Dipole Antenna Radiation Pattern
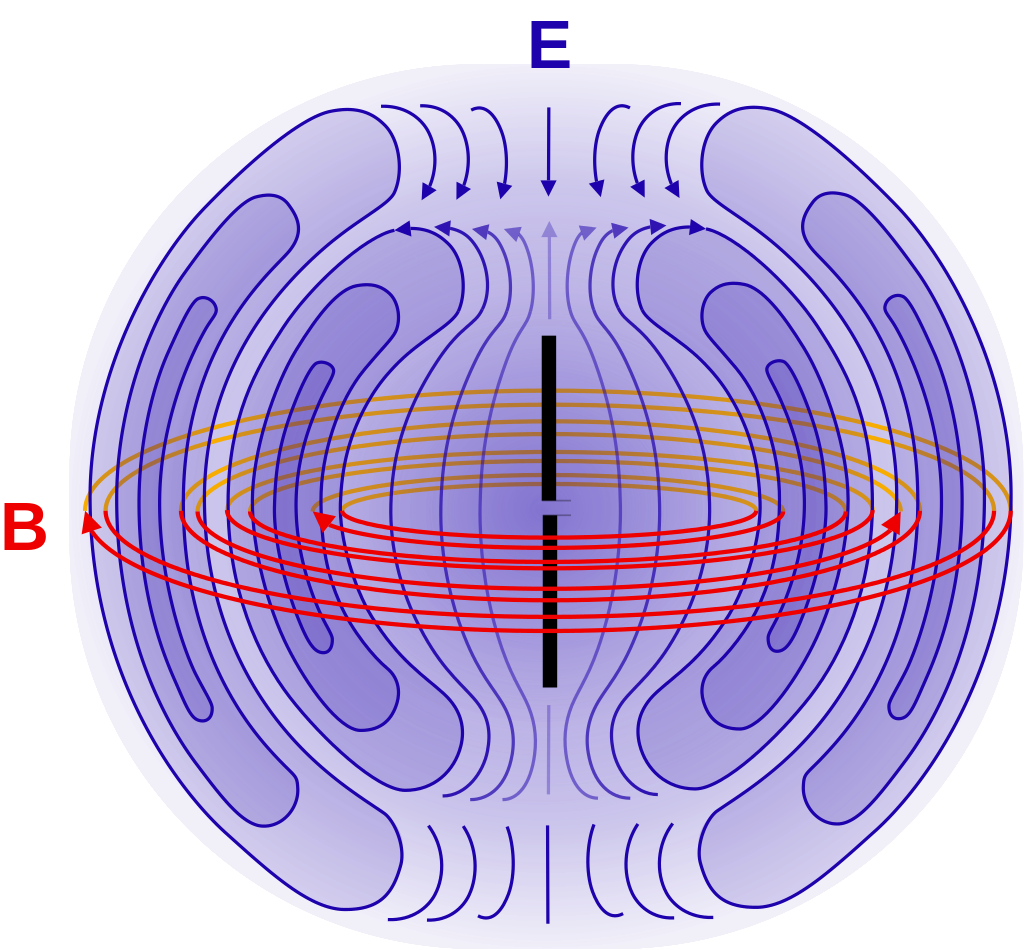
Dipole Antenna Radiation Pattern - Electric field strength e θ and power s(t, θ) s ( t, θ) radiated by a hertzian dipole. Web the radiation pattern remains virtually the same. The above resonant length (0.48 ) is valid if the dipole is very thin. However, the results are not always obvious. Web a dipole antenna in free space exhibits a feed impedance of 72 ohms, and has a doughnutshaped radiation pattern. The simulated normalized radiation patterns for the proposed 8 × 8 conformal and planar arrays are shown in fig. Web the method is to model these relatively complex distributions of current as the sum of hertzian dipoles, which reduces the problem to that of summing the contributions of the individual hertzian dipoles, with each hertzian dipole having the appropriate (i.e., different) position, magnitude, and phase. Web a standard dipole antenna has an omnidirectional radiation pattern. The presence of charge carriers in the wire creates an electric field that emanates from the wire, the movement of the charge carriers creates a magnetic field that encircles the wire, and the acceleration of charge creates electromagnetic waves that propagate outward from the wire. The energy being radiated is represented by the patterns drawn in a particular direction. It takes a larger antenna in general to increase directivity. Web the figure given above shows radiation pattern of a dipole antenna. Three of the cube sides correspond to the intersections of radiation pattern with the coordinate planes. But, as the dipole is brought close to the earth, the radiation pattern changes, and the feed point impedance also changes. Web. E (θ) = e 0 · sin (θ) where: Web a dipole has a radiation pattern like a doughnut on its resonant frequency, but if you're using it on a higher frequency then the radiation pattern becomes skewed because it's not 1/2 wave anymore. It takes a larger antenna in general to increase directivity. Web the radiation pattern remains virtually. Web the method is to model these relatively complex distributions of current as the sum of hertzian dipoles, which reduces the problem to that of summing the contributions of the individual hertzian dipoles, with each hertzian dipole having the appropriate (i.e., different) position, magnitude, and phase. In practice, dipoles are often made with fatter or thicker material, which tends to. Web the radiation pattern (rp) (or antenna pattern) is the representation of a radiation property of the antenna as a function of the angular coordinates. The field patterns are plotted as a function of electric and magnetic fields. Web factor of the radiation pattern. Web a standard dipole antenna has an omnidirectional radiation pattern. Web the radiation pattern remains virtually. Web a standard dipole antenna has an omnidirectional radiation pattern. Web the radiation pattern (rp) (or antenna pattern) is the representation of a radiation property of the antenna as a function of the angular coordinates. The radiation patterns can be field patterns or power patterns. It is independent of the radiation pattern inside the antenna unit cell. Web a dipole. In practice, dipoles are often made with fatter or thicker material, which tends to increase the bandwidth of the antenna. Web a dipole antenna in free space exhibits a feed impedance of 72 ohms, and has a doughnutshaped radiation pattern. The radiation patterns can be field patterns or power patterns. The above resonant length (0.48 ) is valid if the. This is the antenna pattern (toroid) for classical processes like thomson scattering, considered shortly. Similarly with vertical antennas, 5/8 and 1/2 wave verticals have radiation patterns flattened towards the horizon whereas 1/4 wave has more power. Web the radiation pattern remains virtually the same. The field patterns are plotted as a function of electric and magnetic fields. Web factor of. This is a typical result in antenna theory: The trace of the angular variation of the received/radiated power at a constant radius from. For more details, see design and aiantenna documentation. In practice, dipoles are often made with fatter or thicker material, which tends to increase the bandwidth of the antenna. Web a dipole antenna in free space exhibits a. But, as the dipole is brought close to the earth, the radiation pattern changes, and the feed point impedance also changes. All of the results we’ve derived so far apply only in the situation where the antenna is short, i.e., d <<. Web a radiation pattern defines the variation of the power radiated by an antenna as a function of. All of the results we’ve derived so far apply only in the situation where the antenna is short, i.e., d <<. Dipole radiation pattern sin2 μ. Three of the cube sides correspond to the intersections of radiation pattern with the coordinate planes. An awareness of these changes can help ease the task of setting up a dipole for communications. When. The energy being radiated is represented by the patterns drawn in a particular direction. Web a radiation pattern defines the variation of the power radiated by an antenna as a function of the direction away from the antenna. Web the radiation pattern (rp) (or antenna pattern) is the representation of a radiation property of the antenna as a function of the angular coordinates. All of the results we’ve derived so far apply only in the situation where the antenna is short, i.e., d <<. The arrows represent directions of radiation. Web a standard dipole antenna has an omnidirectional radiation pattern. Web the radiation pattern remains virtually the same. For more details, see design and aiantenna documentation. Electric field strength e θ and power s(t, θ) s ( t, θ) radiated by a hertzian dipole. E (θ) = e 0 · sin (θ) where: The directions are shown as red, green, and blue, respectively. The presence of charge carriers in the wire creates an electric field that emanates from the wire, the movement of the charge carriers creates a magnetic field that encircles the wire, and the acceleration of charge creates electromagnetic waves that propagate outward from the wire. E (θ) is the electric field intensity at a point in space as a function of the angle θ. An awareness of these changes can help ease the task of setting up a dipole for communications. Dipole antennas are used in various applications such as in phased arrays and feeding sources to larger antennas. The simulated normalized radiation patterns for the proposed 8 × 8 conformal and planar arrays are shown in fig.
Radiation pattern of dipole antenna. Download Scientific Diagram

Radiation pattern of the dipole antenna Download Scientific Diagram
FM Radio Dipole Antenna Explained

Radiation pattern of a =2 dipole antenna. of the field components

Omnidirectional Antenna Radiation Patterns Explained MP Antenna

Dipole Antenna Radiation Patterns YouTube

3D radiation Pattern of a Dipole Antenna with code MATLAB Programming

Radiation patterns for each printed dipole antenna in Single dipole and

Simulated 3D radiation pattern of the dipole antenna with reflector

Radiation patterns of a dipole antenna on a glass substrate, dipole
The Trace Of The Angular Variation Of The Received/Radiated Power At A Constant Radius From.
It Takes A Larger Antenna In General To Increase Directivity.
The Horizontal And Vertical Polar Patterns Are Projections Of The 3 Dimensional Pattern Onto Horizontal And Vertical Planes, Respectively.
This Is The Antenna Pattern (Toroid) For Classical Processes Like Thomson Scattering, Considered Shortly.
Related Post: