Coding Strand Template Strand
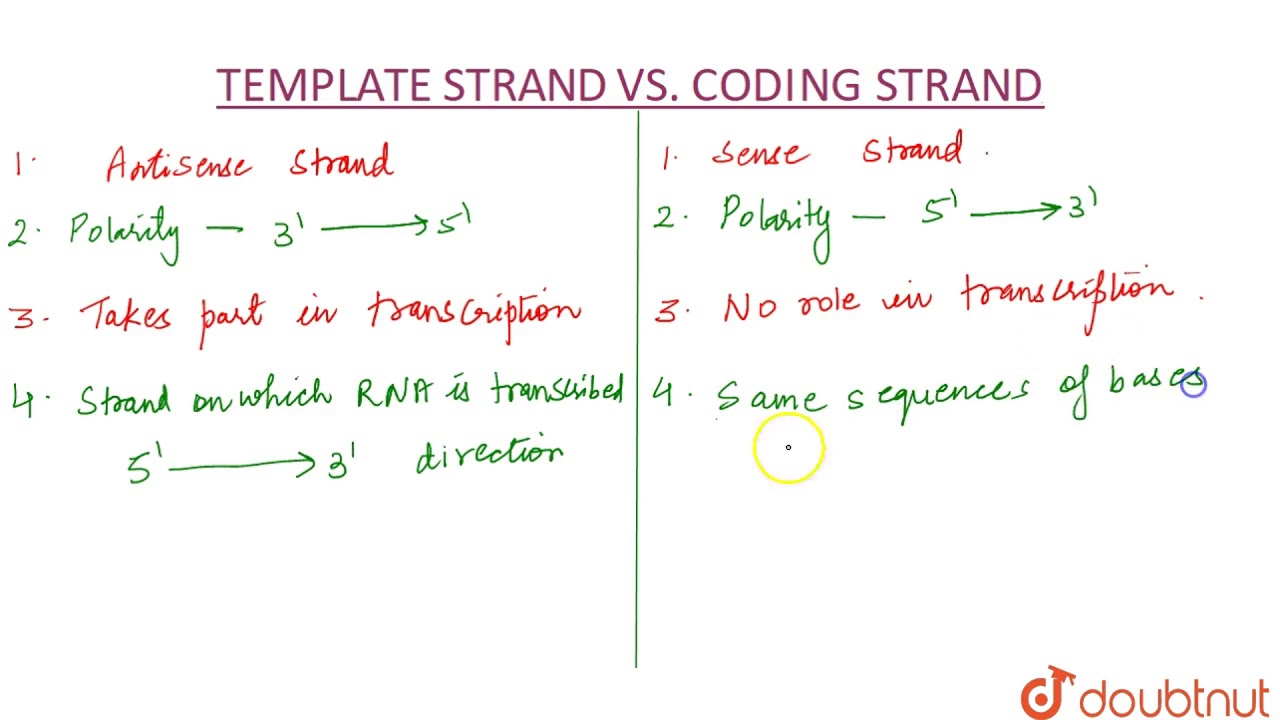
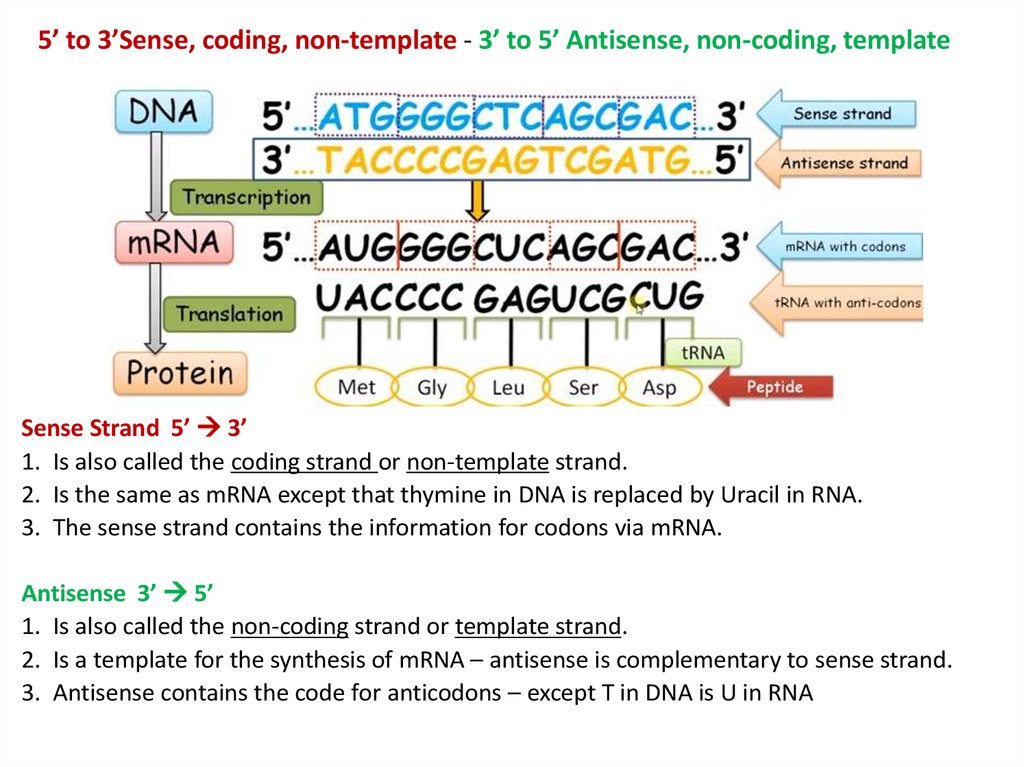
Coding Strand Template Strand - The template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. Web the coding strand and template strand in translation. As it reads this template one base at a time, the polymerase builds an rna molecule out of complementary nucleotides, making a chain that grows from 5' to 3'. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; The coding strand has a complementary nucleotide sequence. Web the template strand, as its name suggests, is used as a template during transcription to synthesize the rna molecule with a complementary sequence to the coding strand. The template strand does not have any complementary sequence. The coding strand and template strand of dna play crucial roles in this process, guiding the mrna’s formation. Web one strand of dna, the template strand, acts as a template for rna polymerase. Web the coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. Web the coding strand and template strand in translation. The coding strand has a complementary base sequence to the template strand, except for thymine (t) being replaced by uracil (u) in rna. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. This strand is called the template strand.the rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical. The template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. This process ensures that the rna carries the correct information dictated by the genetic code. This strand is also called the coding. Web actually, the mrna strand is coded from the template strand of the dna which runs from 3' to 5' end.. In this example, the sequences of the coding strand, template strand, and rna transcript are: Web the template strand, on the other hand, has a sequence of nucleotides that is complementary to the sequence on the coding strand. Web the difference between template and coding strand is mainly due to the following properties: They help in the formation of mrna.. The coding strand is typically located on the 5' to 3' direction, while the template strand is located on the 3' to 5' direction. Web here, they take part in the transcription. The template strand does not have any complementary sequence. Web the coding strand serves as a template for the rna polymerase, which ensures that the rna strand is. The template strand is directed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. As it reads this template one base at a time, the polymerase builds an rna molecule out of complementary nucleotides, making a chain that grows from 5' to 3'. Web in the dna molecule, the coding strand and the template strand differ in their bases’ sequence. The coding strand. This way, both strands work together, ensuring the right information is transferred from dna to rna. Web the coding strand is directly involved in protein synthesis, while the template strand serves as a template for rna synthesis. Web the template strand, on the other hand, has a sequence of nucleotides that is complementary to the sequence on the coding strand.. Web the template strand, on the other hand, has a sequence of nucleotides that is complementary to the sequence on the coding strand. Importance in dna replication both the coding strand and the template strand are vital for the process of dna replication, which ensures the accurate duplication of genetic information during. The coding strand and template strand of dna. The template strand does not have any complementary sequence. For example, if the coding strand reads atg, the mrna reads. The template strand is directed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Understanding the differences between these two strands is crucial in comprehending the complex processes of dna replication, transcription, and translation. In this example, the sequences of the coding strand,. This structural difference ensures that the rna transcript is synthesized in the correct orientation and. Web given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that not all orfs are genes. This way, both strands work together, ensuring the right information is transferred from dna to rna.. This process ensures that the rna carries the correct information dictated by the genetic code. The bases are the same, except. The template strand serves as a guide during transcription and determines the sequence of the. As it reads this template one base at a time, the polymerase builds an rna molecule out of complementary nucleotides, making a chain that. This strand dictates the mrna sequence, aligning with it in a complementary fashion. The coding strand is directed in the 3’ to 5’ direction. Web the difference between template and coding strand is mainly due to the following properties: Web the difference between a template and a coding strand is primarily based on two characteristics: Wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand ), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand or. The coding strand has a complementary base sequence to the template strand, except for thymine (t) being replaced by uracil (u) in rna. The bases are the same, except. As it reads this template one base at a time, the polymerase builds an rna molecule out of complementary nucleotides, making a chain that grows from 5' to 3'. This structural difference ensures that the rna transcript is synthesized in the correct orientation and. Web here, they take part in the transcription. Web the template strand, on the other hand, has a sequence of nucleotides that is complementary to the sequence on the coding strand. Web the coding strand is directly involved in protein synthesis, while the template strand serves as a template for rna synthesis. The coding strand is typically located on the 5' to 3' direction, while the template strand is located on the 3' to 5' direction. Web the coding strand and the template strand have opposite orientations and are aligned in an antiparallel manner. The template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. Web one strand of dna, the template strand, acts as a template for rna polymerase.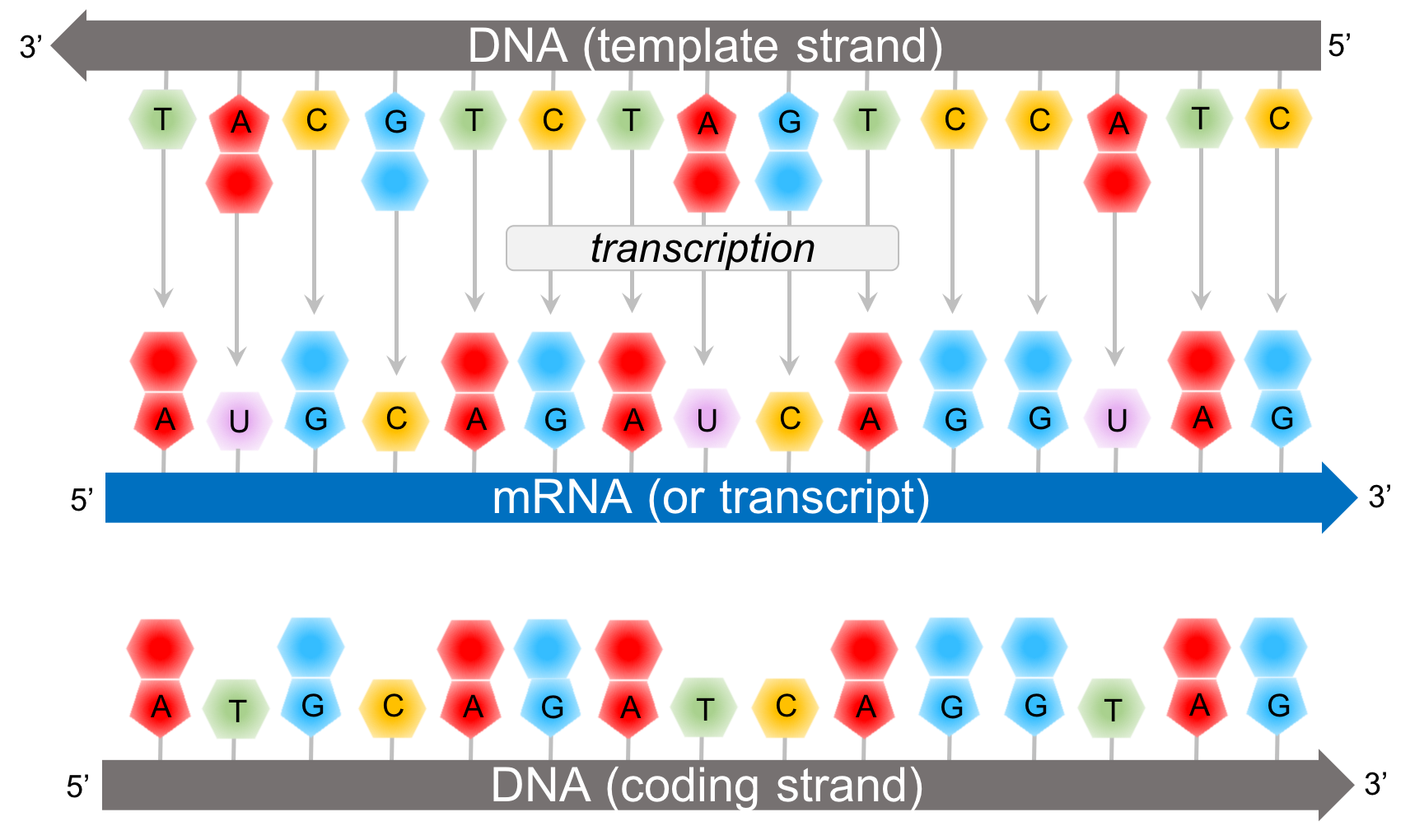
Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer

Coding Strand And Template Strand

Template and coding strand targeting of spacers. A Schematic

Information Flow and Levels of Regulation Medical 1st Ed

Template and coding strands of DNA YouTube

Coding Strand vs. Template Strand 6 Key Variations sciencesavers

Dna Template Strand And Coding Strand

Coding Versus Template Strand
Template Strand And Coding Strand
Template Strand And Coding Strand
It Is Presented In The 5' To 3' Direction.
Importance In Dna Replication Both The Coding Strand And The Template Strand Are Vital For The Process Of Dna Replication, Which Ensures The Accurate Duplication Of Genetic Information During.
Understanding The Differences Between These Two Strands Is Crucial In Comprehending The Complex Processes Of Dna Replication, Transcription, And Translation.
The Coding Strand Is The Other Strand Of Dna Helix Other Than The Template Strand That Runs From 5' To 3' End And Is Parallel To The Mrna Strand.
Related Post: