Dna Strand Template
Dna Strand Template - Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Each nucleotide in the synthesized dna strand is complementary to the nucleotide in the template strand. Web the process occurs in two steps: Here is an overview of the central dogma. Web explain how rna is synthesized using dna as a template. In eukaryotes, the rna must go through additional processing steps to become a messenger rna, or mrna. Distinguish between transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Web the model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. This is because its base sequence is identical to the synthesised mrna, except for the replacement of thiamine bases with uracil. Translation then decodes mrna into amino acids, forming proteins essential for life functions. Web in transcription, the dna sequence of a gene is rewritten in rna. Web only one of the two dna strands serves as a template for transcription. The four ribonucleotide triphosphates (rntps) are atp, gtp, utp, and ctp. Distinguish between transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Web this strand of dna is called the template strand. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Transcription = dna → rna. Distinguish between transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. This is because its base sequence is identical to the synthesised mrna, except for the replacement of thiamine bases with uracil. Web position of the template and coding strands during transcription. Rna polymerases do not need primers to begin transcription. Each nucleotide in the synthesized dna strand is complementary to the nucleotide in the template strand. In translation, the sequence of nucleotides in the mrna is translated into a sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide (protein chain). Replication produces two identical dna double helices, each with one new and one. Replication creates identical dna strands, while transcription converts dna into messenger rna (mrna). Distinguish between transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Translation = rna → protein. Each nucleotide in the synthesized dna strand is complementary to the nucleotide in the template strand. Rna polymerases begin transcription at dna sequences called promoters. Translation = rna → protein. Rna polymerases do not need primers to begin transcription. It uses dna as a template to make an rna molecule. Web only one of the two dna strands serves as a template for transcription. Rna then leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome in the cytoplasm, where translation occurs. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; Web the model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. Once rna polymerase and its related. Web the process occurs in two steps: Replication. Rna polymerase ii also uses a strand of dna as a template. New dna is made by enzymes called dna polymerases, which require a template and a primer (starter) and synthesize dna in the 5' to 3' direction. Web the model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves. Dna serves as the template for the synthesis of rna much as it does for its own replication. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Translation = rna → protein. The rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the. Rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; The four ribonucleotide triphosphates (rntps) are atp, gtp, utp, and ctp. Web transcription takes place in the nucleus. Distinguish between transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In translation, the sequence of nucleotides in the mrna is translated into a sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide (protein chain). This strand is called the template strand. Each nucleotide in the synthesized dna strand is complementary to the nucleotide in the template strand. Web only one strand of dna is used as a template by enzymes called rna. The nontemplate strand is referred to as. Transcription is the first part of the central dogma of molecular biology: Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Web the model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. It uses dna as a template to make an rna molecule. Web in transcription, the dna sequence of a gene is rewritten in rna. Each nucleotide in the synthesized dna strand is complementary to the nucleotide in the template strand. New dna is made by enzymes called dna polymerases, which require a template and a primer (starter) and synthesize dna in the 5' to 3' direction. Rna then leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome in the cytoplasm, where translation occurs. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. Distinguish between transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The other dna strand is referred to as the coding strand. Each strand in the double helix acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. This is because its base sequence is identical to the synthesised mrna, except for the replacement of thiamine bases with uracil. The mrna sequence is complementary to this template strand and identical to the other strand, known as the coding strand.
Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer

DNA Structure & DNA Replication Biology Online Tutorial
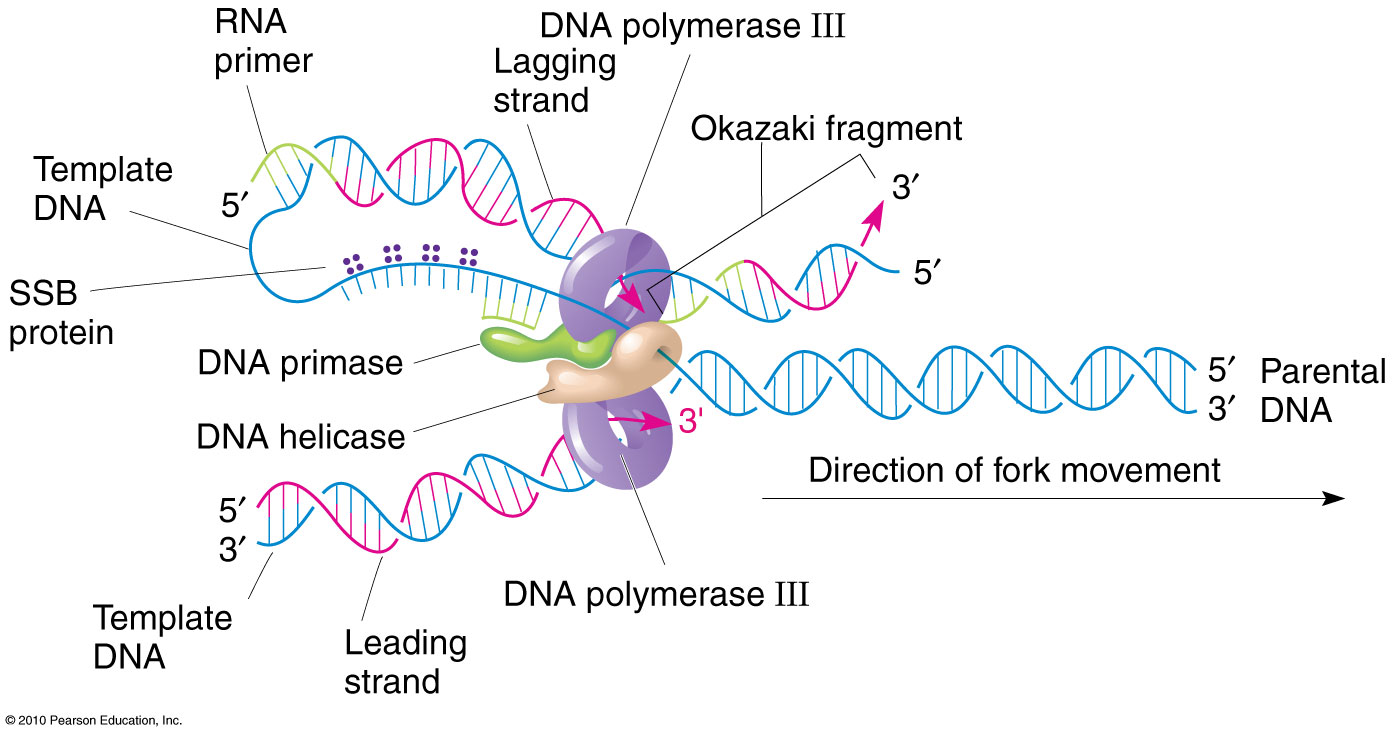
What Is The Template Strand Of Dna
DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel
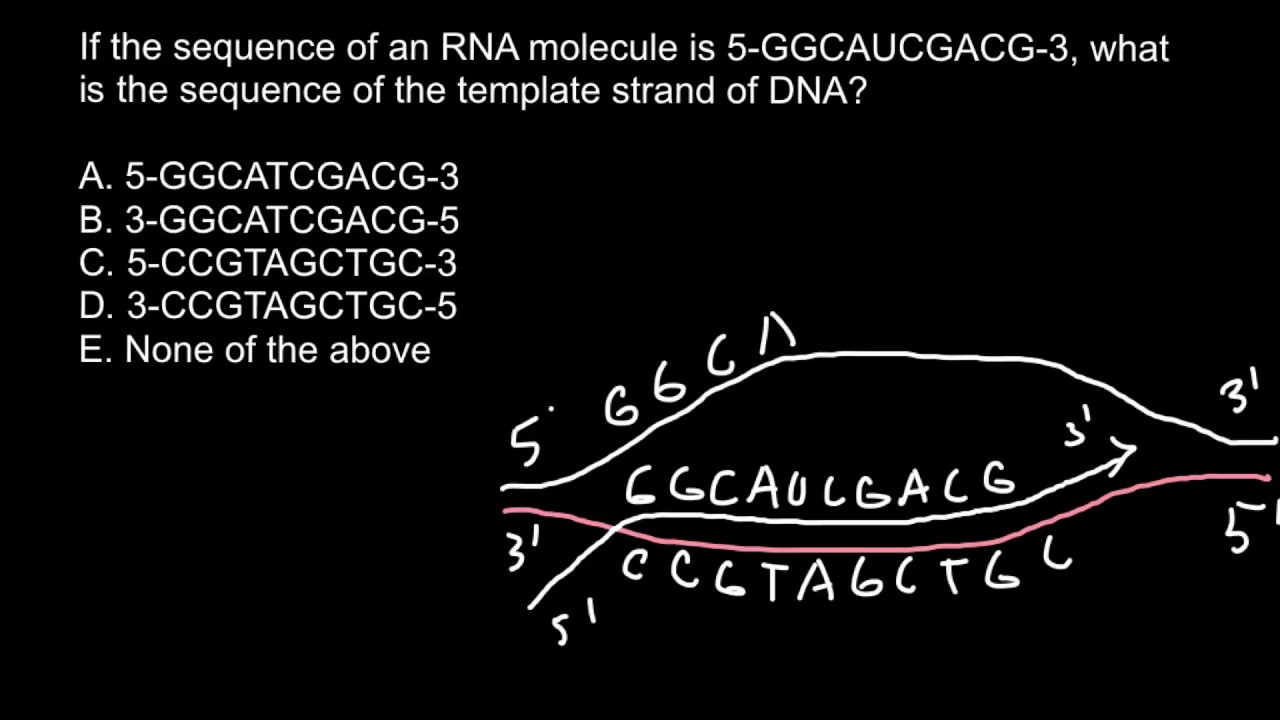
How to find sequence of the template strand of DNA YouTube

DNA Strands Template Download & Edit PowerSlides™

Nucleotides Dna Model Cut Out Worksheet Sketch Coloring Page
Printable Paper Dna Model Template Get What You Need

DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel
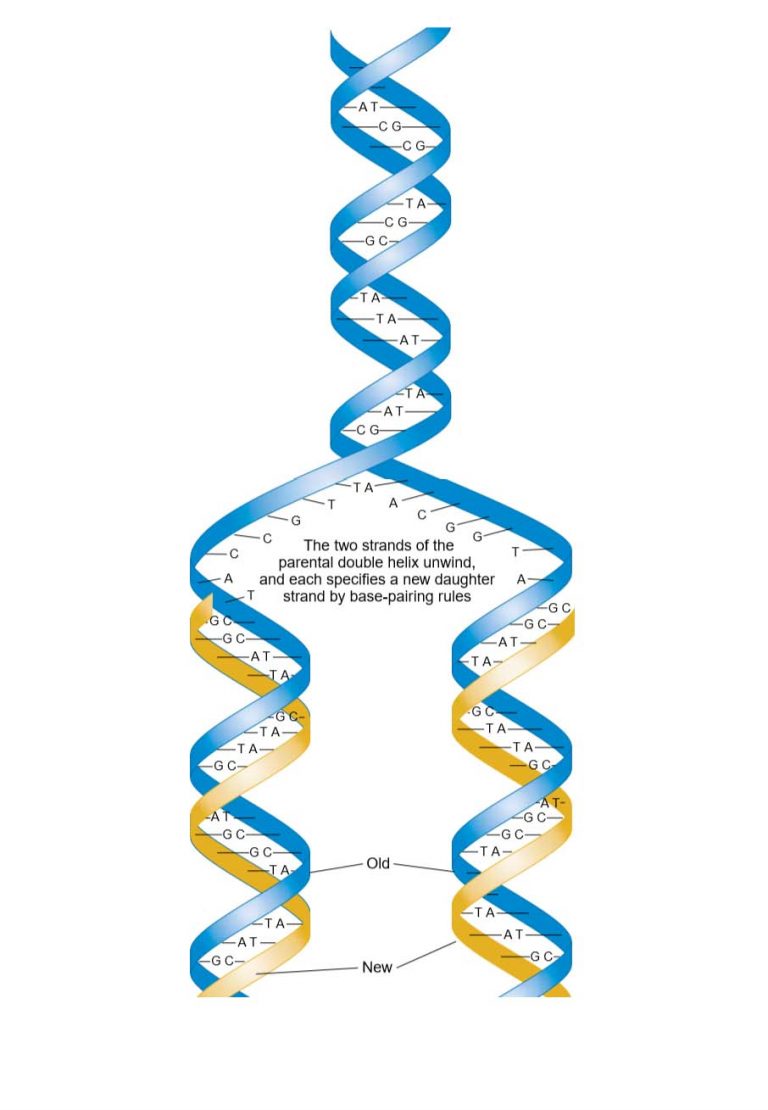
DNA Replication Study Solutions
This Template Strand Is Called The Noncoding Strand.
Web Each Strand Of Dna Acts As A Template For Synthesis Of A New, Complementary Strand.
In Eukaryotes, The Rna Must Go Through Additional Processing Steps To Become A Messenger Rna, Or Mrna.
Replication Creates Identical Dna Strands, While Transcription Converts Dna Into Messenger Rna (Mrna).
Related Post: