Cranial Drawer Sign Dog
Cranial Drawer Sign Dog - Web one of the most common injuries to the knee (stifle) in dogs is tearing of the cranial cruciate ligament (ccl). Web the first sign that owners may observe when their dog has a ccl injury is the dog being lame all of the sudden, according to dr. Web cranial drawer should first be checked in extension, and if positive is likely indicative of a complete tear (typically greater than 75% tearing of the ccl as. Web if it is suspected that your dog has a cranial cruciate ligament tear or rupture, your veterinarian will perform a physical exam to determine whether or not this. It involves being able to move the tibia. Sedation or general anesthesia may be necessary ( 1 , 3 ). When it ruptures, abnormal movement of the joint occurs, resulting in pain and. In a mature dog, a healthy, intact cranial cruciate ligament will not permit cranial tibial. Web an agitated dog with plenty of quadriceps muscle tone can make detection of the drawer sign a challenge. The muscles in that leg may weaken and shrink from disuse,. Web definition cranial cruciate ligament rupture (cclr) is the most common cause of hindlimb lameness in dogs and is underdiagnosed in veterinary patients. In a mature dog, a healthy, intact cranial cruciate ligament will not permit cranial tibial. Web the cranial cruciate ligament helps the stifle (knee) function as a hinge joint. If no drawer is palpated, but crcl injury. Difficulty rising from a sit. Web a positive tibial compression test and cranial drawer test confirm cclr. Web during the lameness examination, your veterinarian will try to demonstrate a particular movement, called a cranial or anterior drawer sign. Web cranial drawer should first be checked in extension, and if positive is likely indicative of a complete tear (typically greater than. Estimated reading time 5 minutes. The veterinarian stabilizes the position of the femur with. Web if it is suspected that your dog has a cranial cruciate ligament tear or rupture, your veterinarian will perform a physical exam to determine whether or not this. Web an agitated dog with plenty of quadriceps muscle tone can make detection of the drawer sign. In order to feel this, you dog will be placed on his/ her side, and the veterinarian will feel the. Web cranial drawer should first be checked in extension, and if positive is likely indicative of a complete tear (typically greater than 75% tearing of the ccl as. In this test, the dog’s knee is slightly bent and anterior pressure. The cranial drawer test and tibial compression tests are important for assessing. It involves being able to move the tibia. Web an agitated dog with plenty of quadriceps muscle tone can make detection of the drawer sign a challenge. Web definition cranial cruciate ligament rupture (cclr) is the most common cause of hindlimb lameness in dogs and is underdiagnosed in. Difficulty rising from a sit. Web diagnosis of cranial cruciate ligament rupture is usually made by a positive cranial drawer sign. Web an agitated dog with plenty of quadriceps muscle tone can make detection of the drawer sign a challenge. Web as expected with a knee injury, a dog with a ccl tear will have signs of hind limb lameness. Ligament injuries are a common cause of lameness in dogs. Web cranial drawer should first be checked in extension, and if positive is likely indicative of a complete tear (typically greater than 75% tearing of the ccl as. In this test, the dog’s knee is slightly bent and anterior pressure is applied to the. Web definition cranial cruciate ligament rupture. Ligament injuries are a common cause of lameness in dogs. The veterinarian stabilizes the position of the femur with. In a mature dog, a healthy, intact cranial cruciate ligament will not permit cranial tibial. Web when the ccl is torn or injured, the shin bone (tibia) slides forward with respect to the thigh bone (femur). Web the key to diagnosis. Sedation or general anesthesia may be necessary ( 1 , 3 ). This ligament is like the anterior cruciate ligament (acl) in. Web a positive tibial compression test and cranial drawer test confirm cclr. This abnormal forward movement of. Web one of the most common injuries to the knee (stifle) in dogs is tearing of the cranial cruciate ligament (ccl). Web definition cranial cruciate ligament rupture (cclr) is the most common cause of hindlimb lameness in dogs and is underdiagnosed in veterinary patients. Ligament injuries are a common cause of lameness in dogs. This abnormal forward movement of. The cranial drawer test and tibial compression tests are important for assessing. Difficulty rising from a sit. Web a positive tibial compression test and cranial drawer test confirm cclr. Web dogs with crcld may exhibit any combination of the following signs (symptoms): Web pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. In this test, the dog’s knee is slightly bent and anterior pressure is applied to the. The muscles in that leg may weaken and shrink from disuse,. Sedation or general anesthesia may be necessary ( 1 , 3 ). Estimated reading time 5 minutes. It involves being able to move the tibia. Web the diagnosis of cclr is typically based on the presence of the “cranial drawer sign”. Web during the lameness examination, your veterinarian will try to demonstrate a particular movement, called a cranial or anterior drawer sign. Web to test for cranial tibial translation, perform the cranial drawer test (figure 6). When it ruptures, abnormal movement of the joint occurs, resulting in pain and. Web the cranial cruciate ligament helps the stifle (knee) function as a hinge joint. This movement is known as a positive drawer sign. This may need to be done under sedation depending on the dog. Web diagnosis of cranial cruciate ligament (ccl) tears is made through a combination of orthopedic examination findings (eg, positive cranial drawer, cranial tibial translation).
Image Gallery Surgical Repair of Cranial Cruciate Ligament Injuries in
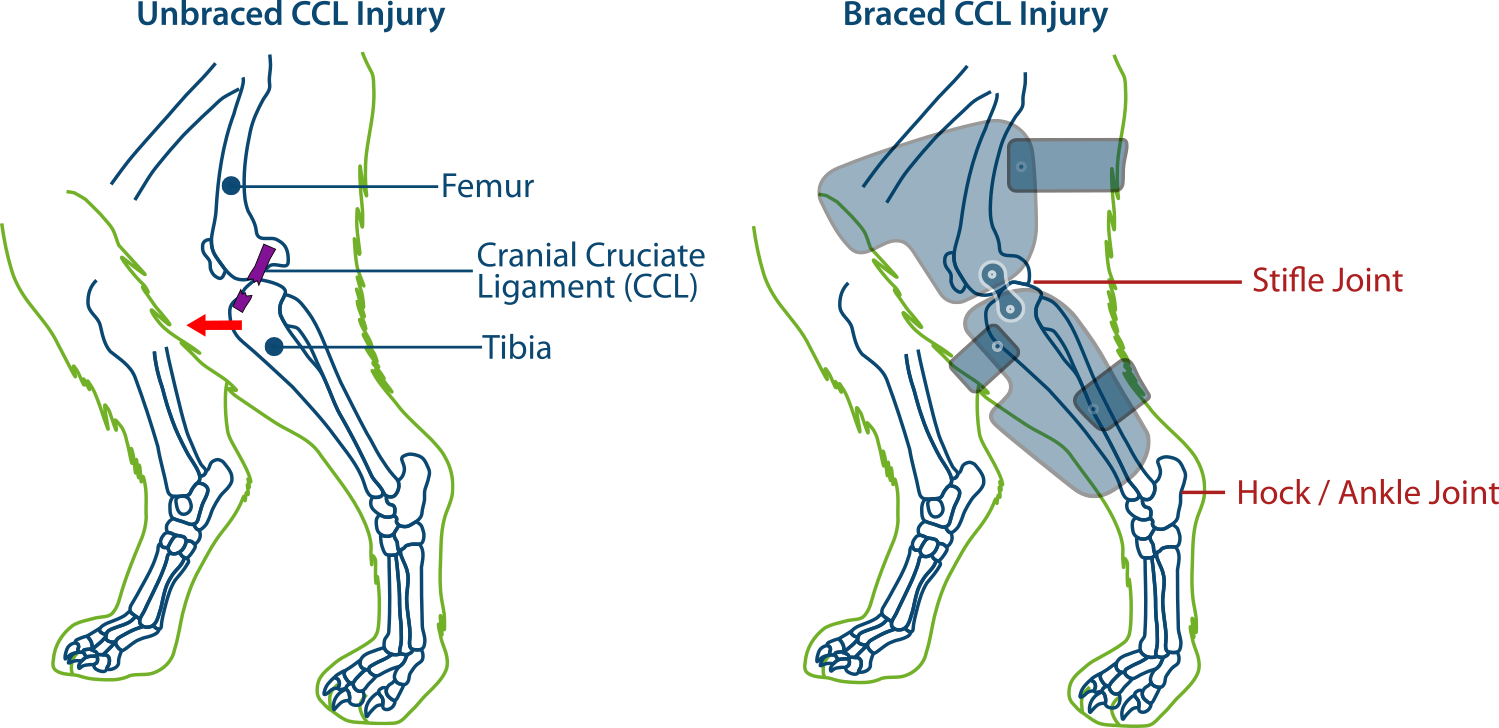
Dog Stifle CCL/ACL Injury Support Brace — PawOpedic
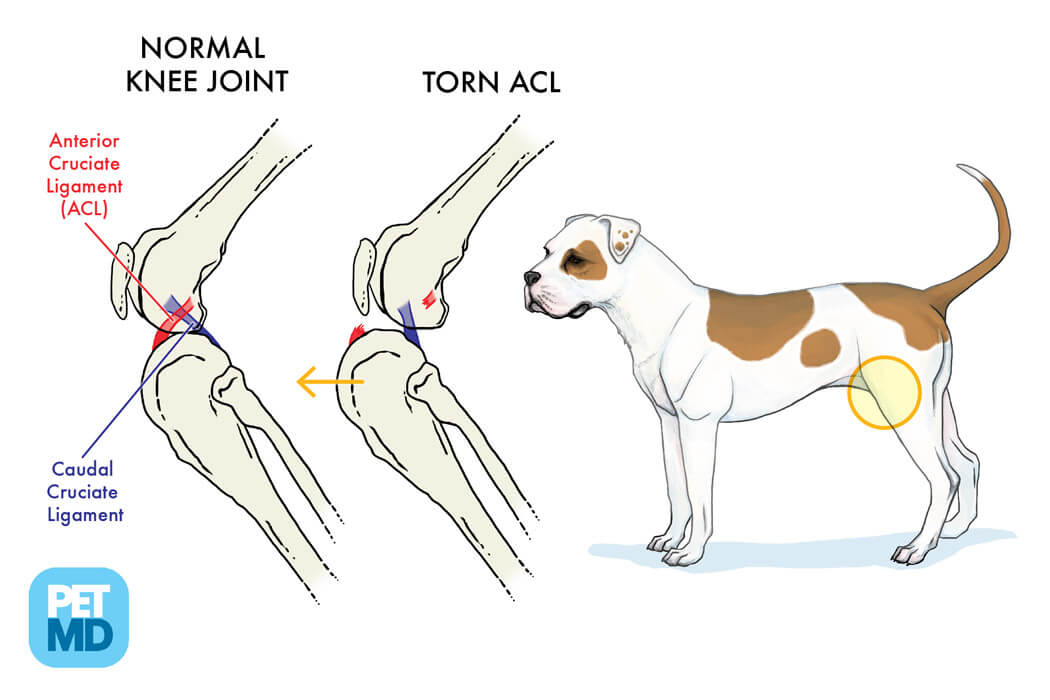
ACL and CCL diagram provided by PetMD

Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Goals of Cranial Cruciate Ligament

Dog with Cranial Drawer YouTube

Torn ACL or CCL in Dogs Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention Daily Paws
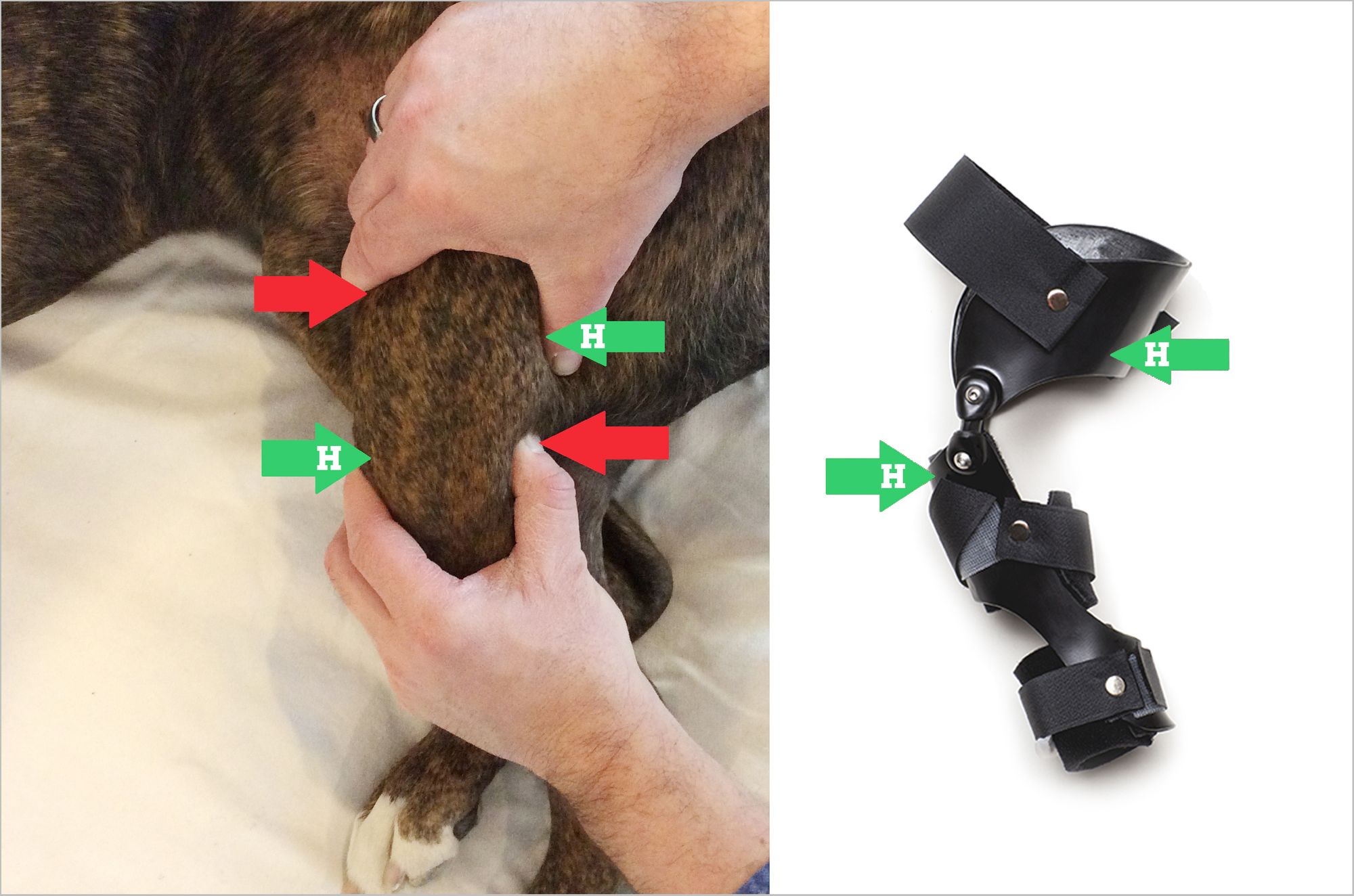
Torn ACL in Dogs How Braces Help

Cruciate Disease The Cranial Drawer Test YouTube

Positive cranial drawer sign in a dog with a cranial (anterior
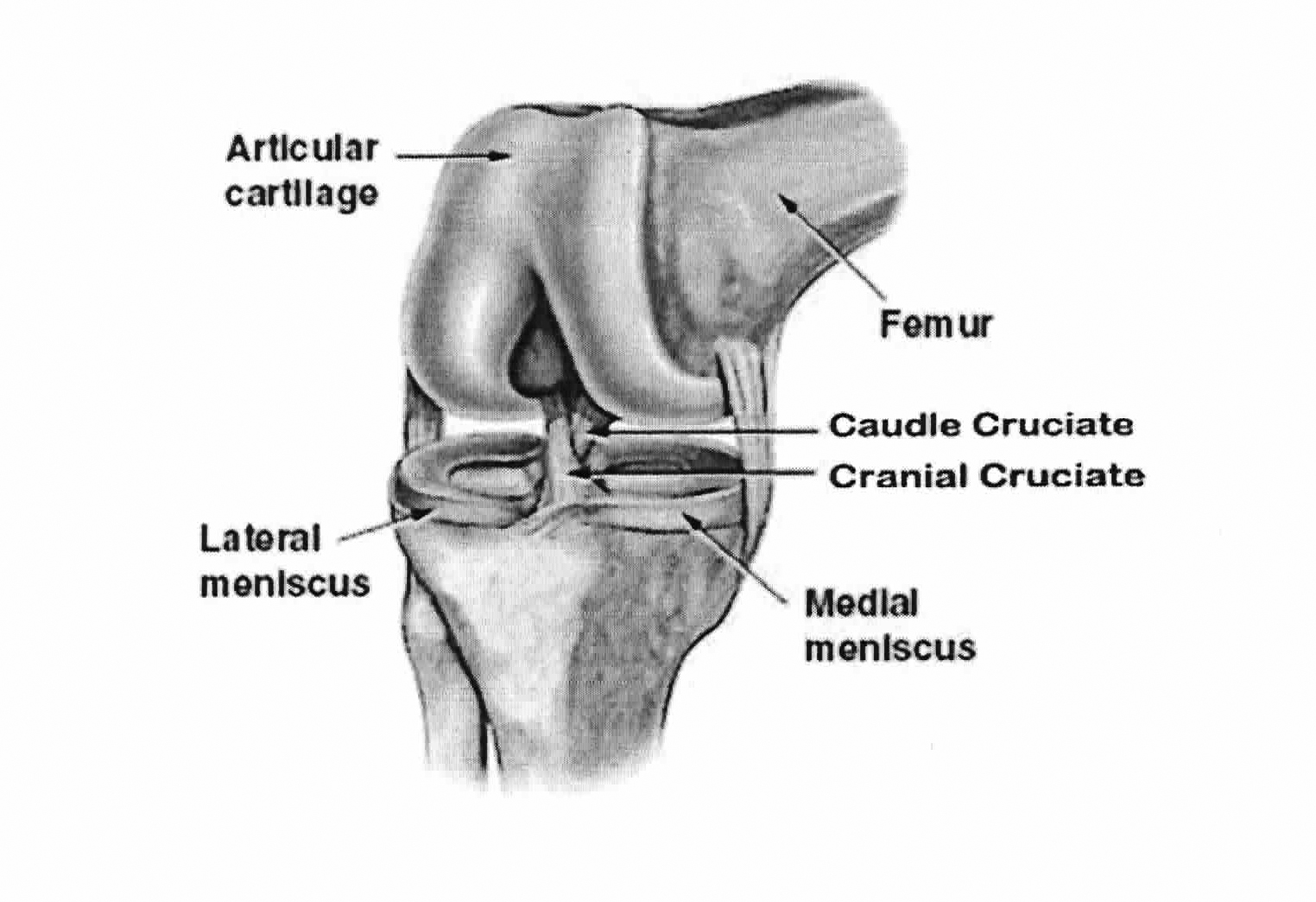
anatomy of the canine knee
Web Definition Cranial Cruciate Ligament Rupture (Cclr) Is The Most Common Cause Of Hindlimb Lameness In Dogs And Is Underdiagnosed In Veterinary Patients.
Web As Expected With A Knee Injury, A Dog With A Ccl Tear Will Have Signs Of Hind Limb Lameness And Limping.
Web When The Ccl Is Torn Or Injured, The Shin Bone (Tibia) Slides Forward With Respect To The Thigh Bone (Femur).
Web The Cranial Drawer Test Should Be Done With The Leg In Flexion And Extension, To Test Both Parts Of The Crcl.
Related Post: