Drawing Longitudinal Waves
Drawing Longitudinal Waves - Recall the definition of longitudinal waves. You could therefore draw the wave by. Transverse waves show areas of crests (peaks) and troughs; Also called the propagation speed. By plotting the displacements of individual particles through which a wave is passing, students can develop their ideas of the underlying process of a wave. A plane pressure pulse wave. Web pressure waves caused by repeated movements in a liquid or gas; Longitudinal wave, wave consisting of a periodic disturbance or vibration that takes place in the same direction as the advance of the wave. Parts of a longitudinal wave. The peaks are the maximum positive displacements the troughs are the maximum negative displacements the direction of the energy transfer is perpendicular to the. (obviously the particles in reality move much shorter distances, and the real movement is very quick.) the nodes, i.e. Also called the propagation speed. Web longitudinal waves form when the particles of the medium vibrate back and forth in the same direction of the traveling wave. Parts of a longitudinal wave. Depends only on the properties of the medium. Parts of a longitudinal wave. Describe the motion of the toy duck. Web longitudinal waves can be described with the same mathematical functions as transverse waves: The distance between adjacent compressions is the wavelength. Water waves are an example of a transverse wave. While the movement of the waves is in a transverse manner. A coiled spring that is compressed at one end and then released experiences a wave of compression that travels its length, followed by a stretching; Points along longitudinal waves vibrate parallel to the direction of energy transfer. Oscillations where particles are displaced perpendicular to the wave direction. Web speed. The wavelength can be measured as the distance from crest to crest or from trough to trough. Also called the propagation speed. We also need to understand that the radius of the particles decreases with an increase in the depth of the water. Describe the motion of the toy duck. The places where the particles don't. You could therefore draw the wave by. We also need to understand that the radius of the particles decreases with an increase in the depth of the water. Web longitudinal waves form when the particles of the medium vibrate back and forth in the same direction of the traveling wave. Web sound waves traveling through a fluid such as air. Draw a displacement vs time and a displacement vs distance graph and explain the difference between the two. The undulations in an electromagnetic wave occur in the electric and magnetic fields. Longitudinal waves are waves in which the vibration of the medium is parallel to the direction the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same (or. Web wave 1, gotham 1. The movement of particles in water waves is in a clockwise direction. The red points move around their equilibrium positions. Draw a displacement vs time and a displacement vs distance graph and explain the difference between the two. Web ocean waves are a peculiar mixture of transverse and longitudinal, with parcels of water moving in. Describe the motion of the toy duck. You could therefore draw the wave by. Water waves are an example of both longitudinal and transverse waves. The wave can be visualized as compressions and expansions travelling along the medium. It repeats itself in a periodic and regular fashion over both time and space. In fact, the wavelength of a wave can be measured as. Mechanical longitudinal waves are also called compressional or compression waves. Web water waves are an example of waves that involve a combination of both longitudinal and transverse motions. The animation at right shows a water wave travelling from left to right in a. Web longitudinal waves can be described. Although, transverse waves resemble physically the plots that we drew in figures 8.1.5 and 8.1.6, we represent harmonic longitudinal wave exactly the same way using sinusoidal functions. Web a wave is a repeating pattern. (obviously the particles in reality move much shorter distances, and the real movement is very quick.) the nodes, i.e. Parts of a longitudinal wave. Web sound. You could therefore draw the wave by. Web sound waves traveling through a fluid such as air travel as longitudinal waves. Particles of the fluid (i.e., air) vibrate back and forth in the direction that the sound wave is moving. The type of wave on the surface of a body of water is a transverse wave. Also called the propagation speed. Web a wave is a repeating pattern. A point on any coil of the spring. Draw a displacement vs time and a displacement vs distance graph and explain the difference between the two. Web this app demonstrates the harmonics of the air in a tube as an example of standing longitudinal waves. Web pressure waves caused by repeated movements in a liquid or gas; Depends only on the properties of the medium. (obviously the particles in reality move much shorter distances, and the real movement is very quick.) the nodes, i.e. Oscillations where particles are displaced perpendicular to the wave direction. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Churchill downs confirmed the draw for the 150th running of the kentucky derby. Water waves are an example of both longitudinal and transverse waves.
Schematic diagram of a sound (longitudinal) wave produced by a

Longitudinal and Transverse wave type, vector illustration scientific
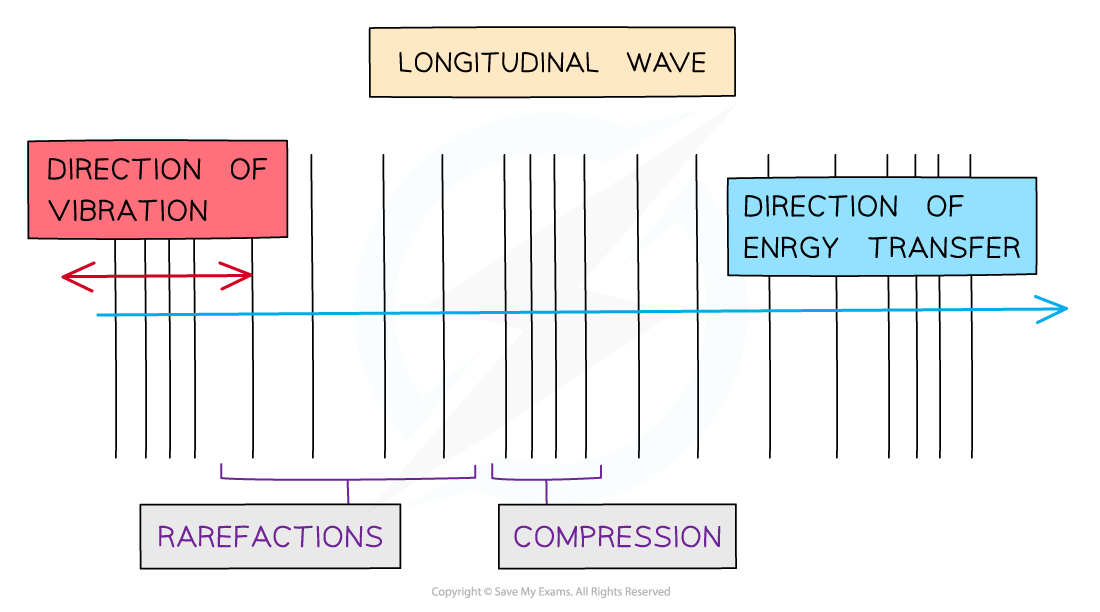
Edexcel A Level Physics复习笔记5.3 Longitudinal Waves翰林国际教育
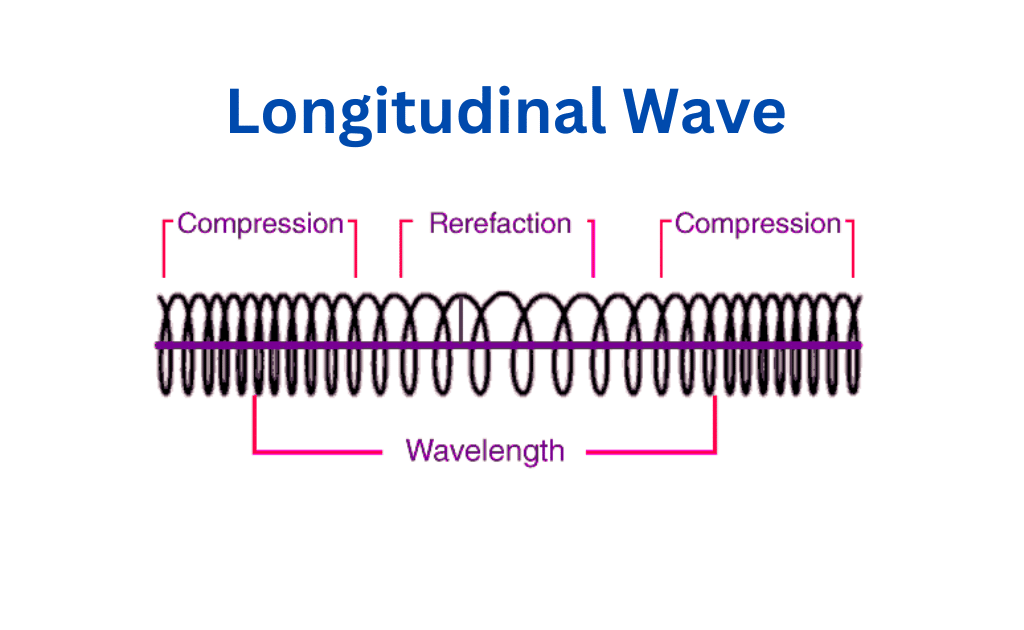
Longitudinal WavesDefinition, Characteristics, And Examples

Properties of waves and wave cycles. Scalar, transverse, energy and
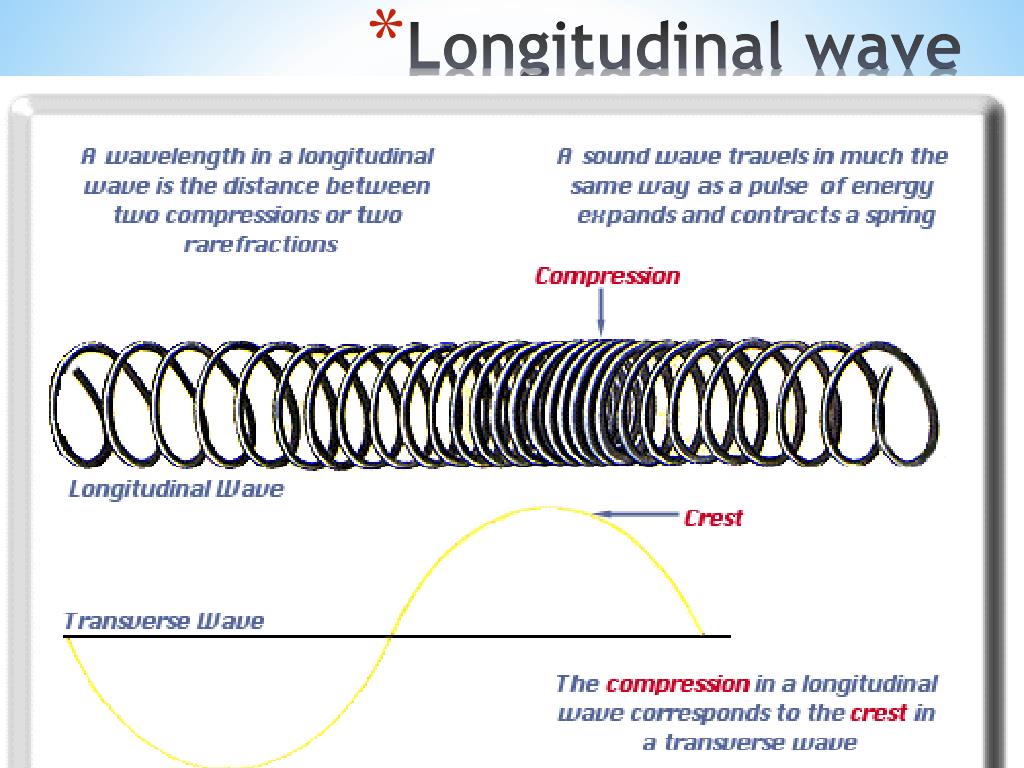
PPT Chapter 11 Waves PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1901329

Lesson Video Transverse and Longitudinal Waves Nagwa
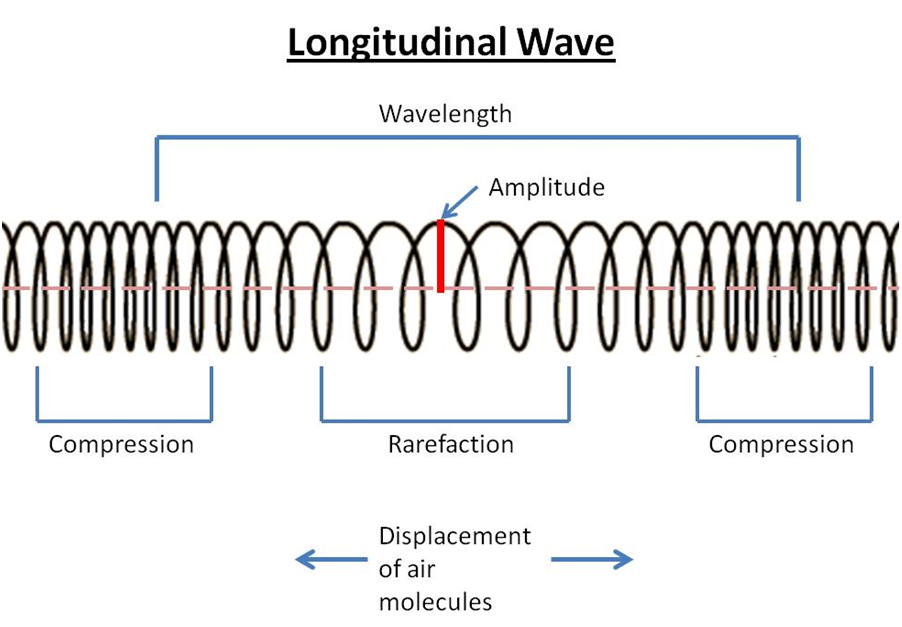
Waves at emaze Presentation
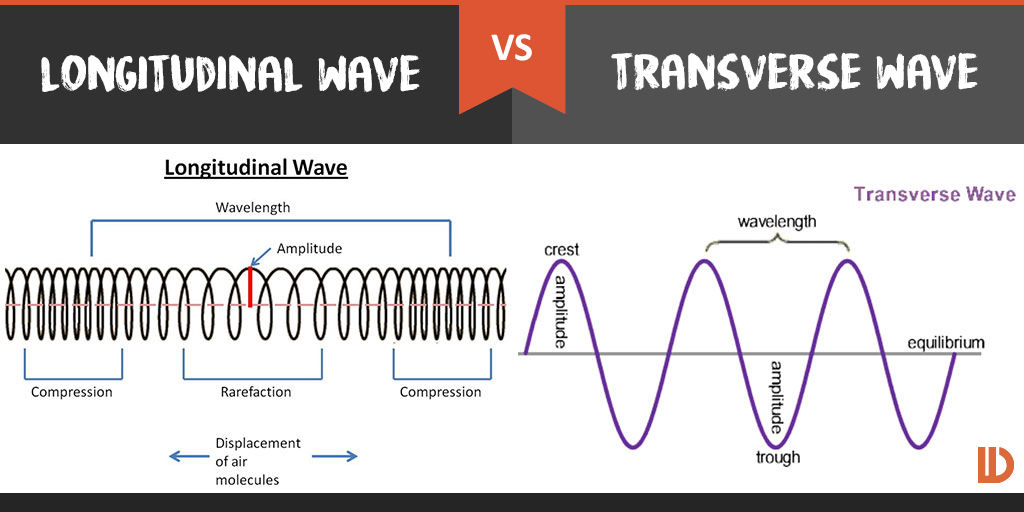
Transverse And Longitudinal Wave Diagram
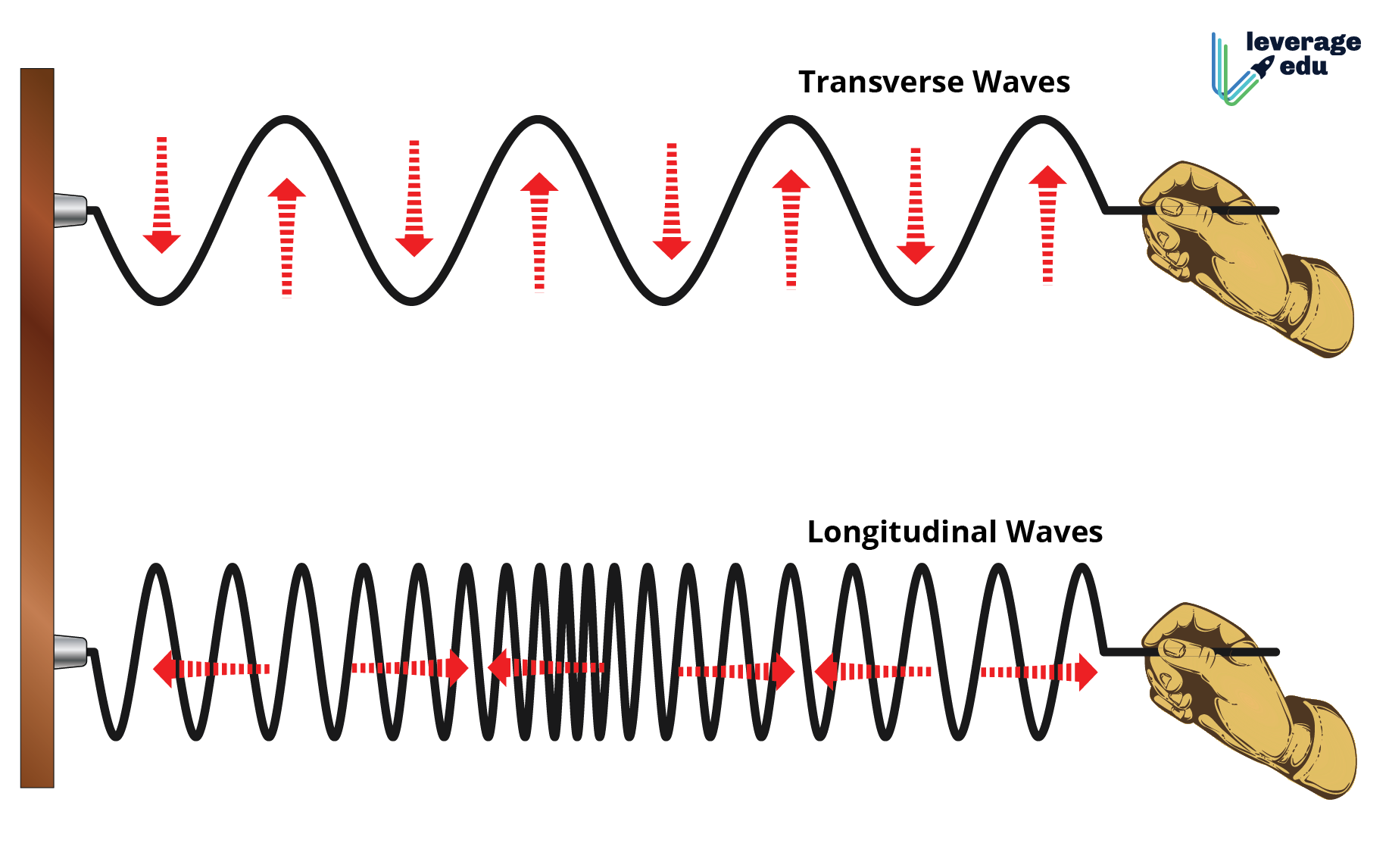
Transverse vs Longitudinal Wave Leverage Edu
Web Use A Table For This.
It Is Made Of Refractions And Compressions.
It Repeats Itself In A Periodic And Regular Fashion Over Both Time And Space.
Longitudinal Waves (Like Sound) Move In The Direction Of Propagation, While Transverse Waves (Like Light) Move Perpendicular To This Direction.
Related Post: