Coding Strand And Template Strand
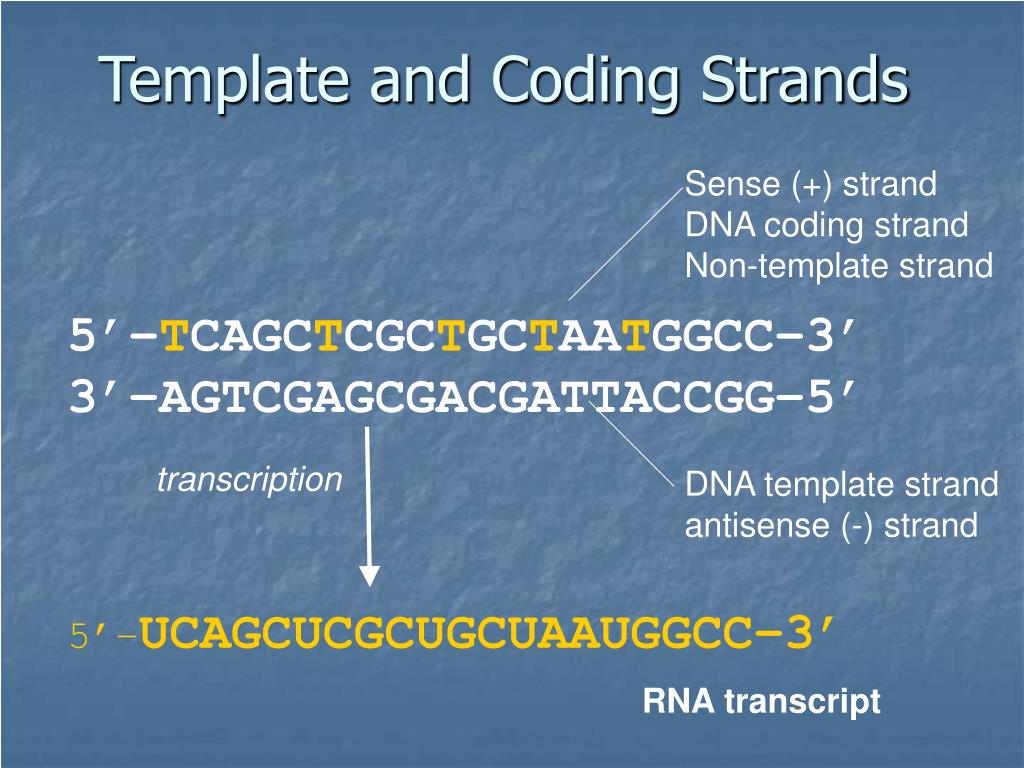
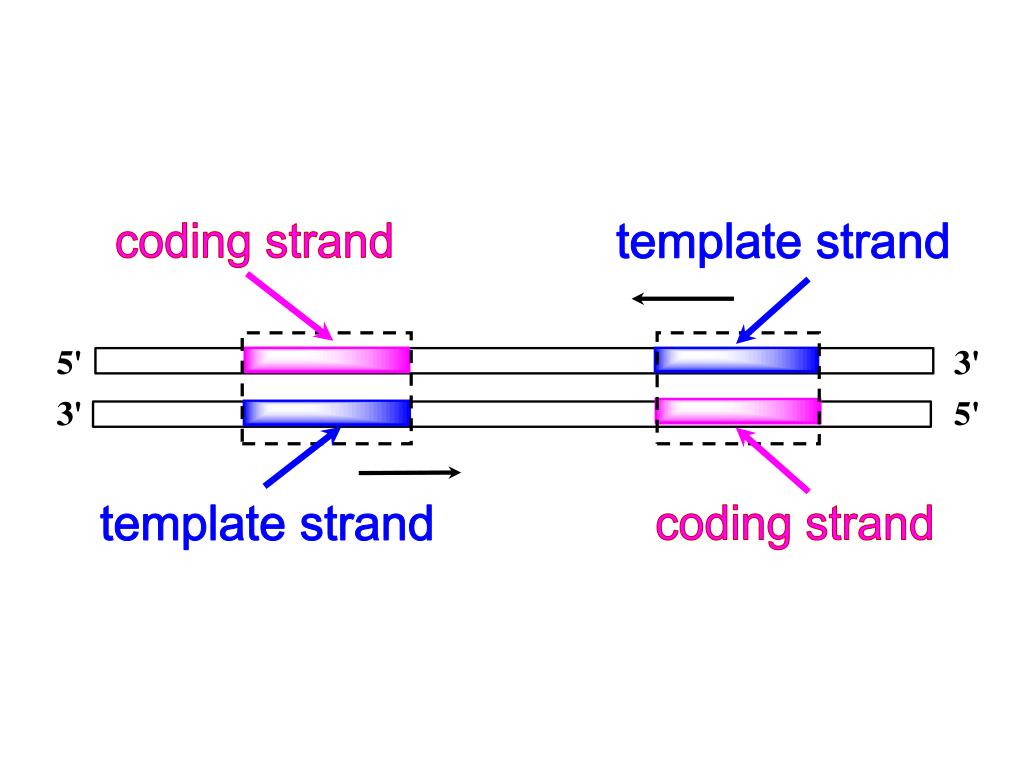
Coding Strand And Template Strand - The coding and template strands work together to transcribe the genetic code into proteins. Imagine these as partners in a genetic dance. Web the nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule. Rna then exits the nucleus and attaches to ribosomes to direct. The coding strand is the strand of dna. Template strand or “ antisense strand. The coding strand is the dna strand. Web the coding and template strands are two complementary strands that make up the dna double helix. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. Web both coding and template strands are distinct strands of a dna structure. Rna then exits the nucleus and attaches to ribosomes to direct. The coding strand is the dna strand. It serves as the direct template for rna synthesis during transcription. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Here are some features of codons: Web coding strand vs template strand. The coding strand is the strand of dna. Web active and dynamic, the coding strand is the mirror image of the template strand. What is the difference between coding strand and template strand? Web the coding and template strands are two complementary strands that make up the dna double helix. Template strand or “ antisense strand. Cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. Web position of the template and coding strands during transcription. Web the strand of dna from which mrna is formed after transcription is known. What is the difference between coding strand and template strand? Web the coding strand and template strand are two complementary strands of dna that play different roles in the process of transcription. Here are some features of codons: Web the nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the. It serves as the direct template for rna synthesis during transcription. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand) is the dna strand whose base. Web the dna strand known as the template strand serves as a blueprint for the production of rna, whereas the coding strand is the other strand. Most codons specify an amino acid.. They differ only by a few properties and functions. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Web the template strand of dna is used to synthesize an rna molecule, which carries the genetic code. The template strand is usually directed 3’ to 5’ in. Web the strand of dna from which. Considering the same dna sequence: Its sequence is used as a template during transcription to produce an rna molecule. Imagine these as partners in a genetic dance. The coding strand is the strand of dna. Cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. They differ only by a few properties and functions. Understand that within a single piece of dna, either strand can be used as the template. Here are some features of codons: Web the dna strand known as the template strand serves as a blueprint for the production of rna, whereas the coding strand is the other strand. Considering the same. Web the dna strand known as the template strand serves as a blueprint for the production of rna, whereas the coding strand is the other strand. The coding strand is the dna strand. Cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. The two distinct strands of double. The coding strand and the template strand. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Imagine these as partners in a genetic dance. Cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. Web the coding and template strands are two complementary strands that make up the dna double helix. Web the dna strand known as the template strand serves as a blueprint. Web the dna strand known as the template strand serves as a blueprint for the production of rna, whereas the coding strand is the other strand. Web the coding and template strands are two complementary strands that make up the dna double helix. Web coding strand vs template strand. What is the difference between coding strand and template strand? Web dna’s intricate design includes two fundamental strands: Imagine these as partners in a genetic dance. Web the strand of dna from which mrna is formed after transcription is known as the template strand or the antisense strand. Understand that within a single piece of dna, either strand can be used as the template. Web both coding and template strands are distinct strands of a dna structure. Most codons specify an amino acid. They differ only by a few properties and functions. Template strand or “ antisense strand. The coding strand is the dna strand. The coding strand is the strand of dna. The two distinct strands of double. Given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify.
Coding Strand And Template Strand
PPT Transcription PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1215212

Gene Expression Transcription Agriculture, and Biotechnology

Dna Template Strand And Coding Strand
AQA A Level Biology复习笔记4.2.3 Transcription翰林国际教育

DNA Transcription Steps and Mechanism • Microbe Online
PPT Chapter 11 Transcription PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer
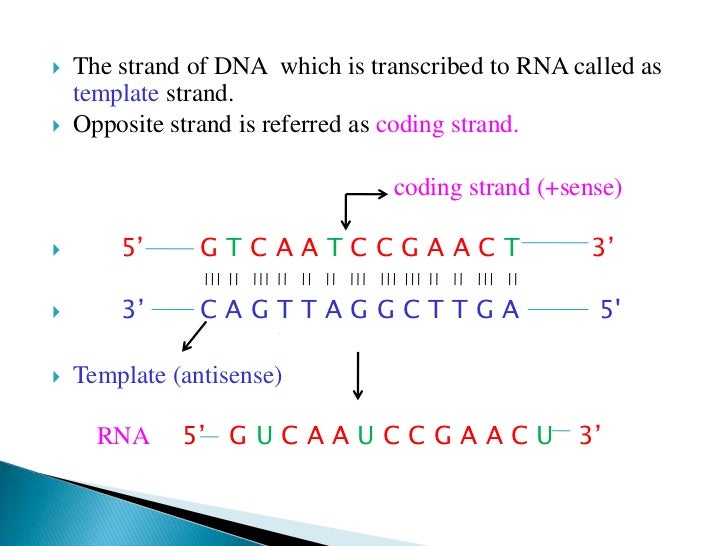
Transcription
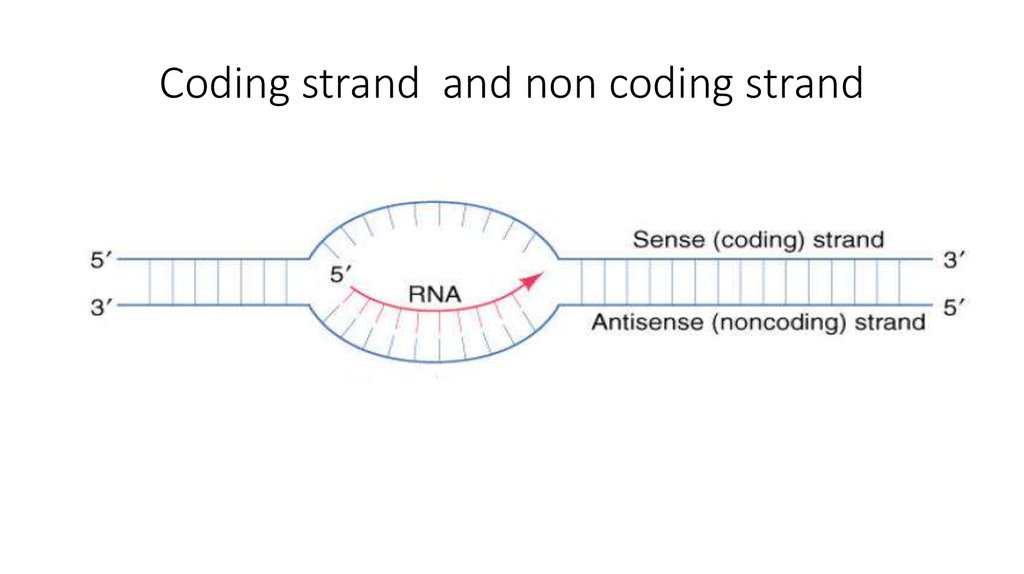
Functions and structures of DNA and nucleotide презентация онлайн
Web The Template Strand Is One Of The Dna Strands Whose Base Sequence Helps In Building Mrna Through Complementary Base Sequencing.
Web Active And Dynamic, The Coding Strand Is The Mirror Image Of The Template Strand.
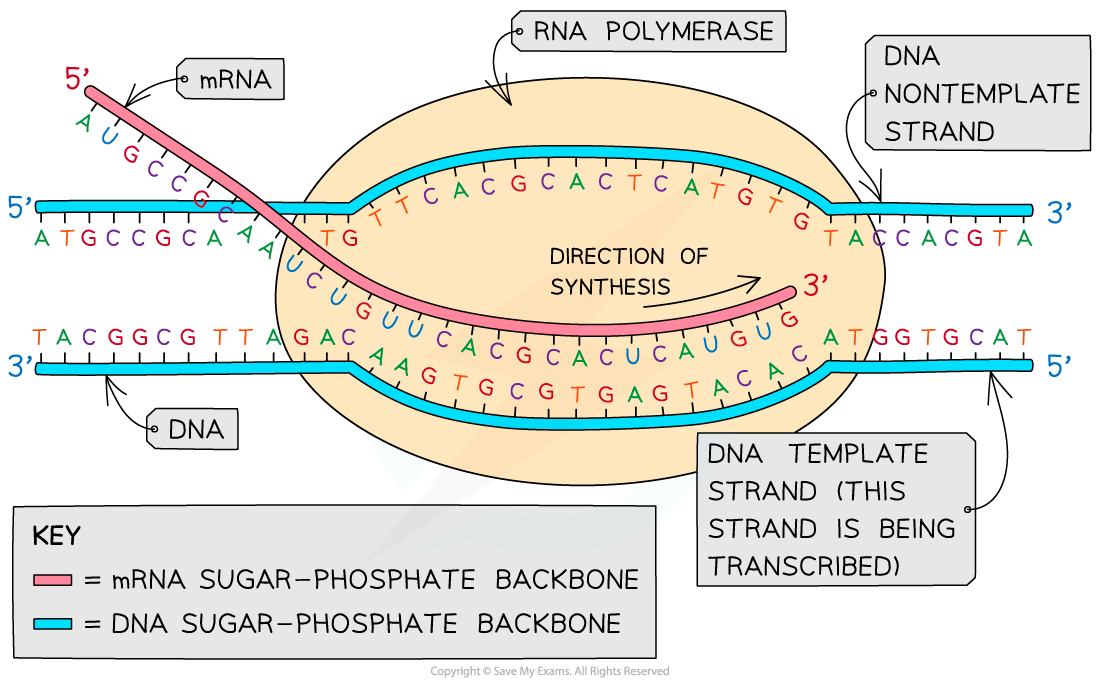
Web Transcription Is Performed By Enzymes Called Rna Polymerases, Which Link Nucleotides To Form An Rna Strand (Using A Dna Strand As A Template).
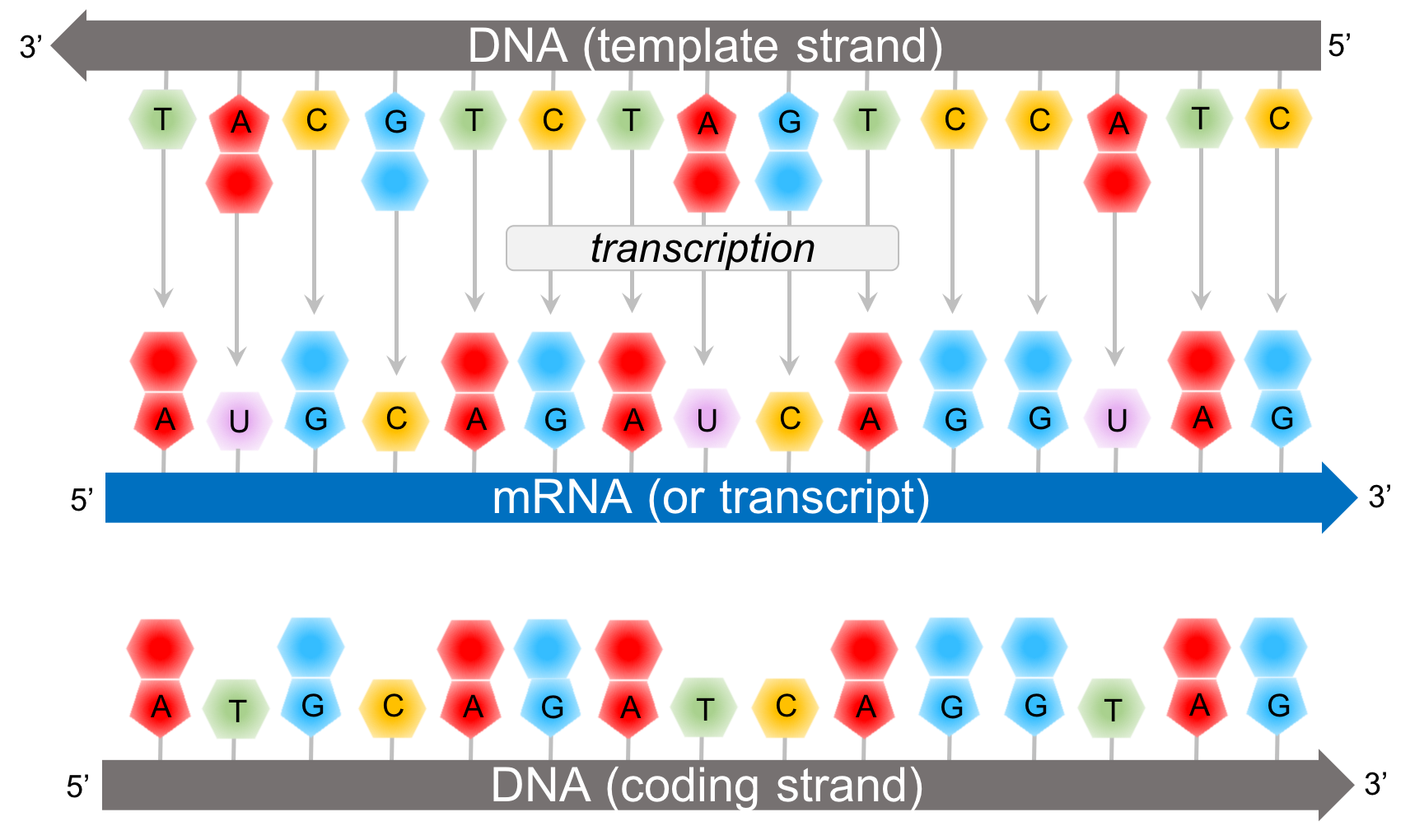
Cells Decode Mrnas By Reading Their Nucleotides In Groups Of Three, Called Codons.
Related Post: