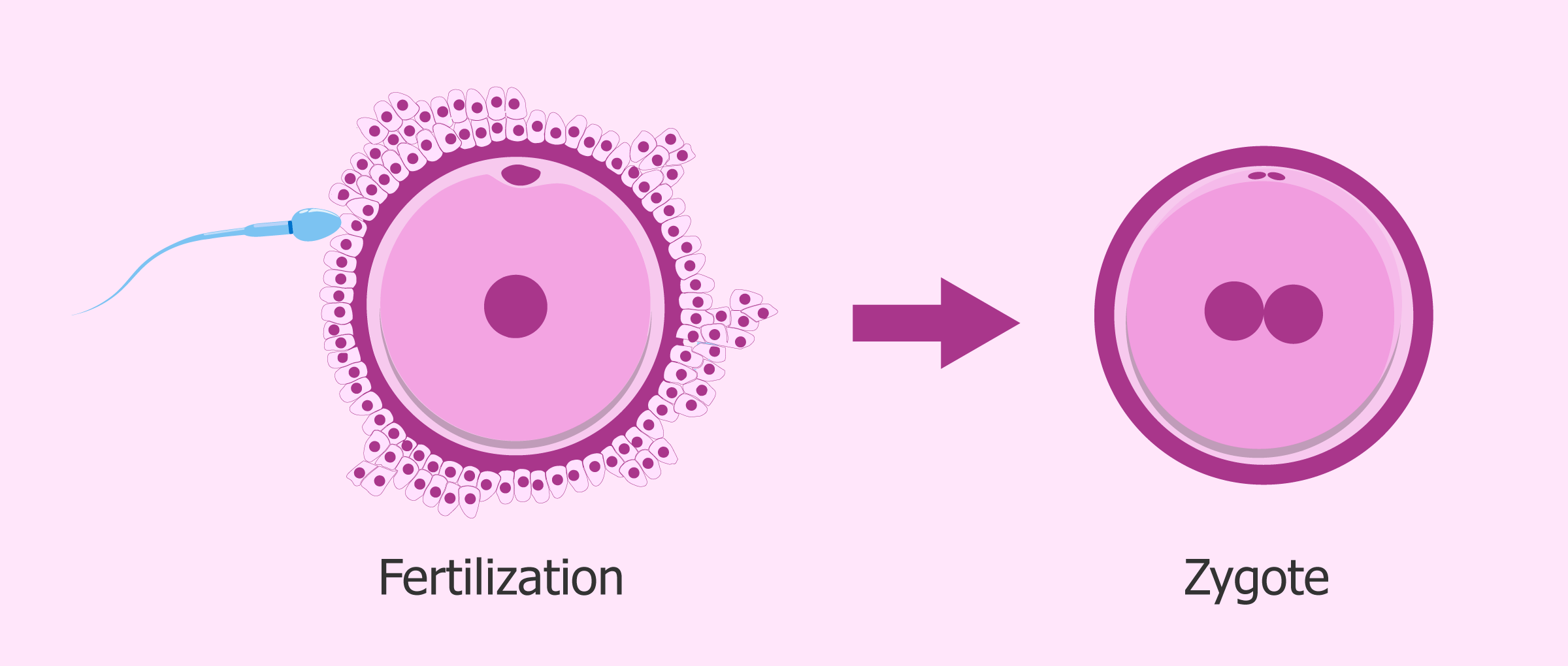
Zygote Definition, Formation and Examples
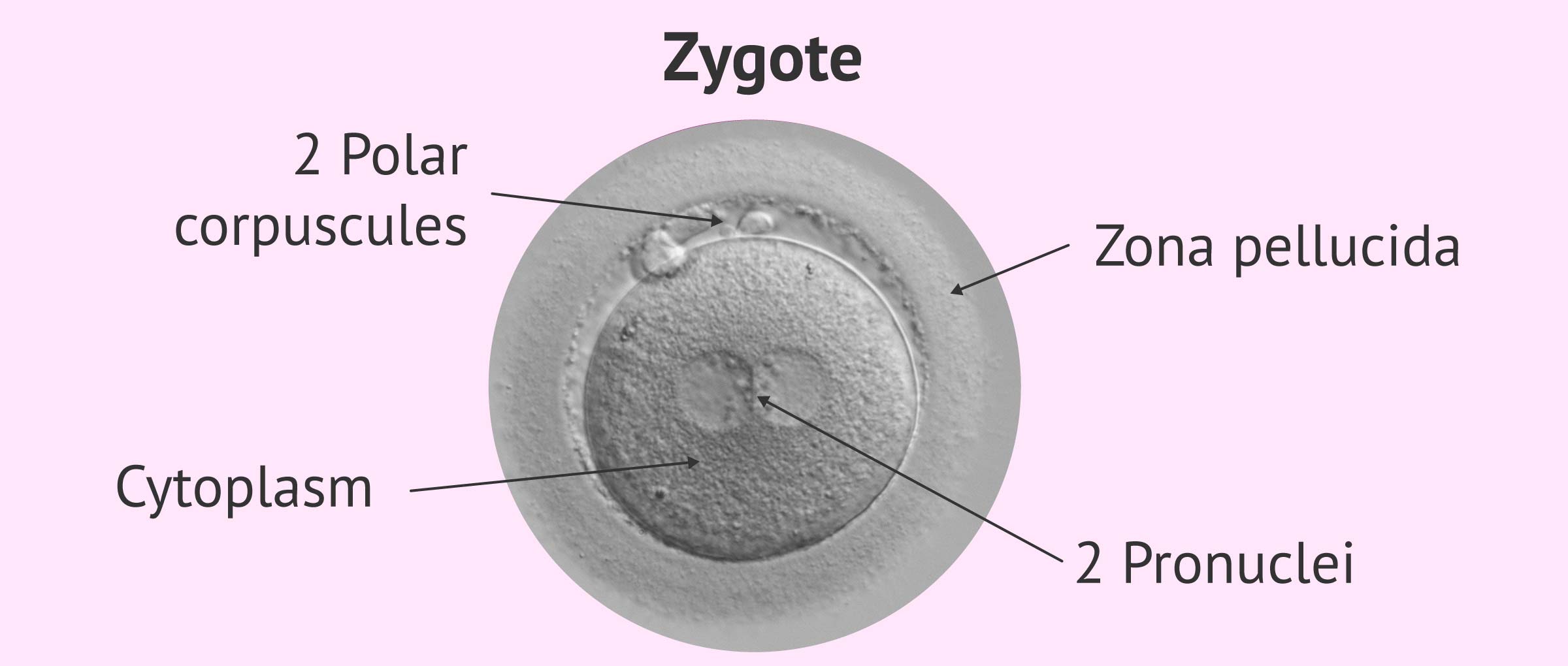
Structure of a zygote
Zygote 2 Drawing by Happy Ingenuity Fine Art America
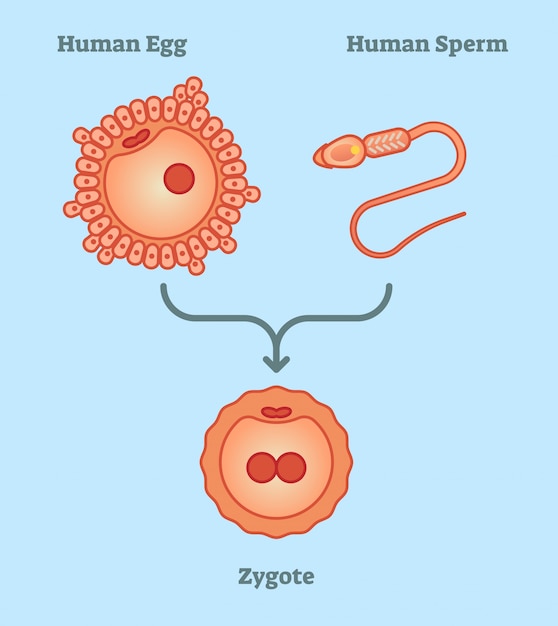
Premium Vector What is zygote vector illustration diagram, simple
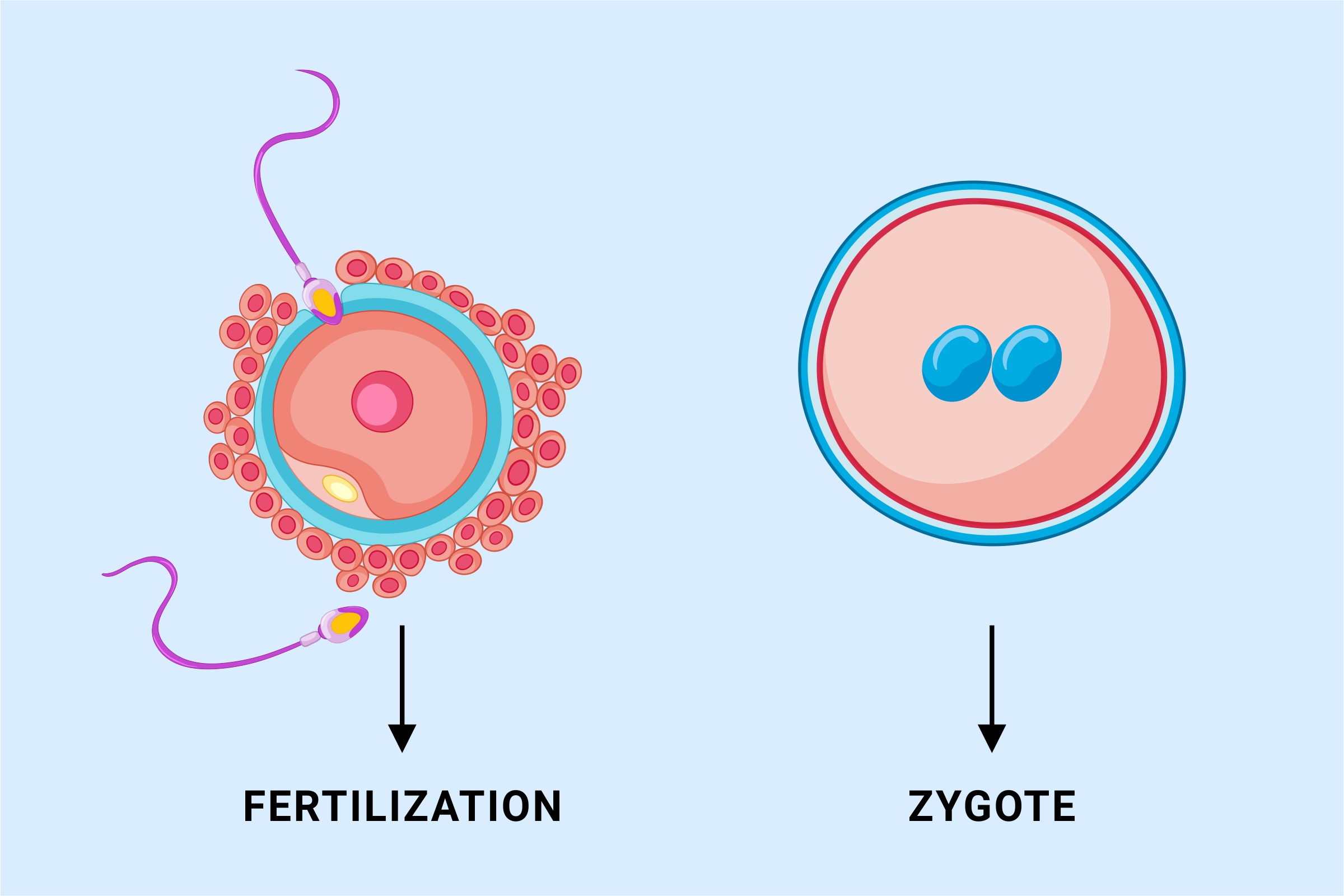
What is a Zygote in biology? Biology concepts Biology questions
Zygote Vectoriels et illustrations libres de droits iStock
The Genome Of The Zygote Is The Combination Of Dna In Each Gamete And Contains All The Genetic Information Required To.
An Embryo At The End Of 7 Weeks Of Development Is Only 10 Mm In Length, But Its Developing Eyes, Limb Buds, And Tail Are Already Visible.
Formation, Development And Growth Stages.
Thus The Zygote Now Has 3 Copies Of Chromosome 21, Hence The Name Trisomy 21.
Related Post:
