Chromosomes Drawing
Chromosomes Drawing - Chromatid:each of the two threadlike strands into which a chromosome divides longitudinally during cell division. It is exactly 1, not 2, not 3!) giving raise to one or more derivative chromosome(s) in the text field below, select the desired map viewer with which. The sex cells of a human are haploid (n), containing only one. Web chromosomes are long strands of dna in cells that carry genetic information. These processes contribute to genetic diversity by shuffling the genes found on the chromosomes. Meiosis involves two divisions, so it’s typically broken down into meiosis i and meiosis ii. During prophase i, chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material, creating more variation. Chromosome 1 is the largest and is over three times bigger than chromosome 22. Redraw the nuclear membrane around the chromosomes and draw a nucleolus inside of each nucleus. Eukaryotic cells, with their much larger genomes, have multiple, linear chromosomes. Most prokaryotic cells contain a single circular chromosome. For example, humans are diploid (2n) and have 46 chromosomes in their normal body cells. It is exactly 1, not 2, not 3!) giving raise to one or more derivative chromosome(s) in the text field below, select the desired map viewer with which. It is crucial for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes. Prophase. 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes. The length and linear nature of eukaryotic chromosomes increase the challenge of keeping the genetic material. Every species has its own specific number of chromosomes. Web the drawing of a genetic map is decomposed into 8 modules inmg2c program as follows: Web chromosomes undergo segregation and independent assortment during meiosis. Web in meiosis i, cells go through four phases: During prophase i, chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material, creating more variation. Web how to draw structure of chromosome. Many species have chromosomes that come in matched pairs. In metaphase i, chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. Chromatid:each of the two threadlike strands into which a chromosome divides longitudinally during cell division. Human sperm and eggs, which have only one homologous chromosome from each pair, are said to be haploid ( 1n ). Chromosome 1 is the largest and is over three times bigger than chromosome 22. Web in meiosis i, cells go through four phases: Redraw. It is exactly 1, not 2, not 3!) giving raise to one or more derivative chromosome(s) in the text field below, select the desired map viewer with which. Chromosomes:a threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes. Web dna structure and function. Human sperm and. Redraw the nuclear membrane around the chromosomes and draw a nucleolus inside of each nucleus. Usually, the centromere lies within the primary constriction (thinner chromosomal. For example, humans are diploid (2n) and have 46 chromosomes in their normal body cells. Human sperm and eggs, which have only one homologous chromosome from each pair, are said to be haploid ( 1n. Different species have different numbers of chromosomes. Human sperm and eggs, which have only one homologous chromosome from each pair, are said to be haploid ( 1n ). It is crucial for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes. Every species has its own specific number of chromosomes. Chromosome 1 is the largest and is over three times bigger than chromosome 22. Web dna structure and function. Chromosome 1 is the largest and is over three times bigger than chromosome 22. Human sperm and eggs, which have only one homologous chromosome from each pair, are said to be haploid ( 1n ). Passed from parents to offspring, dna contains the specific instructions that make each type of living creature unique. Chromosomes:a threadlike. Our genetic information is stored in 23 pairs of chromosomes that vary widely in size and shape. Each chromosome is made of protein and a single molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid (dna). Web in meiosis i, cells go through four phases: Long strands of dna wind around proteins called histones, giving rise to a “beads on a string” structure. In humans,. In metaphase i, chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. These processes contribute to genetic diversity by shuffling the genes found on the chromosomes. Eukaryotic cells, with their much larger genomes, have multiple, linear chromosomes. Web in meiosis i, cells go through four phases: Web model cytokinesis l by drawing the formation of a cleavage furrow to divide. Web chromosomes are complex molecules with several levels of organization, allowing cells to cram 2 meters of dna into a nucleus that is only one hundredth of a millimeter in diameter. Many species have chromosomes that come in matched pairs. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of dna, called genes. Web model cytokinesis l by drawing the formation of a cleavage furrow to divide the cytoplasm into two and form two separate cells. Chromosome 1 is the largest and is over three times bigger than chromosome 22. The sex cells of a human are haploid (n), containing only one. The length and linear nature of eukaryotic chromosomes increase the challenge of keeping the genetic material. Web during mitosis, chromosomes become attached to the structure known as the mitotic spindle.in the late 1800s, theodor boveri created the earliest detailed drawings of the spindle based on his. Anaphase i separates homologous pairs, while telophase i forms two new cells with a. It is crucial for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes. Every species has its own specific number of chromosomes. For example, the 46 chromosomes in a human cell can be organized into 23 pairs. Prophase i, metaphase i, anaphase i, and telophase i. It is exactly 1, not 2, not 3!) giving raise to one or more derivative chromosome(s) in the text field below, select the desired map viewer with which. For example, humans are diploid (2n) and have 46 chromosomes in their normal body cells. Enter the karyotype described by an iscn formula in the text field below, select the desired map viewer with which chromosomal bands are to be linked, banding resolution, color style, and the sequence of the.
Chromosome Structure
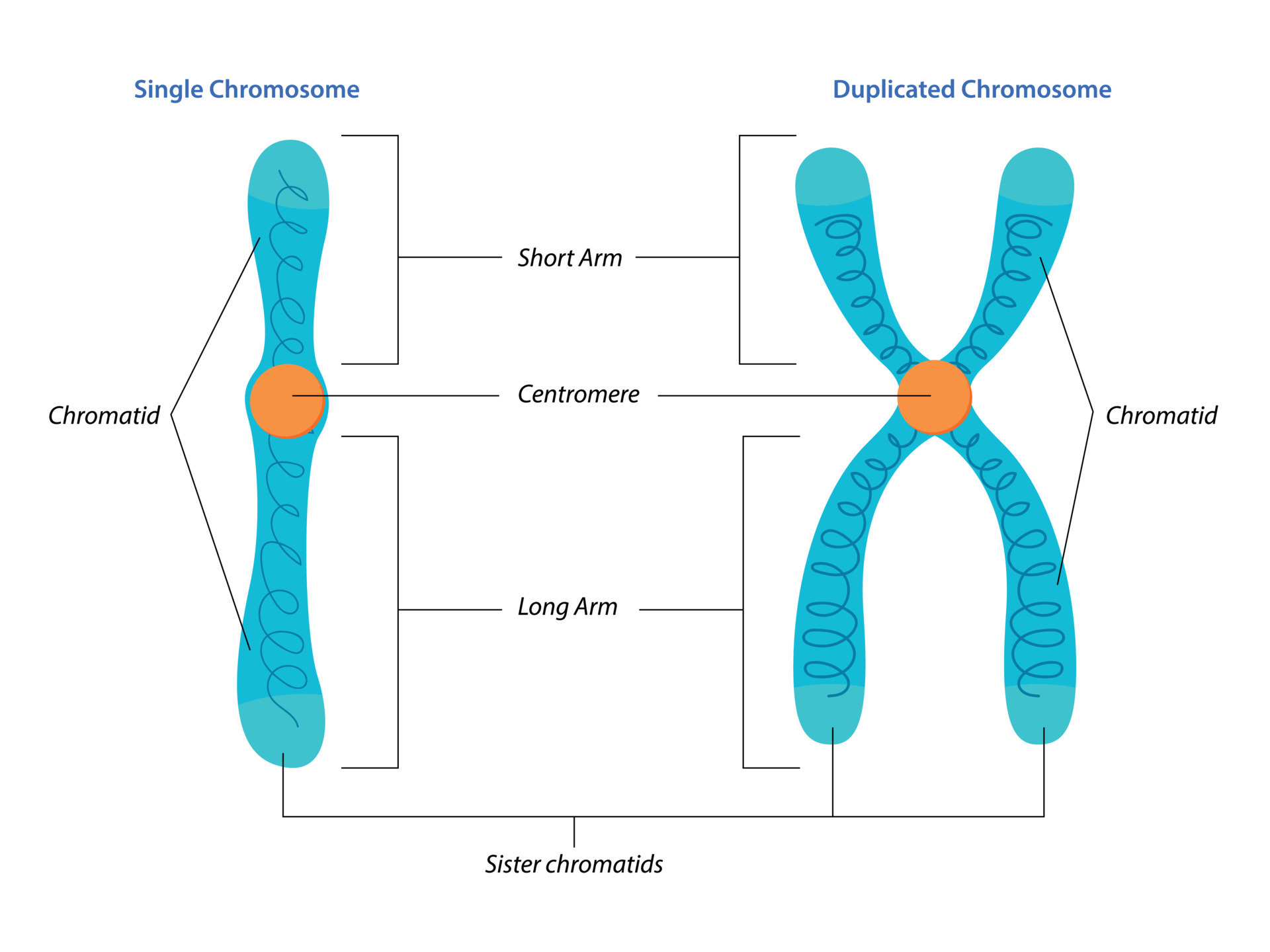
Illustration of Singel and duplicated chromosome structure 12324913

how to draw chromosomes in easy way drawing chromosomes step by step

Human Chromosome Drawing Stock Illustration Download Image Now
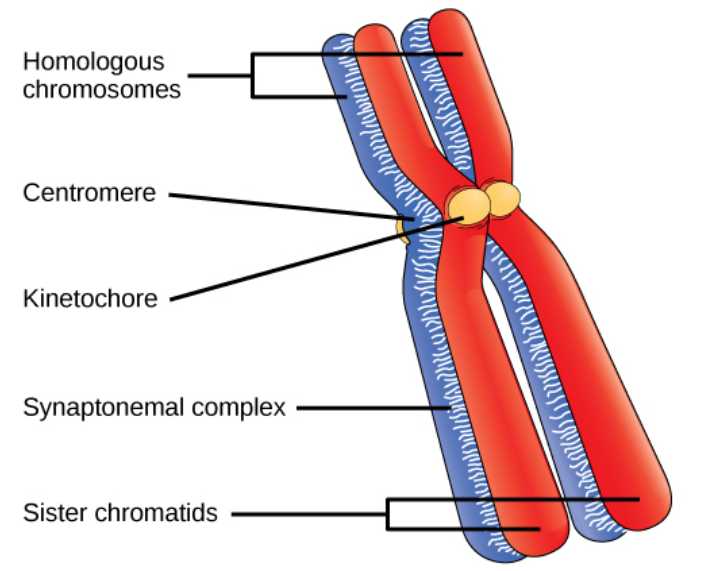
Draw the structure of the chromosome and label its parts.

Drawing dna molecule chromosome biology Vector Image

How to draw TYPES OF CHROMOSOMES easily Class 11 Biology YouTube

Parts of Chromosome Diagram Quizlet
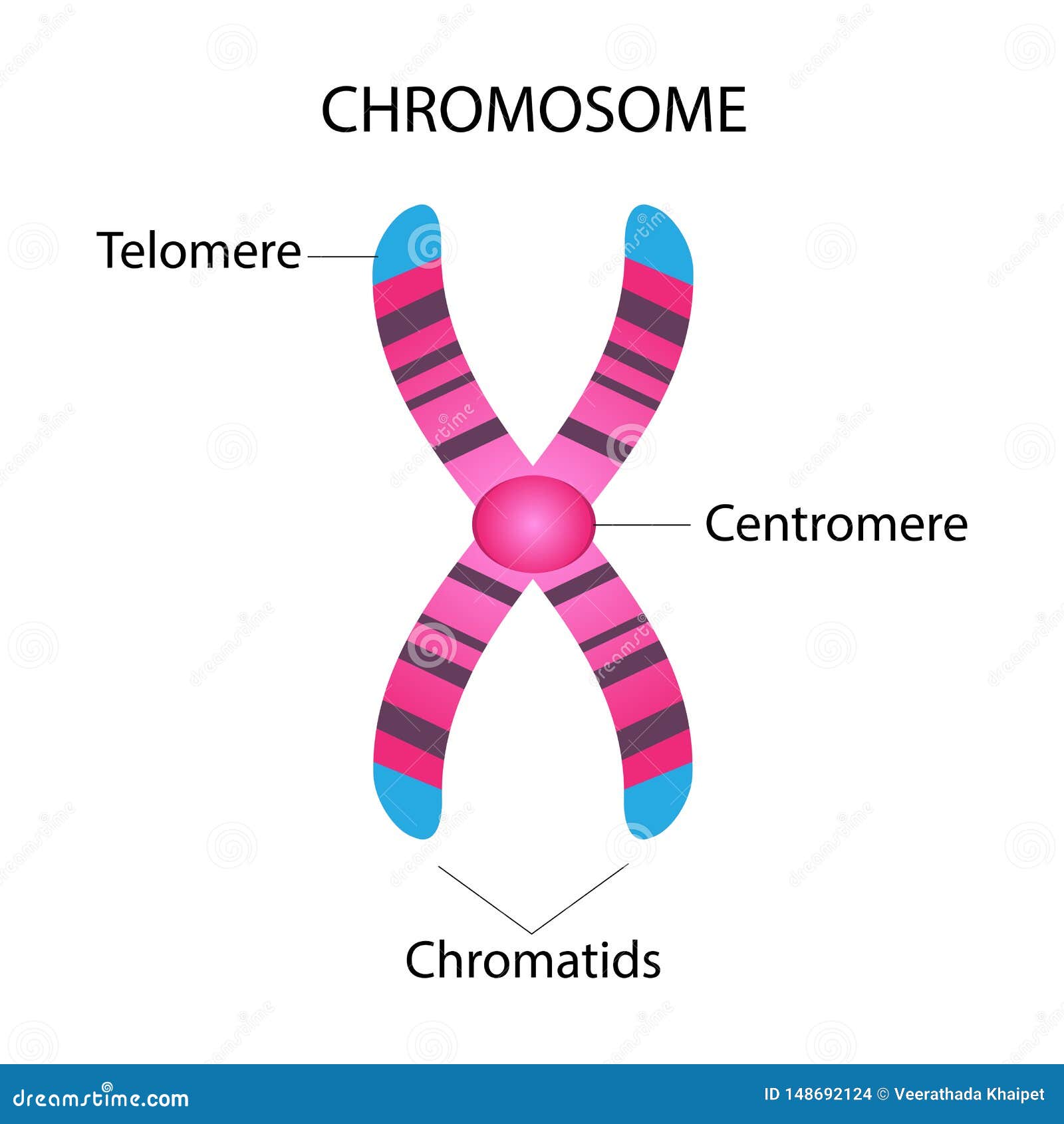
Parts Of A Chromosome
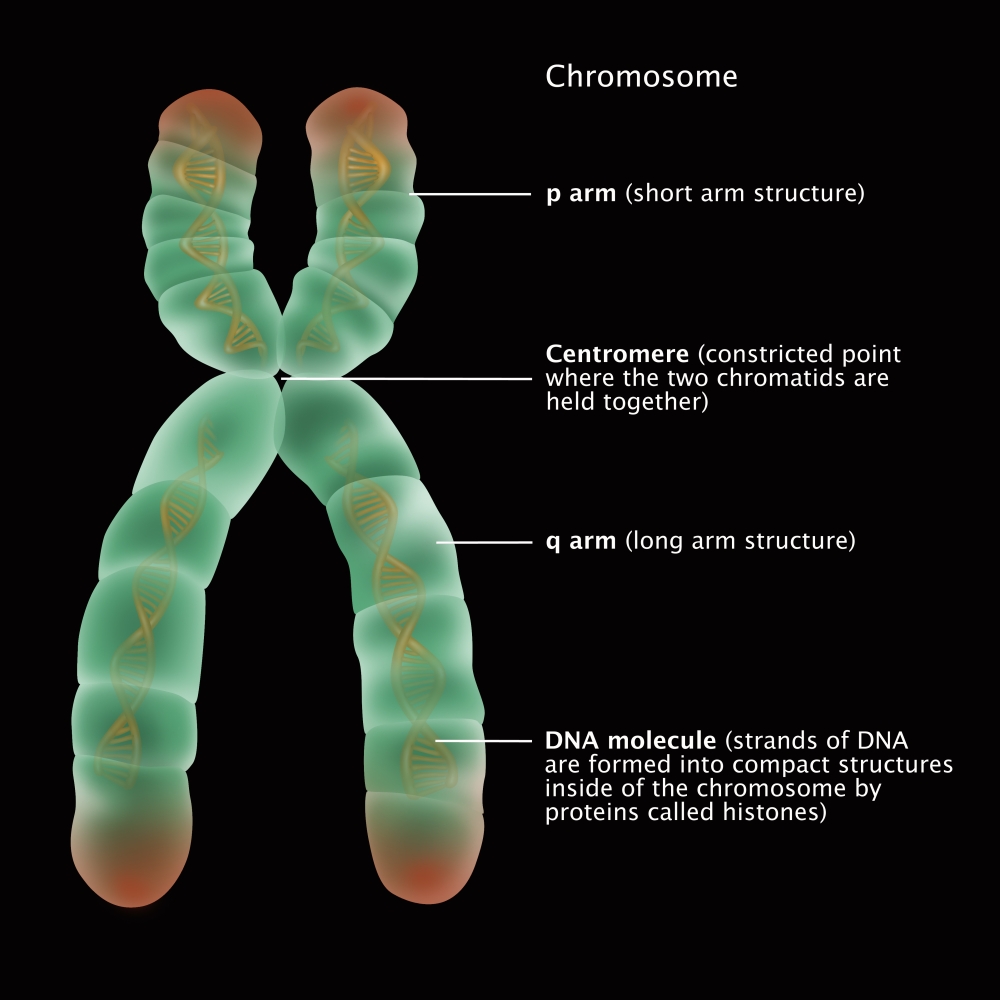
Chromosome Structure, Illustration Poster Print by Gwen Shockey/Science
Web The Drawing Of A Genetic Map Is Decomposed Into 8 Modules Inmg2C Program As Follows:
Web To Put That Another Way, Meiosis In Humans Is A Division Process That Takes Us From A Diploid Cell—One With Two Sets Of Chromosomes—To Haploid Cells—Ones With A Single Set Of Chromosomes.
Web Chromosomes Are Long Strands Of Dna In Cells That Carry Genetic Information.
This Software Draws An Image For One Chromosomal Rearrangement.
Related Post: