Disordered Proliferative Pattern Endometrium
Disordered Proliferative Pattern Endometrium - Web disordered proliferative endometrium is common in the perimenopausal years because of anovulatory cycles. Here are some words and phrases you might see on your biopsy results: Web women with a proliferative endometrium had a higher risk of developing endometrial hyperplasia or cancer (11.9% vs 2.9%; Early detection of endometrial cancer, especially its precancers, remains a critical and evolving issue in patient management and the quest to decrease. Endometrial hyperplasia thickens your uterine lining, causing heavy or abnormal bleeding. Web endometrial hyperplasia (eh) comprises a spectrum of changes in the endometrium ranging from a slightly disordered pattern that exaggerates the alterations. Web proliferative endometrium in menopause. Web disordered proliferative endometrium. Web this work aims to review the concept of impaired inflammatory state of the endometrium (iise) as a multifaceted approach to the problem of endometrial. Web the commonest pathology irrespective of the age group was disordered proliferative pattern (20.5%). Web proliferative endometrium in menopause. Web disordered proliferative endometrium is a condition of abnormal thickening of the uterine lining due to excessive estrogen and lack of. Early detection of endometrial cancer, especially its precancers, remains a critical and evolving issue in patient management and the quest to decrease. Web disordered proliferative endometrium is common in the perimenopausal years because of. Web women with a proliferative endometrium had a higher risk of developing endometrial hyperplasia or cancer (11.9% vs 2.9%; Other causes identified were complications of pregnancy. It is a normal finding. Proliferative endometrium isn’t a symptom or. Abnormal proliferative endometrium with architectural changes due to persistent unopposed estrogen stimulation. Is this a diagnosable condition? Web proliferative endometrium in menopause. Web focally evident cystically dilated glands with intervening tubular proliferative phase glands are characteristics of disordered proliferative endometrium [figure 3]. An understanding of the normal proliferative phase endometrium is essential to appreciate menopausal and atypical changes. Early detection of endometrial cancer, especially its precancers, remains a critical and evolving issue. Is this a diagnosable condition? Web the commonest pathology irrespective of the age group was disordered proliferative pattern (20.5%). The primary symptom of disordered proliferative endometrium is bleeding between menstrual periods. Web disordered proliferative endometrium is a condition of abnormal thickening of the uterine lining due to excessive estrogen and lack of. Web proliferative endometrium in menopause. Web focally evident cystically dilated glands with intervening tubular proliferative phase glands are characteristics of disordered proliferative endometrium [figure 3]. Web disordered proliferative endometrium (anovulatory) •common, especially in perimenopausal years •response to increased oestrogenic drive without opposition of. P<.0001), any endometrial cancer (5.8% vs. It is a normal finding. Web disordered proliferative endometrium, abbreviated dpe, is an abnormal endometrial finding. Early detection of endometrial cancer, especially its precancers, remains a critical and evolving issue in patient management and the quest to decrease. Atypical endometrial hyperplasia raises your. Proliferative endometrium isn’t a symptom or. Abnormal proliferative endometrium with architectural changes due to persistent unopposed estrogen stimulation. Web disordered proliferative endometrium is a condition of abnormal thickening of the uterine lining due. Here are some words and phrases you might see on your biopsy results: Atypical endometrial hyperplasia raises your. Web proliferative endometrium is a term pathologists use to describe the changes seen in the endometrium during the first half of the menstrual cycle. It is a normal finding. Web disordered proliferative endometrium (anovulatory) •common, especially in perimenopausal years •response to increased. Web out of 200 cases, the most common histopathological finding was proliferative phase in 65 cases (42.4%), followed by disordered proliferation in 46 cases (30%). Web sampling of the endometrium, via biopsy or dilation and curettage, is an important diagnostic tool in a wide variety of clinical scenarios, ranging from infertility and. Here are some words and phrases you might. Web out of 200 cases, the most common histopathological finding was proliferative phase in 65 cases (42.4%), followed by disordered proliferation in 46 cases (30%). Web disordered proliferative endometrium, abbreviated dpe, is an abnormal endometrial finding with some features of simple endometrial hyperplasia. Web this work aims to review the concept of impaired inflammatory state of the endometrium (iise) as. Early detection of endometrial cancer, especially its precancers, remains a critical and evolving issue in patient management and the quest to decrease. Is this a diagnosable condition? It is a normal finding. Web disordered proliferative endometrium, abbreviated dpe, is an abnormal endometrial finding with some features of simple endometrial hyperplasia. Web focally evident cystically dilated glands with intervening tubular proliferative. Early detection of endometrial cancer, especially its precancers, remains a critical and evolving issue in patient management and the quest to decrease. In any case, the management of simple endometrial hyperplasia and. The primary symptom of disordered proliferative endometrium is bleeding between menstrual periods. Web sampling of the endometrium, via biopsy or dilation and curettage, is an important diagnostic tool in a wide variety of clinical scenarios, ranging from infertility and. Web disordered proliferative endometrium, abbreviated dpe, is an abnormal endometrial finding with some features of simple endometrial hyperplasia. Other causes identified were complications of pregnancy. Web endometrial hyperplasia (eh) comprises a spectrum of changes in the endometrium ranging from a slightly disordered pattern that exaggerates the alterations. Web this work aims to review the concept of impaired inflammatory state of the endometrium (iise) as a multifaceted approach to the problem of endometrial. An understanding of the normal proliferative phase endometrium is essential to appreciate menopausal and atypical changes. To treat or not to treat? Is this a diagnosable condition? Here are some words and phrases you might see on your biopsy results: Web the endometrium, a tissue of continuously changing patterns and immense proliferative activity during a woman’s reproductive life, becomes atrophic after the menopause as a. P<.0001), any endometrial cancer (5.8% vs. Web focally evident cystically dilated glands with intervening tubular proliferative phase glands are characteristics of disordered proliferative endometrium [figure 3]. Atypical endometrial hyperplasia raises your.
Benign and Premalignant Lesions of the Endometrium Surgical Pathology

Pathology Outlines Disordered proliferative
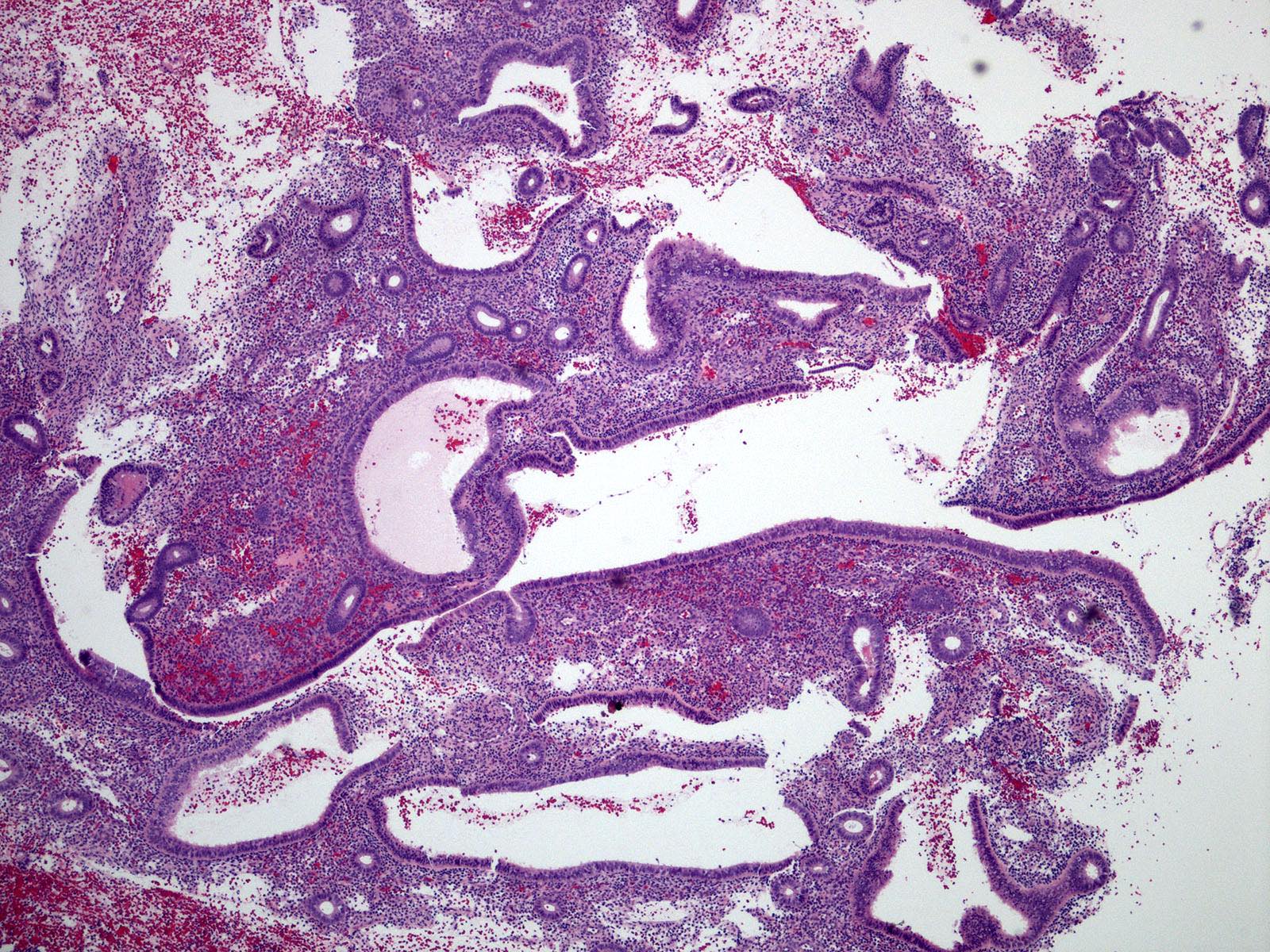
Pathology Outlines Disordered proliferative
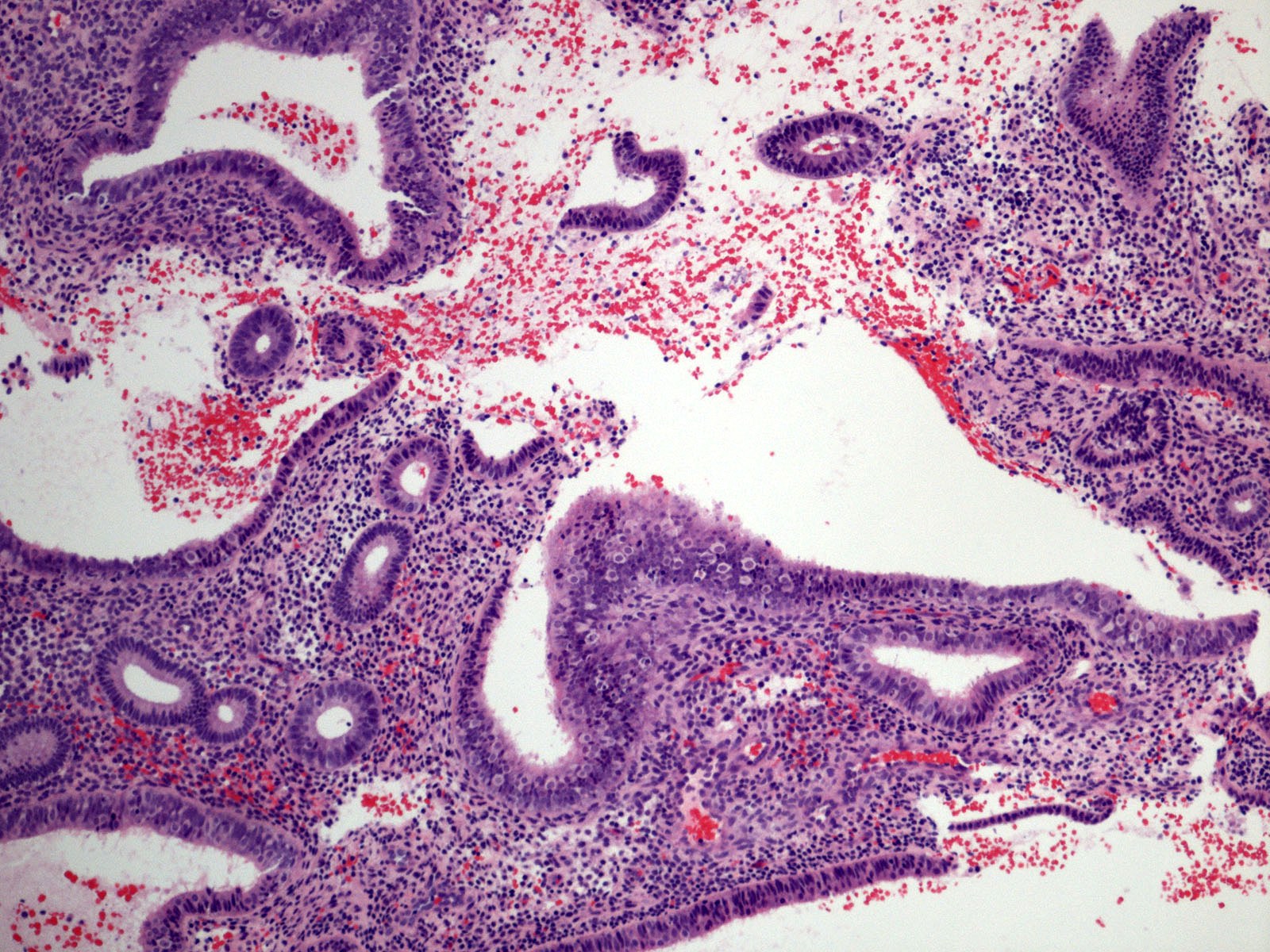
Pathology Outlines Disordered proliferative

FileDisordered proliferative endometrium low mag.jpg Wikimedia
Histology of the human endometrium across the menstrual cycle. PE

H and E STAINED IMAGE INDICATING a Disordered Proliferative Endometrium

Photomicrographs of the endometrium in the proliferative phase (a, b
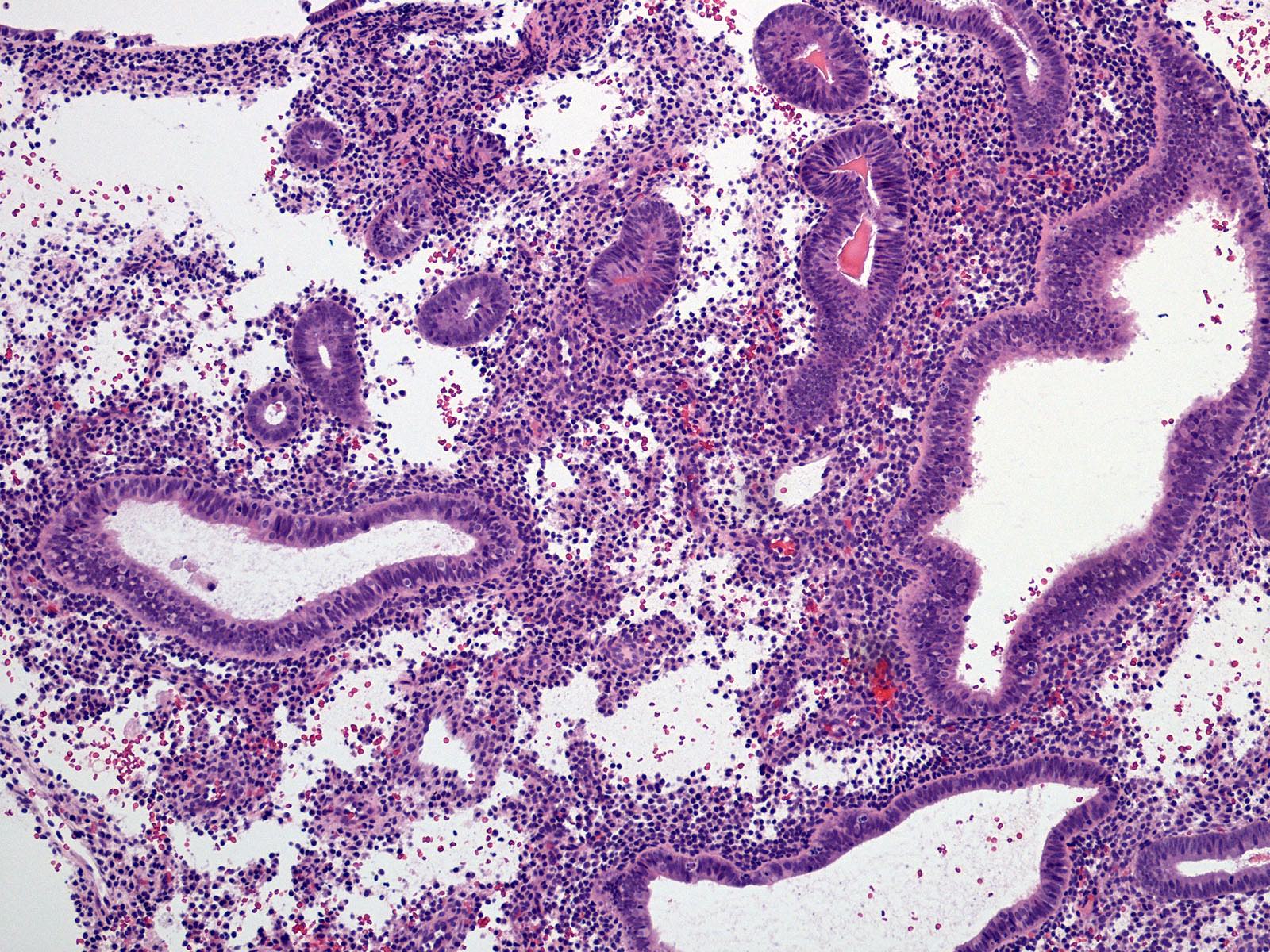
Pathology Outlines Disordered proliferative

dysfunctional uterine bleeding pathology
Web Women With A Proliferative Endometrium Had A Higher Risk Of Developing Endometrial Hyperplasia Or Cancer (11.9% Vs 2.9%;
Web Disordered Proliferative Endometrium Is Common In The Perimenopausal Years Because Of Anovulatory Cycles.
Abnormal Proliferative Endometrium With Architectural Changes Due To Persistent Unopposed Estrogen Stimulation.
Web Disordered Proliferative Endometrium Is A Condition Of Abnormal Thickening Of The Uterine Lining Due To Excessive Estrogen And Lack Of.
Related Post: