Draw And Label Cell Cycle
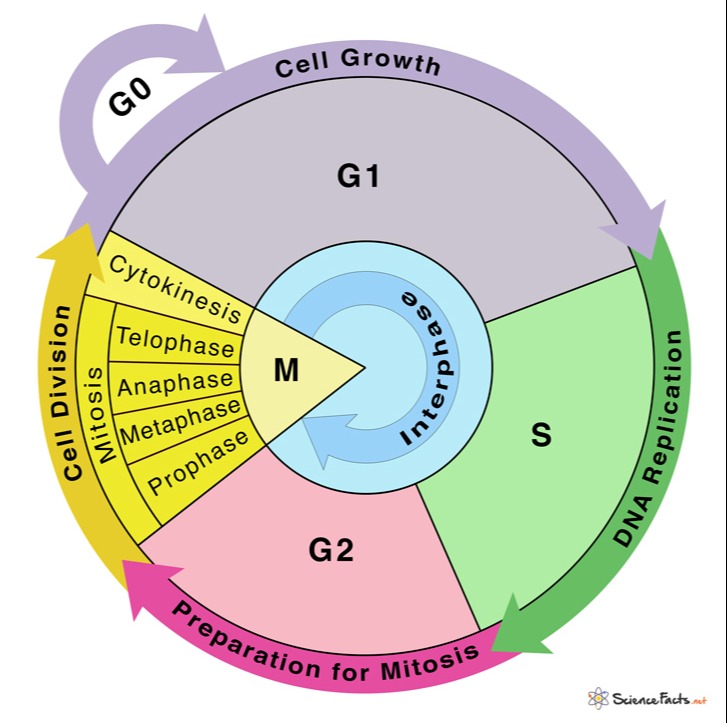
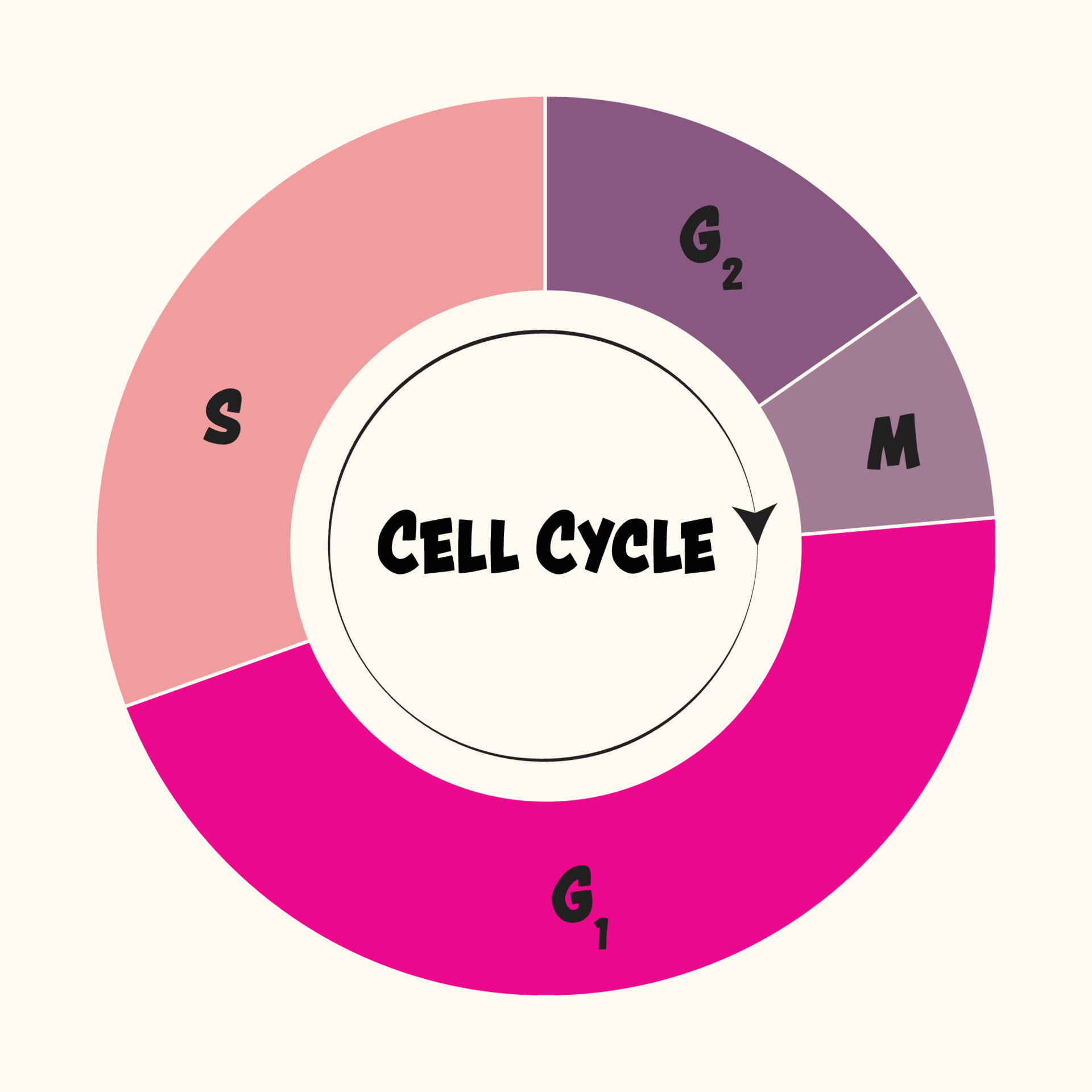
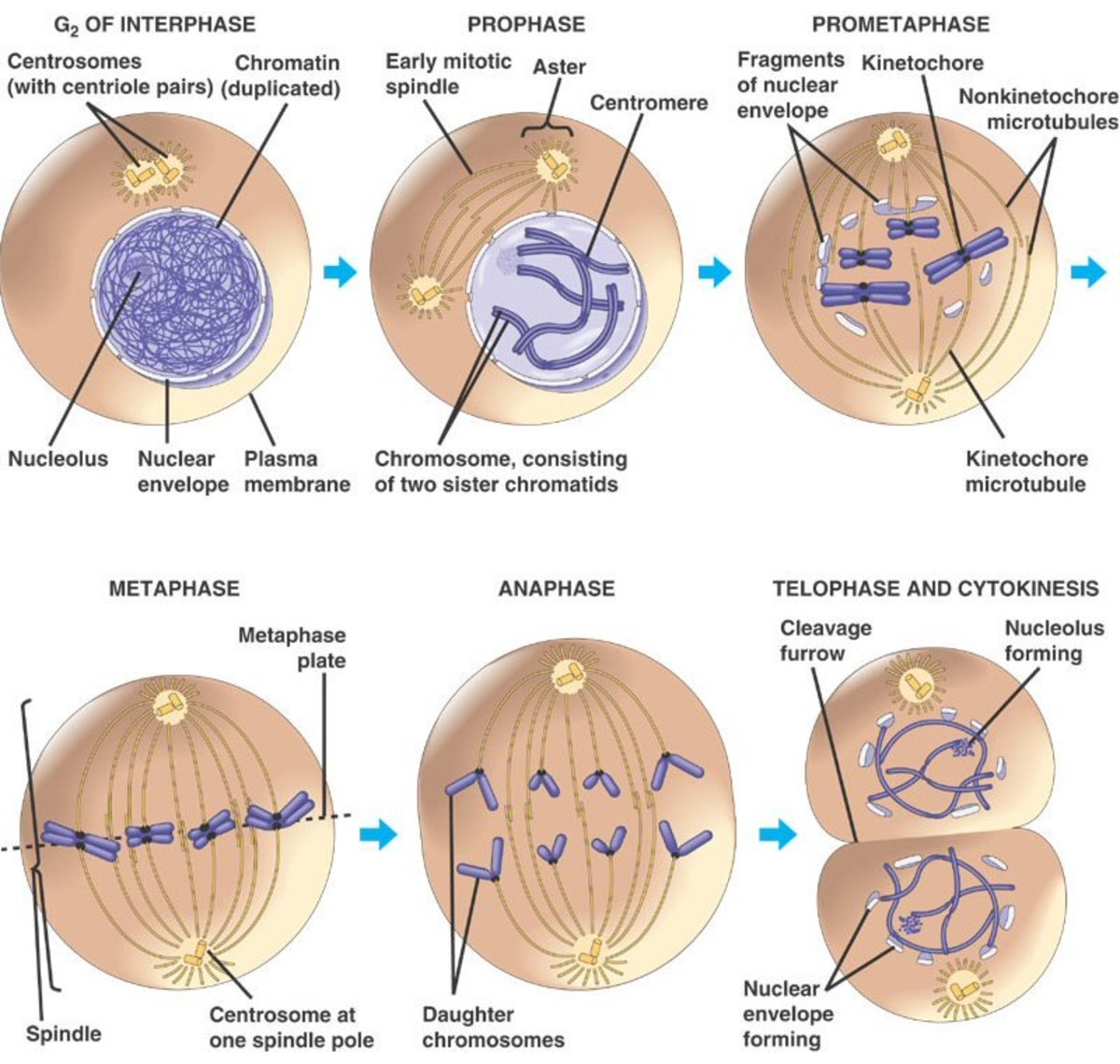
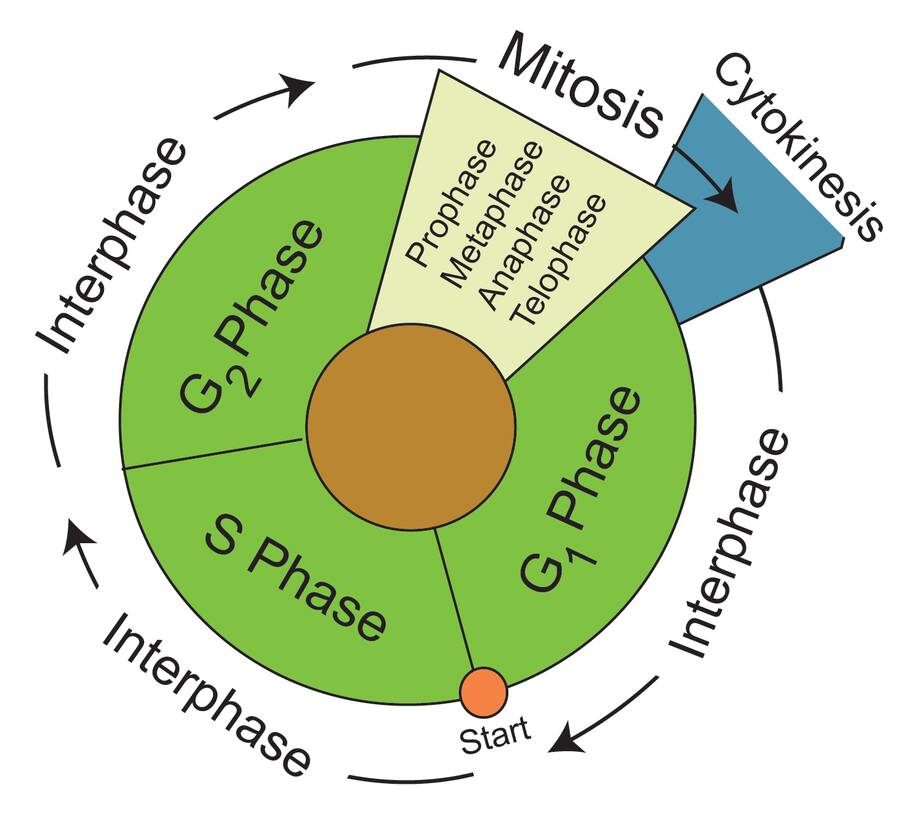
Draw And Label Cell Cycle - Some cells exit the cycle and enter g 0. During interphase, the cell grows and dna is replicated. Some textbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase (called prophase) and a late phase (called prometaphase). Mitosis is the process of nuclear division. The mitotic phase follows interphase. _____ how many daughter cells are created from mitosis and cytokinesis? Web the cell continues to grow but also prepares for what’s to come in the next phase. Identify and draw a cell in each of the four stages of mitosis in the onion slide. A common task of many research teams is the analysis of cell cycle progression through the distinct cell cycle phases. During the mitotic phase, the replicated dna and cytoplasmic contents are separated and the cell divides. Interphase is the phase where the cell grows, replicates its dna and prepares for division. The small section labeled “m” represents mitosis, while interphase is shown subdivided into its major components: Web in the cell pictured above, how many chromosomes are present during prophase? Web cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and. Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. A cell moves through a series of phases in an orderly manner. Students describe each stage of the cell cycle (s and g2 phases shown) using the picture of the cell at that stage. Web locate the region of active cell division, known as the root apical meristem, which is. Various methods can be used for this purpose. Mitosis is nuclear division during. Interphase and the mitotic phase (figure 1). Interphase and the mitotic (m) phase. The mitotic phase follows interphase. In eukaryotic cells, or cells with a nucleus, the stages of the cell cycle are divided into two major phases: Collectively, we consider g 1, s, and g 2 to be interphase (i.e., the phases “in between” m phase). Interphase is divided into g 1, s, and g 2 phases. Cells grow following division and produce proteins and organelles. Observe. While most of the high. In eukaryotic cells, the cell cycle is divided into two major phases: Mitosis is the process of nuclear division. Web the cell cycle. Web the graphic below shows a visual representation of the cell cycle. During interphase, the cell grows and dna is replicated. Then draw cells in cytokinesis and interphase as well. At the end of mitosis, a cell contains two identical nuclei. Web mitosis consists of four basic phases: Students describe each stage of the cell cycle (s and g2 phases shown) using the picture of the cell at that stage. The mitotic phase follows interphase. Interphase is the longest part of the cell cycle. The small section labeled “m” represents mitosis, while interphase is shown subdivided into its major components: Mitosis is divided into four stages (pmat) listed below. Identify and draw a cell in each of the four stages of mitosis in the onion slide. This cell cycle is used by all eukaryotic cells to produce new cells. In eukaryotic cells, the cell cycle is divided into two major phases: Web in the cell pictured above, how many chromosomes are present during prophase? Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. What structure holds the individual chromatids together? _____ how many daughter cells are created from mitosis and cytokinesis? Interphase and the mitotic phase (figure 6.2.1 6.2. The image shows a cell in interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, chromosomes will align, separate, and move into new daughter cells. Interphase is divided into g 1, s, and g 2 phases. During interphase, the cell grows and dna is replicated. Interphase is divided into g 1, s, and g 2 phases. The mitotic phase follows interphase. Web locate the region of active cell division, known as the root apical meristem, which is about 1 mm behind the actual tip of the root. Then draw cells in cytokinesis and interphase as well. Prophase → metaphase → anaphase → telophase. Identify and draw a cell in each of the four stages of mitosis in the onion slide. During the mitotic phase, the replicated dna and cytoplasmic contents are separated and the cell divides. Less overwhelm for students = a win. Web dna molecules in the cell nucleus are duplicated before mitosis, during the s (or synthesis) phase of interphase. _____ what anchors the spindle? Some cells exit the cycle and enter g 0. In eukaryotic cells, the cell cycle is divided into two major phases: _____ during what phase does cytokinesis begin? Web the cell cycle has two major phases: Interphase and the mitotic phase (figure 6.2.1 6.2. Web the cell cycle. The cell cycle has two major phases: During interphase, the cell grows and dna is replicated. The image shows a cell in interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Various methods can be used for this purpose.
Cell Division An Intro AmoebaMike

Cell Cycle Phase Definition, Fours phases of Cell cycle Division
The Cell Cycle Study Guide Inspirit
Phases of the cell cycle 6894530 Vector Art at Vecteezy

Cell Cycle Diagram Quizlet
Stages of the Cell Cycle Mitosis (Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase

6 Stages Of Mitosis In Plant Cells What Are The 6 Stages Of Mitosis Riset
Cell Biology, Mitosis Cell Cycle

The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation TeachMePhysiology

Labeled Diagram Of The Cell Cycle Diagram Cell Cycle Science Mitosis
Web Cells On The Path To Cell Division Proceed Through A Series Of Precisely Timed And Carefully Regulated Stages Of Growth, Dna Replication, And Division That Produces Two Identical (Clone) Cells.
Web The Graphic Below Shows A Visual Representation Of The Cell Cycle.
During Interphase, The Cell Grows And Dna Is Replicated.
Students Label Each Phase And Then Identify Structures Within The Cell That.
Related Post: