Draw A Molecule Of Atp
Draw A Molecule Of Atp - The bonds between the phosphates store available energy, which is released when they are broken. This is a small, relatively simple molecule ( figure 6.13 ), but within some of its. Failed to load structure from its database. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like explain the purpose of atp, draw the structure and label the parts of a molecule of atp, describe the atp. Explore how glucose oxidation contributes to atp synthesis, understand the roles of nadh and fadh2, and learn why. Web atp consists of an adenosine base (blue), a ribose sugar (pink) and a phosphate chain. Web background it is generally accepted that endothelial cells (ecs), primarily rely on glycolysis for atp production, despite having functional mitochondria. Atp is a small, relatively simple molecule (figure 6.3.1 6.3. Web adenosine triphosphate, abbreviated atp, is an organic molecule that supplies energy for all cellular activities in plants, animals, and lower organisms. The bonds that connect the. Failed to load structure from its database. Web adenosine triphosphate, abbreviated atp, is an organic molecule that supplies energy for all cellular activities in plants, animals, and lower organisms. Web at the heart of atp is a molecule of adenosine monophosphate (amp), which is composed of an adenine molecule bonded to a ribose molecule and to a single. Adenosine triphosphate. The bonds that connect the. The bonds between the phosphates store available energy, which is released when they are broken. Explore how glucose oxidation contributes to atp synthesis, understand the roles of nadh and fadh2, and learn why. Web atp consists of an adenosine base (blue), a ribose sugar (pink) and a phosphate chain. Atp is a small, relatively simple. Web background it is generally accepted that endothelial cells (ecs), primarily rely on glycolysis for atp production, despite having functional mitochondria. Web unravel the mystery of atp production in cellular respiration. The bonds that connect the. Atp captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food. Explore how glucose oxidation contributes to atp synthesis, understand the roles of nadh and. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like draw and annotate a molecule of atp to show how it stores ad releases energy, list the three main cellular. Web glucose, a sugar that is delivered via the bloodstream, is the product of the food you eat, and this is the molecule that is used to create atp. Web. The bonds that connect the. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like explain the purpose of atp, draw the structure and label the parts of a molecule of atp, describe the atp. Web at the heart of atp is a molecule of adenosine monophosphate (amp), which is composed of an adenine molecule bonded to a ribose molecule. The bonds between the phosphates store available energy, which is released when they are broken. Web atp consists of an adenosine base (blue), a ribose sugar (pink) and a phosphate chain. Failed to load structure from its database. Web the process of aerobic respiration requires several steps, but the overall reaction is that one glucose molecule requires six oxygen molecules. Web adenosine triphosphate, abbreviated atp, is an organic molecule that supplies energy for all cellular activities in plants, animals, and lower organisms. Sweet foods provide a rich source of. Web background it is generally accepted that endothelial cells (ecs), primarily rely on glycolysis for atp production, despite having functional mitochondria. The bonds between the phosphates store available energy, which is. Web background it is generally accepted that endothelial cells (ecs), primarily rely on glycolysis for atp production, despite having functional mitochondria. Atp captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food. Web the process of aerobic respiration requires several steps, but the overall reaction is that one glucose molecule requires six oxygen molecules for a reaction that. Sweet foods provide. 1 ), but within some of its. Atp is a small, relatively simple molecule (figure 6.3.1 6.3. Web glucose, a sugar that is delivered via the bloodstream, is the product of the food you eat, and this is the molecule that is used to create atp. Web at the heart of atp is a molecule of adenosine monophosphate (amp), which. Failed to load structure from its database. Web background it is generally accepted that endothelial cells (ecs), primarily rely on glycolysis for atp production, despite having functional mitochondria. The bonds between the phosphates store available energy, which is released when they are broken. Web cells actually draw their energy from the phosphate tail of atp. Explore how glucose oxidation contributes. Web atp consists of an adenosine base (blue), a ribose sugar (pink) and a phosphate chain. Atp captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food. Web background it is generally accepted that endothelial cells (ecs), primarily rely on glycolysis for atp production, despite having functional mitochondria. Explore how glucose oxidation contributes to atp synthesis, understand the roles of nadh and fadh2, and learn why. Web the process of aerobic respiration requires several steps, but the overall reaction is that one glucose molecule requires six oxygen molecules for a reaction that. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like draw and annotate a molecule of atp to show how it stores ad releases energy, list the three main cellular. Web unravel the mystery of atp production in cellular respiration. Web cells actually draw their energy from the phosphate tail of atp. Adenosine triphosphate (atp) is the energy currency for cellular processes. Web adenosine triphosphate, abbreviated atp, is an organic molecule that supplies energy for all cellular activities in plants, animals, and lower organisms. Web chemistry in context december 2, 2019. 1 ), but within some of its. This is a small, relatively simple molecule ( figure 6.13 ), but within some of its. Web glucose, a sugar that is delivered via the bloodstream, is the product of the food you eat, and this is the molecule that is used to create atp. Failed to load structure from its database. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like explain the purpose of atp, draw the structure and label the parts of a molecule of atp, describe the atp.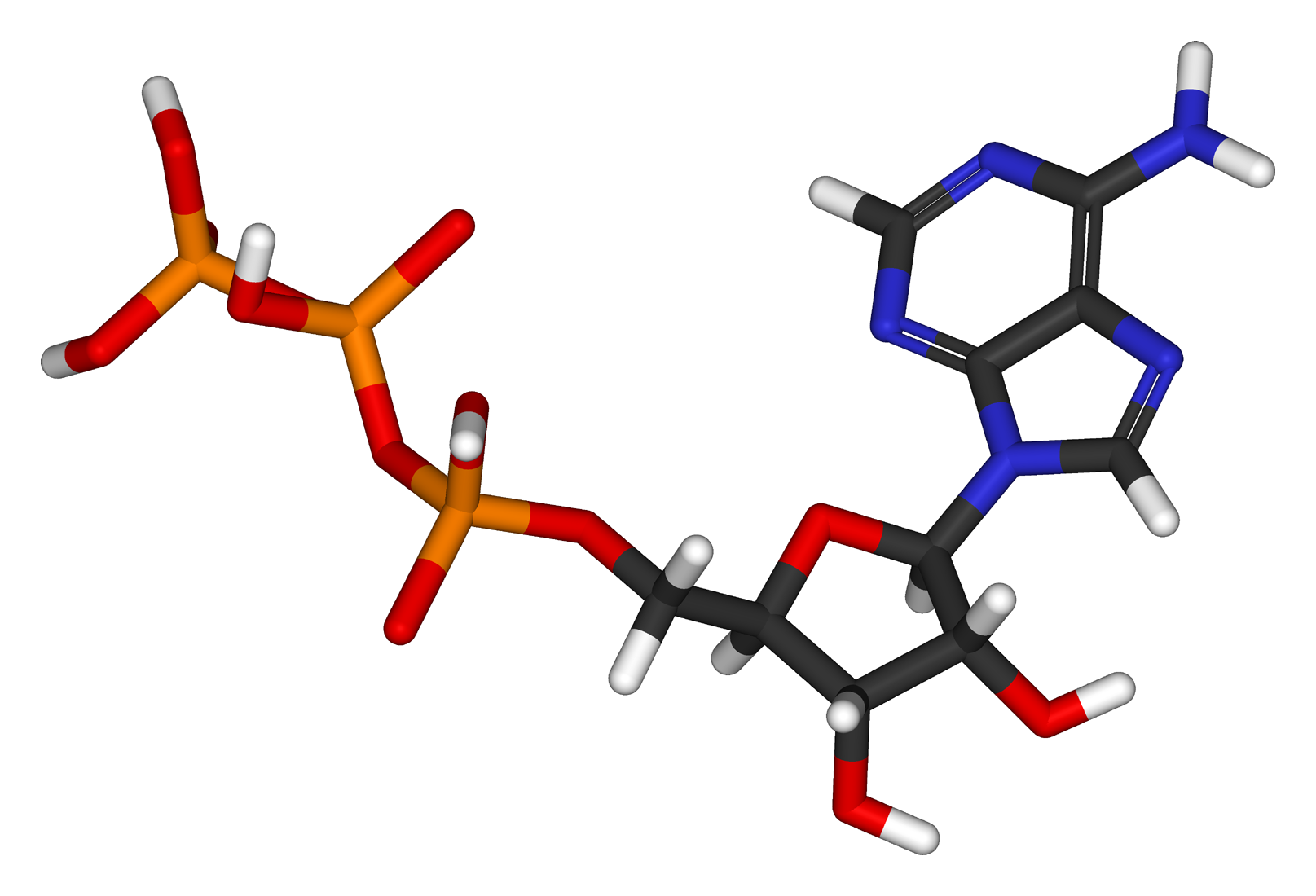
ATP The Fuel that Powers Our Cells Learn how to Feed a Brain!
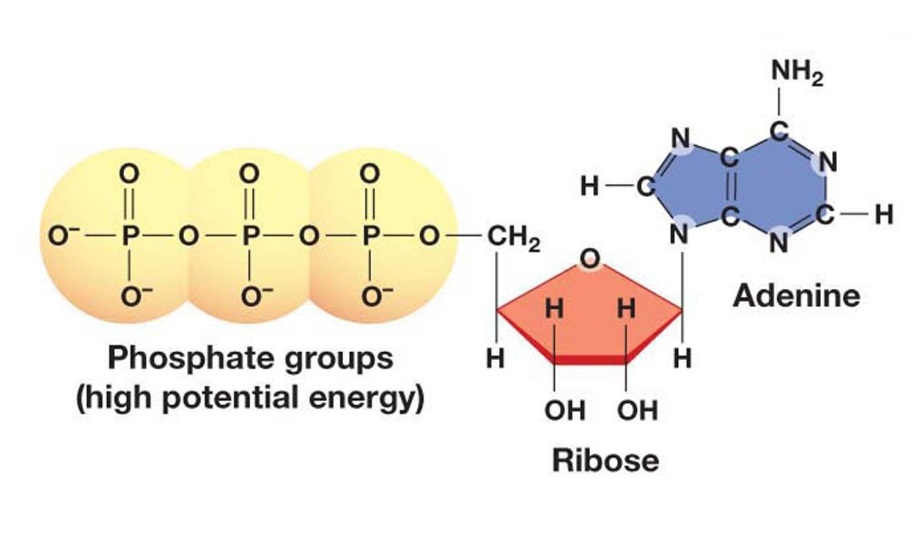
35 Label Each Part Of The Atp Molecule Labels Database 2020

ATP définition et explications

Atp Definition Biology Examples and Forms
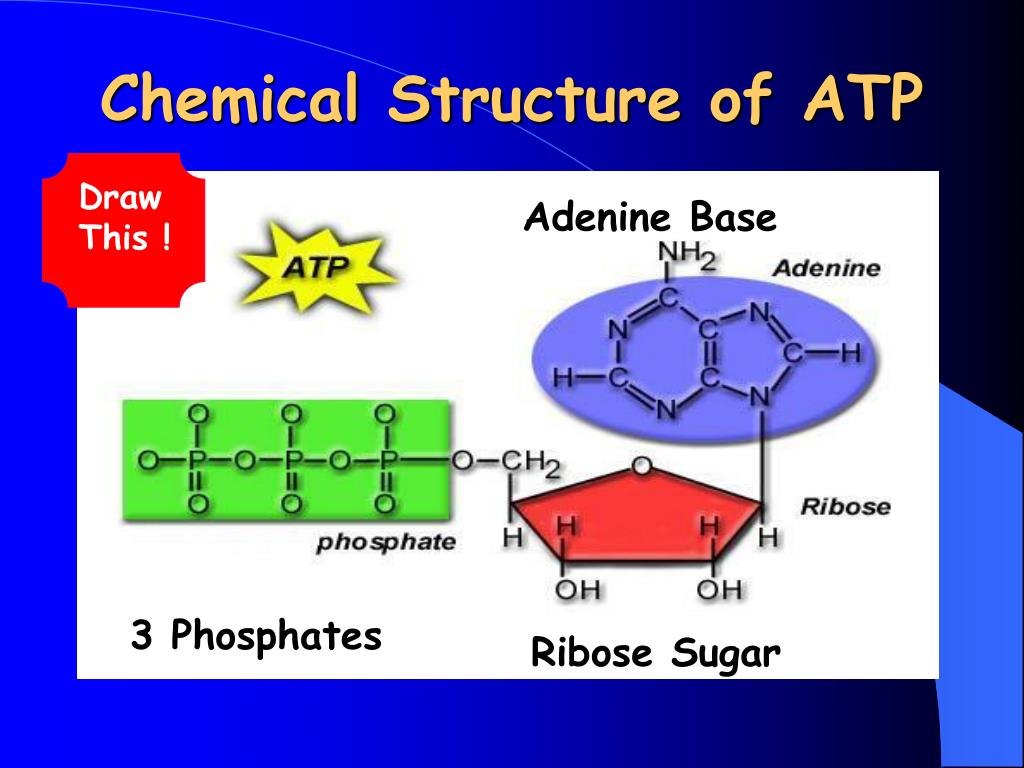
PPT ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration PowerPoint Presentation, free
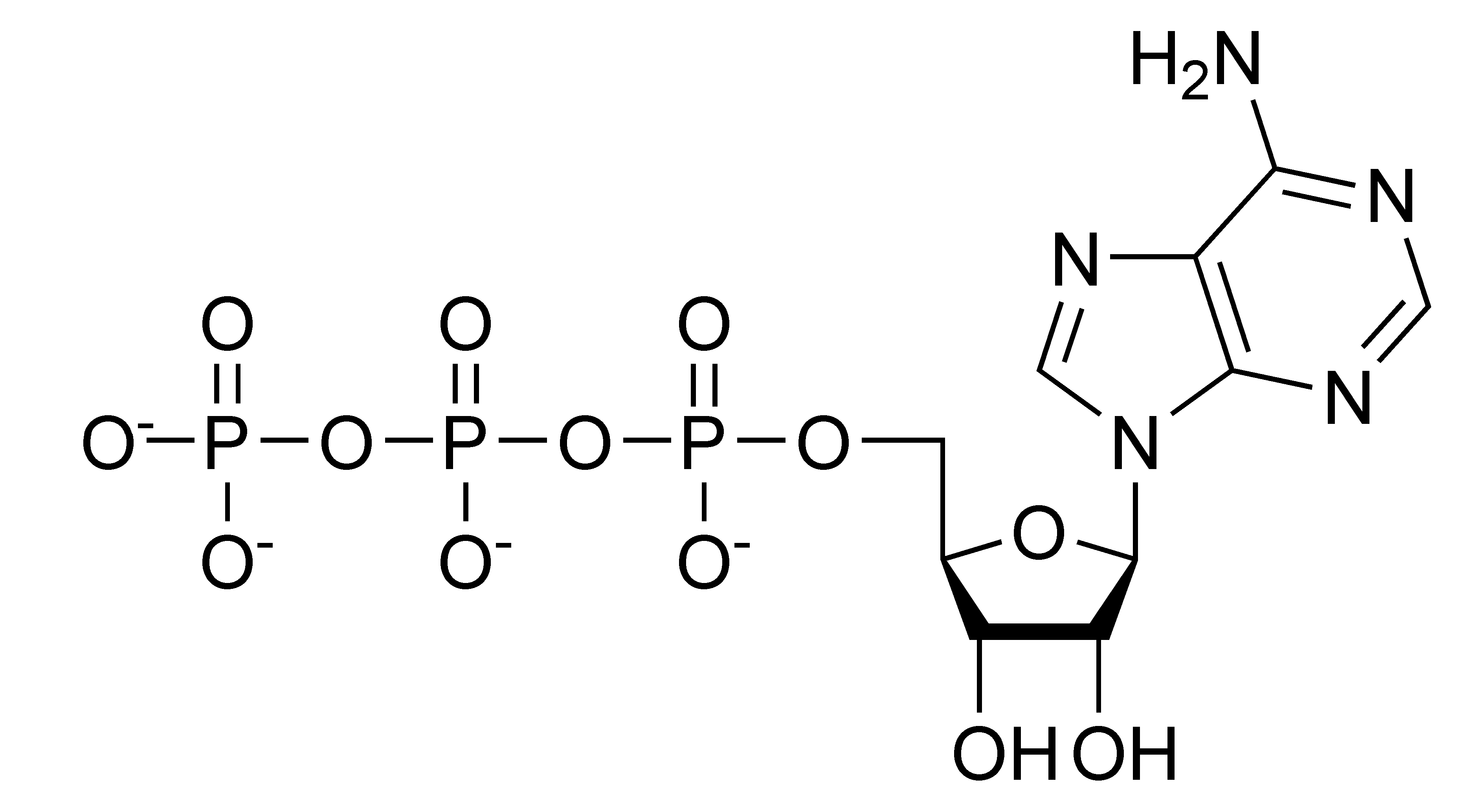
FileATP chemical structure.png Wikipedia
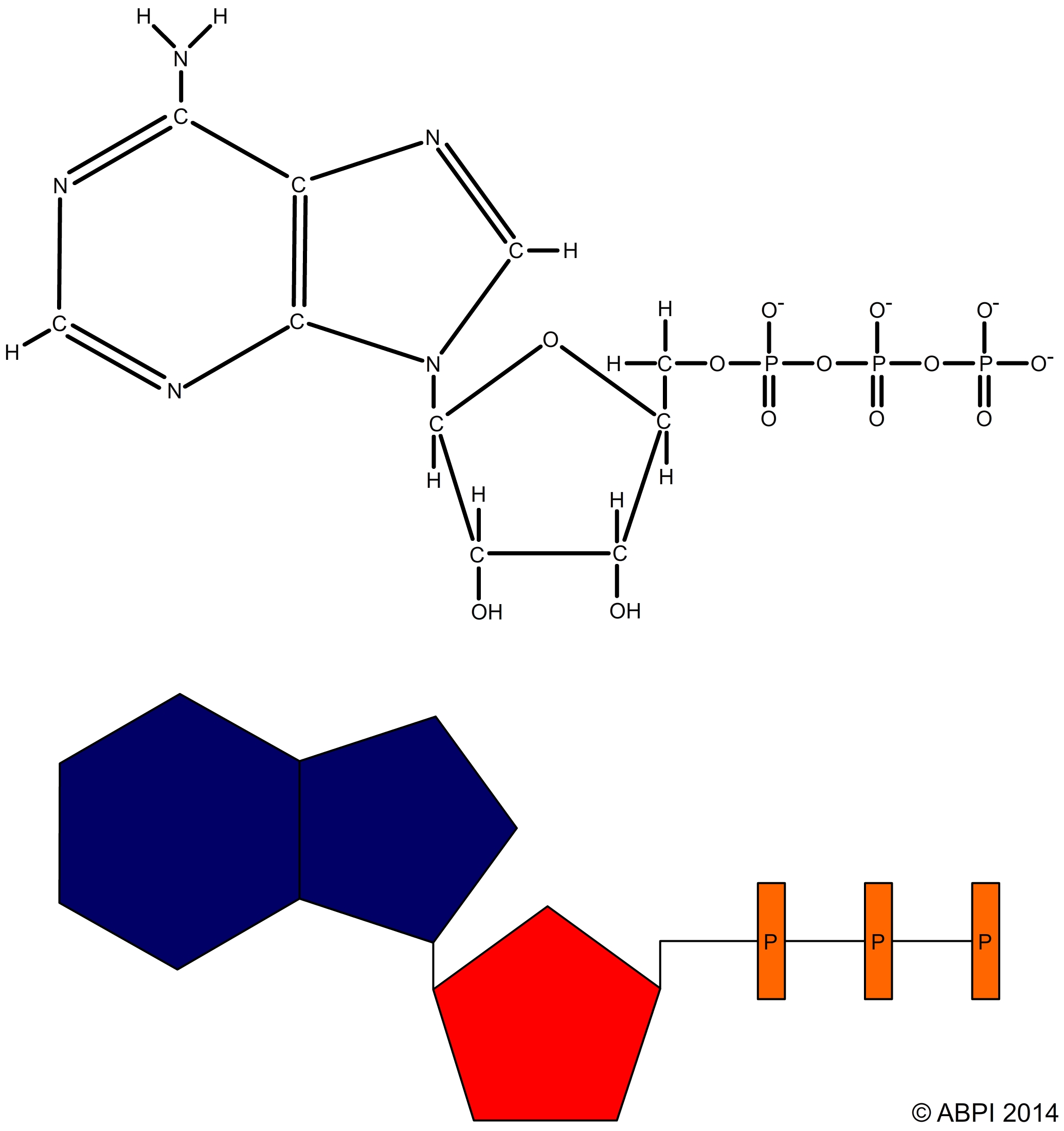
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
ATP Molecule

Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Definition and Synthesis
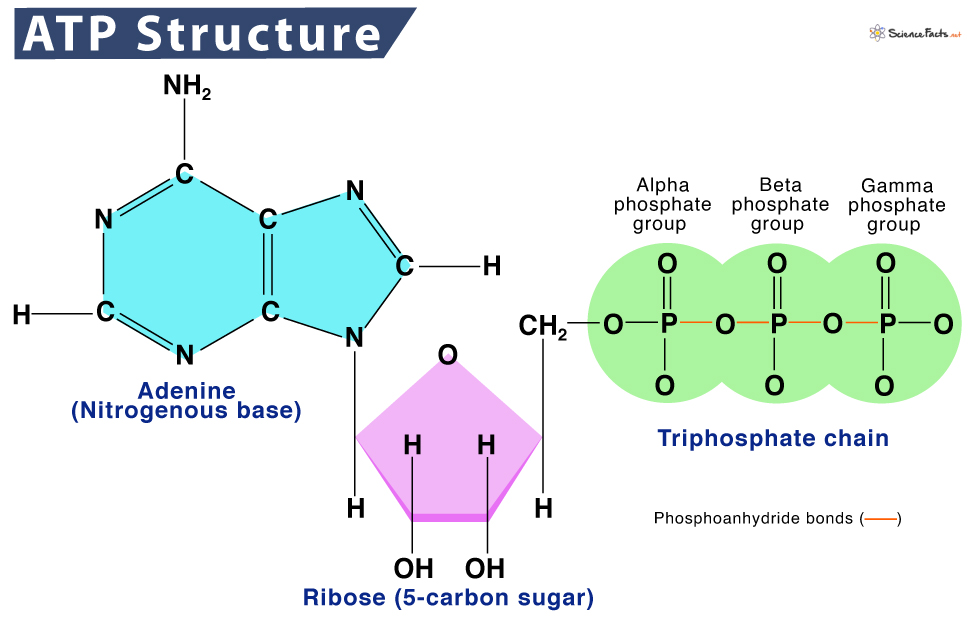
Atp Diagram
Web At The Heart Of Atp Is A Molecule Of Adenosine Monophosphate (Amp), Which Is Composed Of An Adenine Molecule Bonded To A Ribose Molecule And To A Single.
Atp Is A Small, Relatively Simple Molecule ( Figure 6.13 ), But Within Some Of Its Bonds, It.
The Bonds Between The Phosphates Store Available Energy, Which Is Released When They Are Broken.
The Bonds That Connect The.
Related Post:
