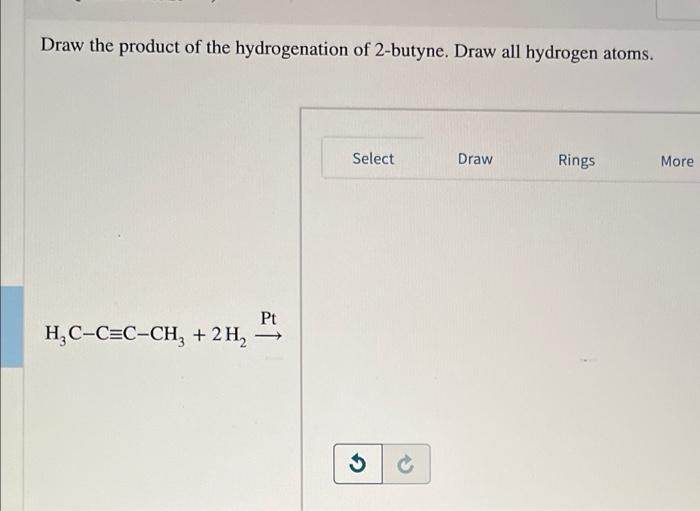
Draw The Product Of The Hydrogenation Of 2 Butyne
Draw The Product Of The Hydrogenation Of 2 Butyne - The final structure will be: Web the dehydrohalogenation occurs twice, in two steps, the first product is a haloalkene, and the second product is the alkyne. Web hydrogen atoms are not drawn if they are attached to a carbon. Write equations for the catalytic hydrogenation of alkynes to alkanes and cis alkenes. H2 c ch3 2 h This problem has been solved! You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. This problem has been solved! Other atoms besides carbon and hydrogen are represented by their elemental symbols. Approach to solving the question: You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Amide, usually nanh2, is a base. Web the dehydrohalogenation occurs twice, in two steps, the first product is a haloalkene, and the second product is the alkyne. This problem has been solved! The final structure will be: This problem has been solved! Web the dehydrohalogenation occurs twice, in two steps, the first product is a haloalkene, and the second product is the alkyne. Approach to solving the question: Draw the product of the. When we add the second mole of hydrogen (h₂), the double bond between the second and third carbons will be reduced to a single. Draw the product of the. Approach to solving the question: Hydrogenation is a reduction reaction that transforms an alkyne. This problem has been solved! This problem has been solved! Select draw more erase h3cch2ch2ch3 + 2h2 3 rings. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Draw the product of the. Write equations for the catalytic hydrogenation of alkynes to alkanes and cis alkenes. Other atoms besides carbon and hydrogen are represented by their elemental symbols. H2 c ch3 2 h This problem has been solved! When we add the second mole of hydrogen (h₂), the double bond between the second and third carbons will be reduced to a single bond. Select draw more erase h3cch2ch2ch3 + 2h2 3 rings. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Amide, usually nanh2, is a base. Hydrogenation means adding hydrogen (h₂) to. Other atoms besides carbon and hydrogen are represented by their elemental symbols. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Approach to solving the question: Hydrogenation is a reduction reaction that transforms an alkyne. When we add the second mole of hydrogen (h₂), the double bond between the second and third carbons will be reduced to a single bond. Web hydrogen atoms are not drawn if they are attached to a carbon. H2 c ch3 2 h Amide, usually nanh2, is a base. Write equations for the catalytic hydrogenation of alkynes to alkanes and cis alkenes. Web hydrogen atoms are not drawn if they are attached to a carbon. The final structure will be: Amide, usually nanh2, is a base. Hydrogenation means adding hydrogen (h₂) to. Web hydrogen atoms are not drawn if they are attached to a carbon. Approach to solving the question: Other atoms besides carbon and hydrogen are represented by their elemental symbols. Web the dehydrohalogenation occurs twice, in two steps, the first product is a haloalkene, and the second product is the alkyne. Hydrogenation is a reduction reaction that transforms an alkyne. When we add the second mole of hydrogen (h₂), the double bond between the second and third carbons will be reduced to a single bond. Hydrogenation is a reduction reaction that transforms an alkyne. This problem has been solved! You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. The final structure will be: H2 c ch3 2 h Approach to solving the question: When we add the second mole of hydrogen (h₂), the double bond between the second and third carbons will be reduced to a single bond. Amide, usually nanh2, is a base. Select draw more erase h3cch2ch2ch3 + 2h2 3 rings. Other atoms besides carbon and hydrogen are represented by their elemental symbols. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. This problem has been solved! Hydrogenation means adding hydrogen (h₂) to. Write equations for the catalytic hydrogenation of alkynes to alkanes and cis alkenes. The final structure will be: Web the dehydrohalogenation occurs twice, in two steps, the first product is a haloalkene, and the second product is the alkyne. Draw the product of the.
SOLVED Draw = the product of the hydrogenation of 2butyne. Draw all
Solved Draw the product of the hydrogenation of 2butyne.
Solved Draw the product of the hydrogenation of 2butyne.
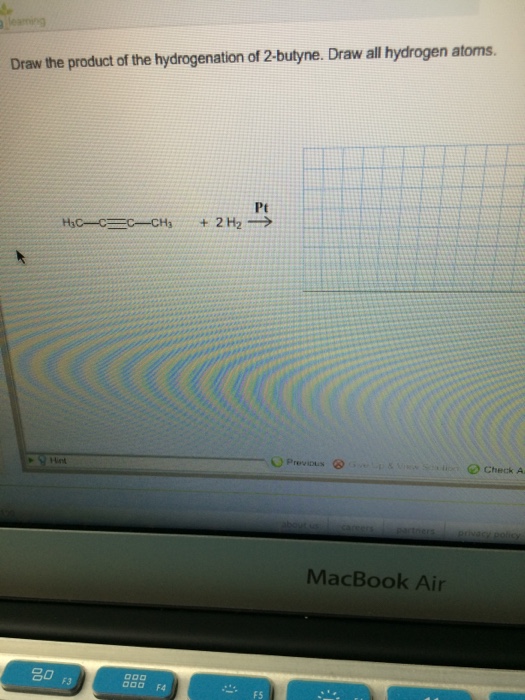
Solved Draw the product of the hydrogenation of 2butyne.
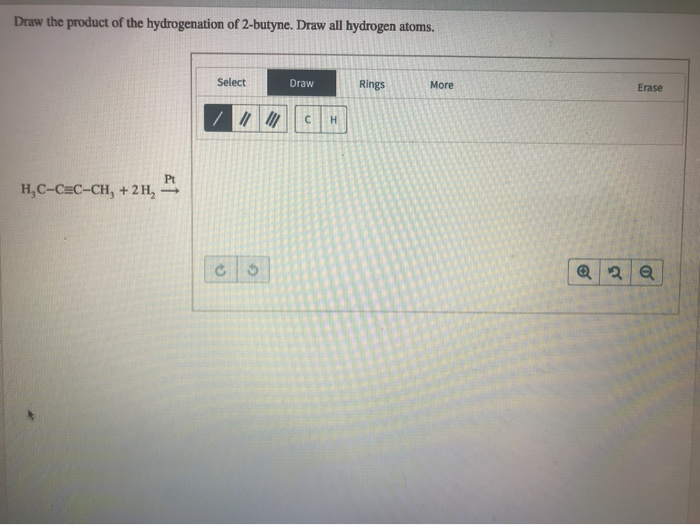
Solved Draw the product of the hydrogenation of 2butyne.
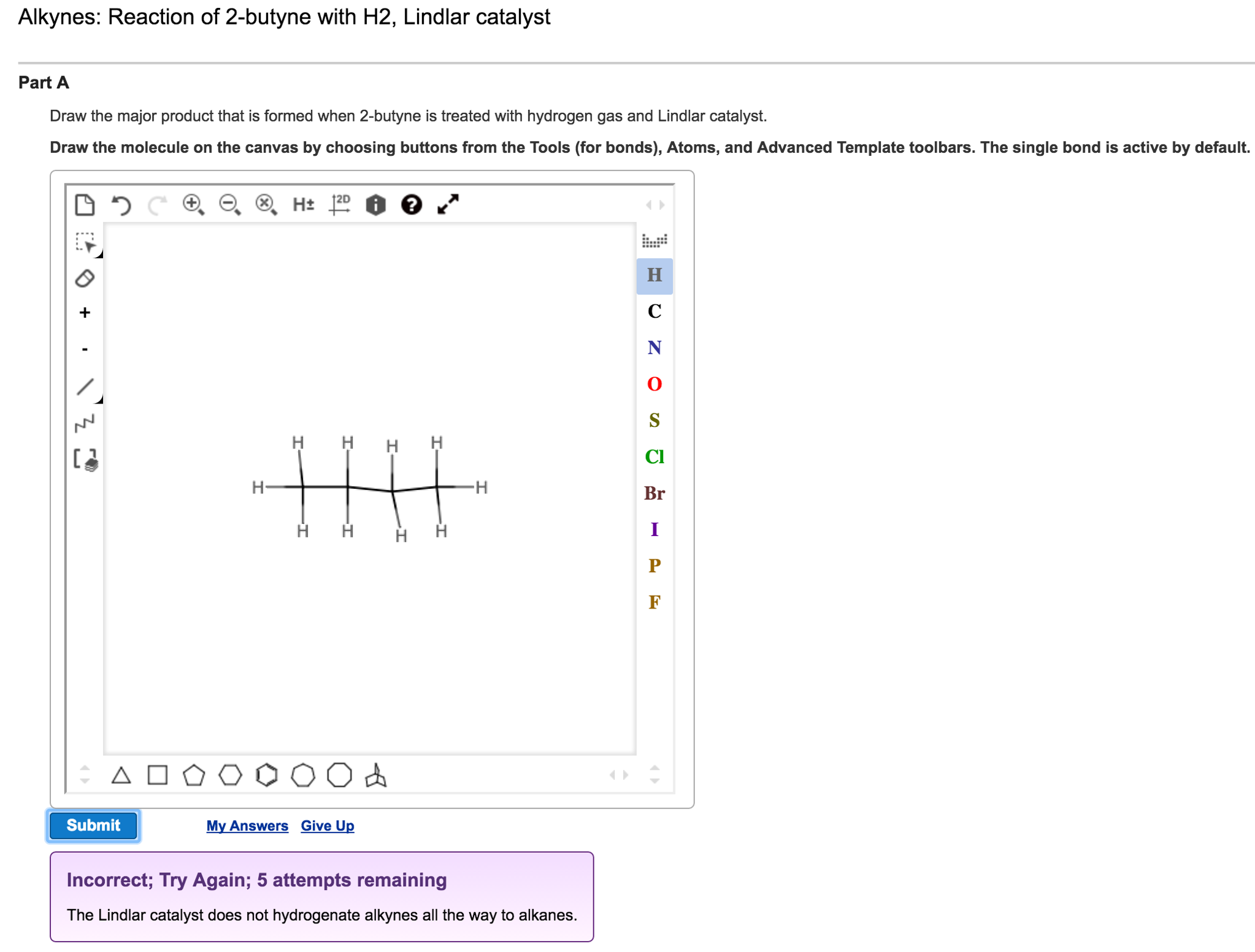
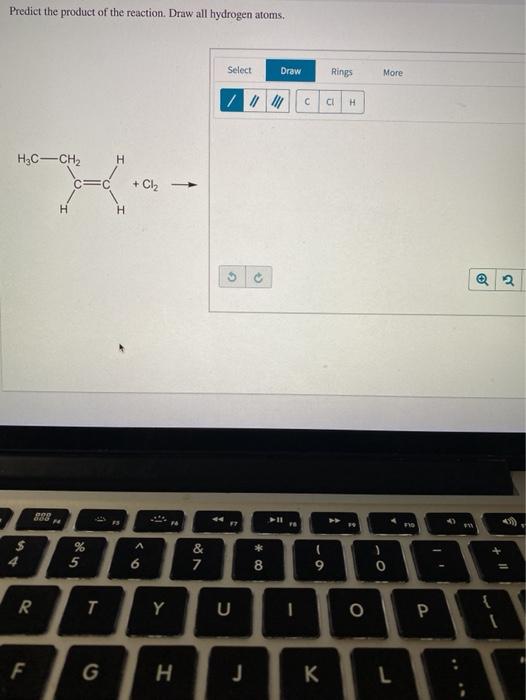
Solved Draw the major product that is formed when 2butyne
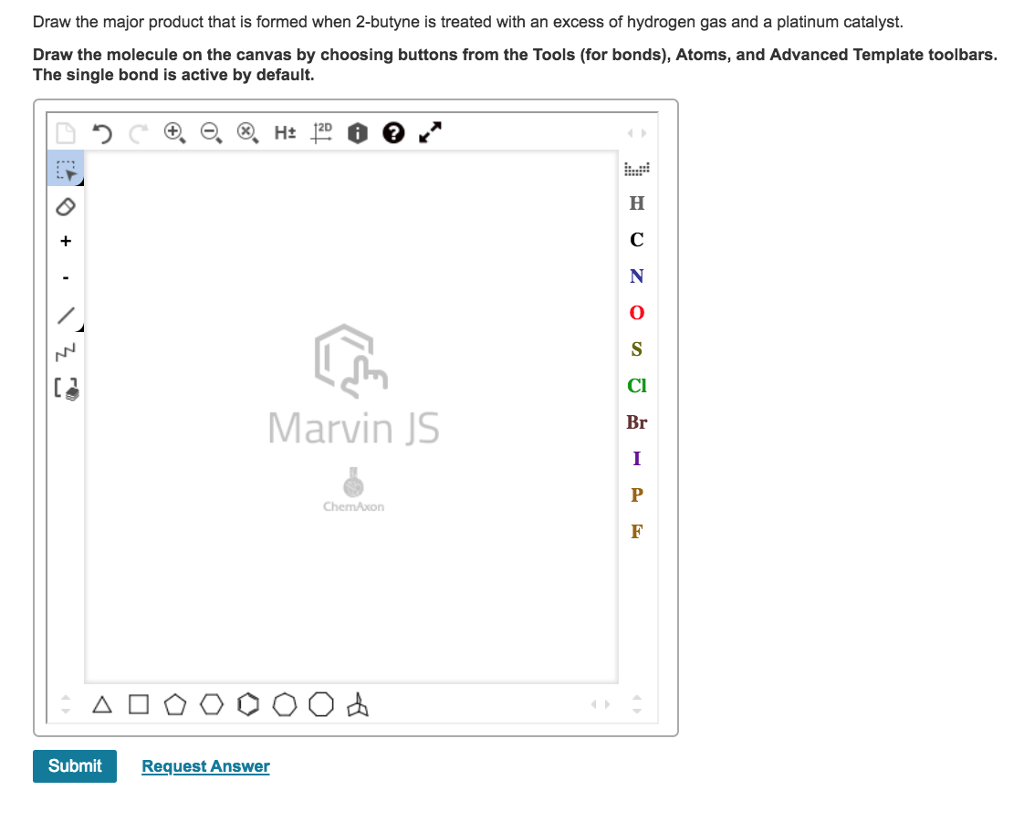
Solved Draw the major product that is formed when 2butyne
Solved Draw the product of the hydrogenation of 2butyne.

Draw the product of the hydrogenation of 2butyne. Draw all hydrogen
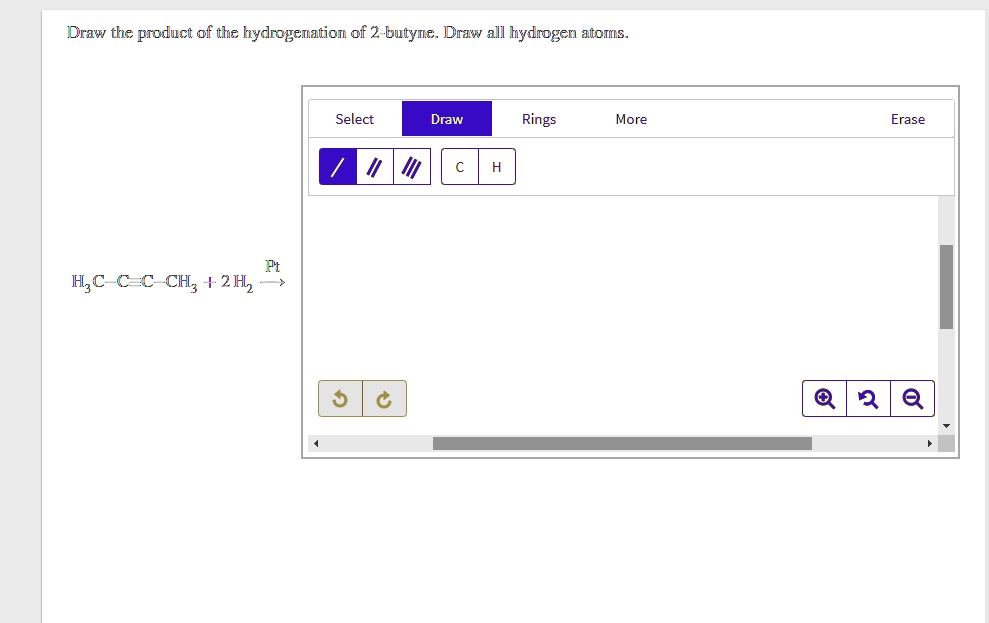
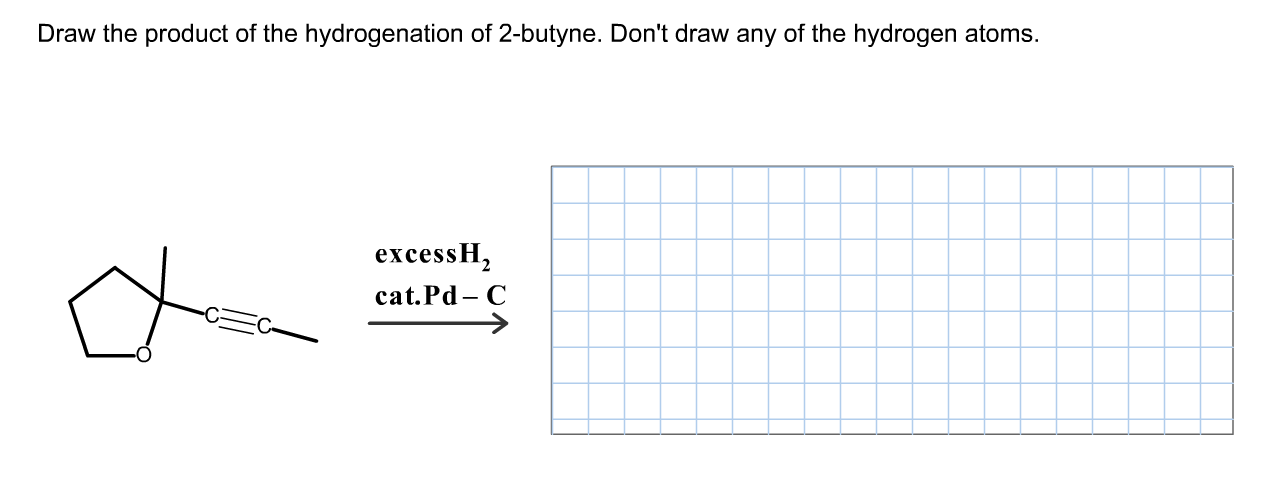
SOLVED Draw the product of the hydrogenation of 2butyne. Draw all
Web Hydrogen Atoms Are Not Drawn If They Are Attached To A Carbon.
After Completing This Section, You Should Be Able To.
Hydrogenation Is A Reduction Reaction That Transforms An Alkyne.
This Problem Has Been Solved!
Related Post: