Diagram Of Global Wind Patterns
Diagram Of Global Wind Patterns - An animated map of global wind and weather. Prevailing winds are air currents that blow mainly in one direction. Lies primarily in the westerly wind belt with prevailing winds from the west. Each of these wind belts represents a cell that circulates air through the atmosphere from the surface to high altitudes and back again. Surface winds (0 to 40 meters/second) are shown in white and trace features including atlantic and pacific cyclones. Global atmospheric circulation creates winds across the planet as air moves from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. Warm air around the equator is lifted, which creates a suction effect for air masses coming from higher (or lower) latitudes. Web seasonal variations of major global wind patterns | the geography of transport systems. In this section you will find materials that support the implementation of earthcomm, section 1: Because more solar energy hits the equator, the air warms and forms a low pressure zone. In this section you will find materials that support the implementation of earthcomm, section 1: Understanding global wind belts is crucial for various reasons. Web use your mouse to pan/zoom and the turn the globe in any direction. Web seasonal variations of major global wind patterns | the geography of transport systems. Because more solar energy hits the equator, the. Each of these wind belts represents a cell that circulates air through the atmosphere from the surface to high altitudes and back again. Winds shape regional climate and influence daily weather by. Global atmospheric circulation creates winds across the planet as air moves from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. Web the global atmospheric circulation pattern is. Global wind patterns have both a historical and contemporary significance for transportation. Learn about the different global wind belts & how they affect the climate on earth. These prevailing wind patterns distribute heat and precipitation unevenly between the tropics, temperate and polar regions of the. Web global wind patterns | the geography of transport systems. A current is the steady. Web seasonal variations of major global wind patterns | the geography of transport systems. The importance of understanding global wind belts. Warm air around the equator is lifted, which creates a suction effect for air masses coming from higher (or lower) latitudes. In this data visualization, faster winds are colored red while slower winds are colored blue. Web the global. Warm air around the equator is lifted, which creates a suction effect for air masses coming from higher (or lower) latitudes. It explains how thermal energy and storm systems move over the earth's surface. Without the earth’s rotation, tilt relative to the sun, and surface. Analyze data on world maps to identify patterns in incoming solar radiation, air temperature range,. In the bay area, the prevailing winds come from the notice how the winds in the southern hemisphere are a mirror reflection of the Web global wind patterns, page of 42 this diagram shows the true pattern of earth’s prevailing winds. Web the global wind pattern is also known as the general circulation and the surface winds of each hemisphere. The air pressure at mean sea level and the global wind patterns, in january (top panel) and july (bottom panel), indicating the main wind systems. Tap on the map to set a marker. This curving has to do with the rotation of earth and is called the coriolis effect. Web seasonal variations of major global wind patterns | the geography. Web global wind patterns, page of 42 this diagram shows the true pattern of earth’s prevailing winds. Web the global atmospheric circulation pattern is determined by temperature differences, especially the difference between heating at the equator and the poles, and by the earth’s rotation. Global wind patterns have both a historical and contemporary significance for transportation. Web the global wind. Global wind patterns and weather. Global wind patterns have both a historical and contemporary significance for transportation. Web this comprehensive diagram will provide a detailed overview of each wind belt, including their origins, characteristics, and importance in the earth’s atmospheric circulation system. Web the global atmospheric circulation pattern is determined by temperature differences, especially the difference between heating at the. This curving has to do with the rotation of earth and is called the coriolis effect. Web it's important to remember that everything in this diagram is just an overall model. Web global winds described with a labeled diagram. Interactive map that shows the current wind pattern around the world in the form of streamlines. Web this comprehensive diagram will. Web global winds described with a labeled diagram. Web it's important to remember that everything in this diagram is just an overall model. A current is the steady flow of a fluid (such as air or water) within a larger body of that fluid. Global wind patterns and weather. Global wind patterns are even more complicated because water covered areas and land covered areas absorb solar energy differently. Because more solar energy hits the equator, the air warms and forms a low pressure zone. Each of these wind belts represents a cell that circulates air through the atmosphere from the surface to high altitudes and back again. In this data visualization, faster winds are colored red while slower winds are colored blue. Lies primarily in the westerly wind belt with prevailing winds from the west. The air pressure at mean sea level and the global wind patterns, in january (top panel) and july (bottom panel), indicating the main wind systems. Wind is mainly the outcome of a thermodynamic principle and the coriolis effect due to the counterclockwise rotation of the earth. Winds shape regional climate and influence daily weather by. In the bay area, the prevailing winds come from the notice how the winds in the southern hemisphere are a mirror reflection of the The illustration below portrays the global wind belts, three in each hemisphere. Web this comprehensive diagram will provide a detailed overview of each wind belt, including their origins, characteristics, and importance in the earth’s atmospheric circulation system. An animated map of global wind and weather.
Global Wind Circulations
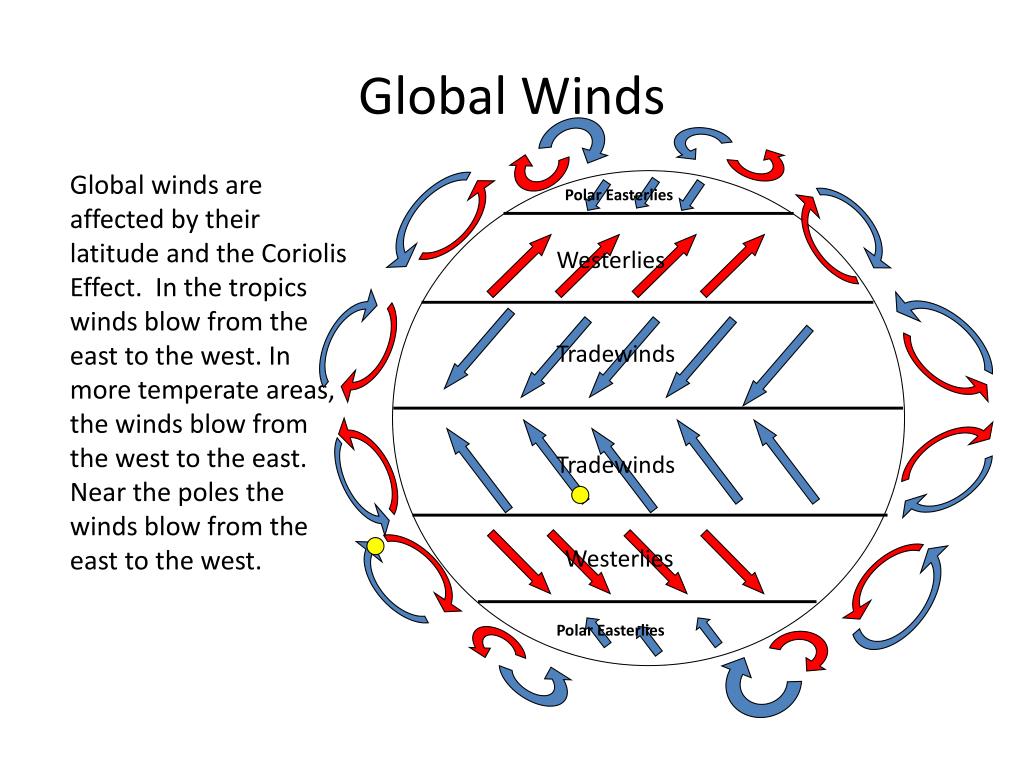
PPT Global Wind Patterns PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID

Global Winds Diagram Quizlet

The three wind patterns of the Earth

Global Wind Circulations
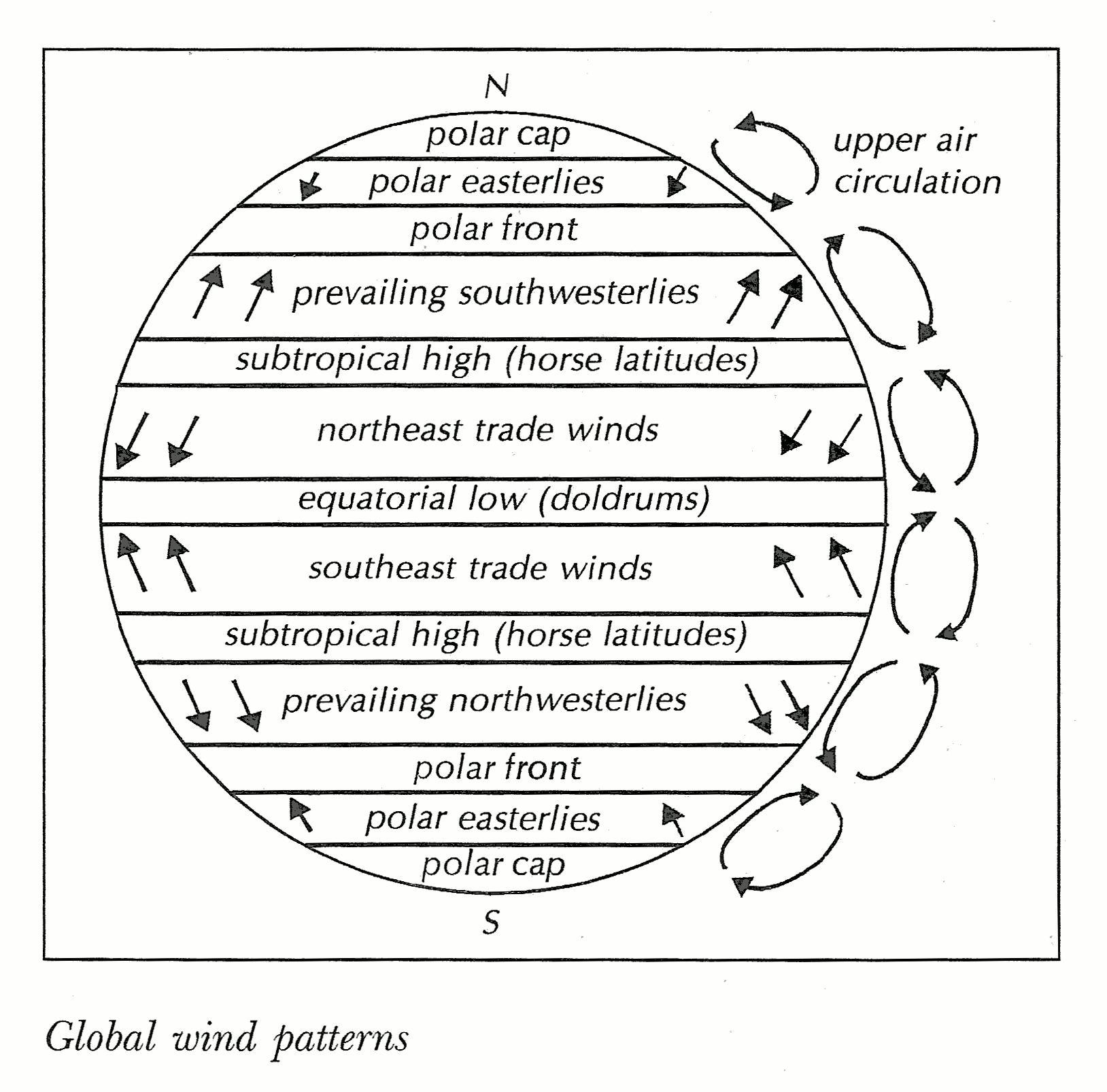
Global Wind Patterns Diagram

Global Wind

5. Idealized depiction of global wind patterns reproduced from EoO
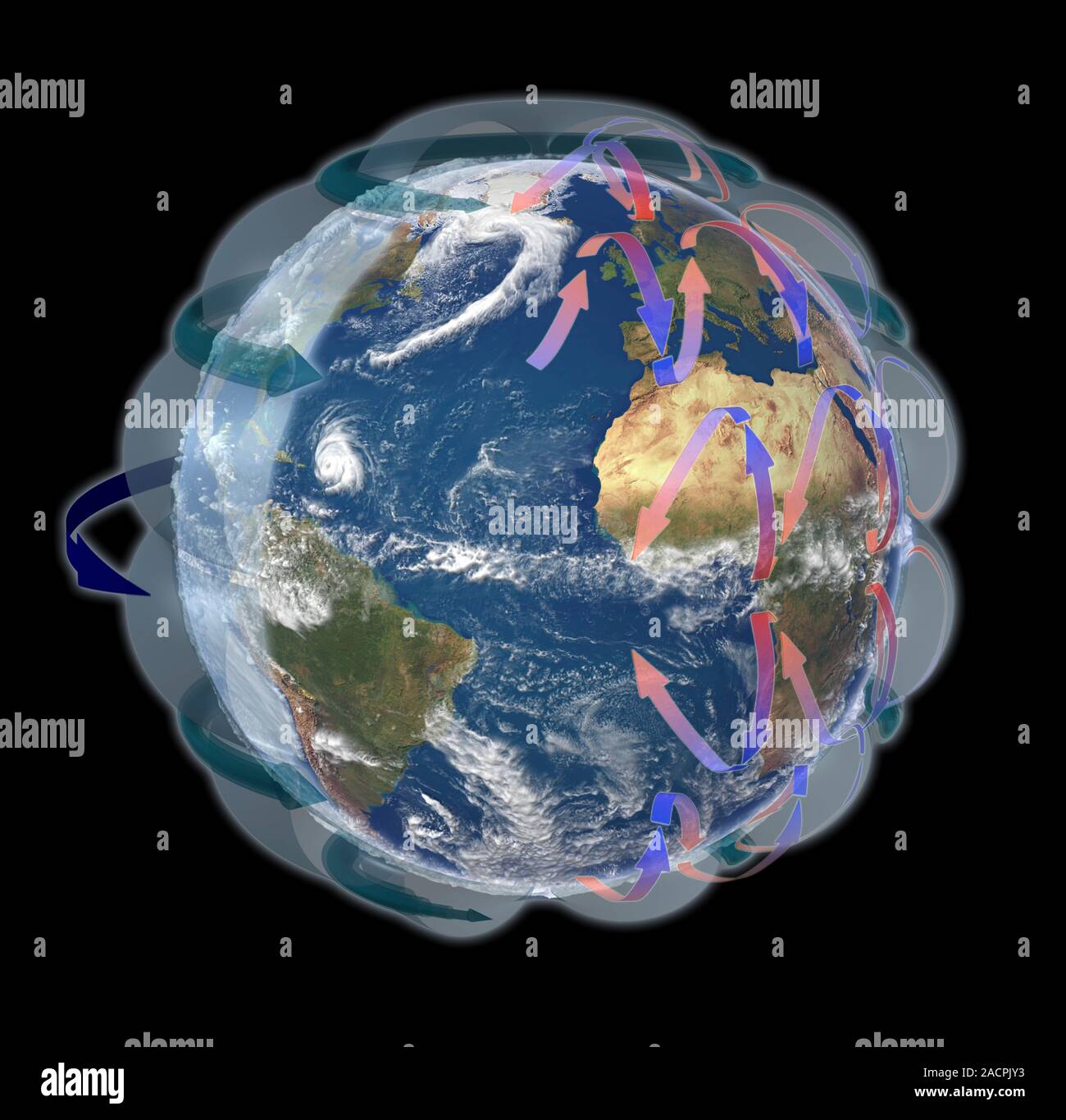
Global winds, satellitebased diagram. The rotation of this Earth globe

Currents, Waves, and Tides Smithsonian Ocean
Analyze Data On World Maps To Identify Patterns In Incoming Solar Radiation, Air Temperature Range, And Air Pressure At Earth’s Surface.
Web Global Atmospheric Circulation Is The Movement Of Air Around The Planet.
Without The Earth’s Rotation, Tilt Relative To The Sun, And Surface.
It Also Leads To Areas Of High Rainfall, Like Tropical Rainforests, And Areas Of Dry Air, Like Deserts.
Related Post: