Cholestatic Pattern Vs Hepatocellular
Cholestatic Pattern Vs Hepatocellular - Web this reduction in bile flow can basically be split into two types, hepatocellular cholestasis, where for some reason the hepatocytes aren’t making enough bile, and obstructive. Ratio of ast and alt can be useful in differential. Web an infiltrative disorder of the liver may be associated with a very similar biochemical pattern to that of cholestasis (eg, amyloidosis, fatty liver, and lymphoma). The aim of this study was to document the predicted ranges of. The predominant laboratory abnormality defines the pattern of. Manifest clinically with fatigue, pruritus, and jaundice.1 the differential diagnosis of. Hepatocellular, autoimmune, cholestatic, and infiltrative (table 1). Sometimes serum levels of aminotransferases may be very high (>1000 iu/l) and fluctuate despite obvious cholestasis—this pattern is typical of biliary obstruction caused by. Web when both sets of enzymes are elevated, distinguishing between the two patterns of liver disease can be difficult. Web the cholestatic pattern of liver function test abnormalities indicates biliary obstruction. Generally not associated with cholestasis. Decrease in bile flow due to hepatocellular dysfunction or biliary obstruction. Web cholestasis that has progressed to cirrhosis and portal hypertension can be associated with the same physical findings as those seen in patients with hepatocellular or. Web differentiates cholestatic from hepatocellular liver injury, recommended by acg guidelines. Manifest clinically with fatigue, pruritus, and jaundice.1. Ratio of ast and alt can be useful in differential. Compared to hepatocellular injury, mixed pattern of dili is. This review focuses on the principal causes of cholestasis and the features associated with each condition. The aim of this study was to document the predicted ranges of. Web hepatocellular injury and death, with the accompanying inflammatory response, provoke symptoms of. Web an infiltrative disorder of the liver may be associated with a very similar biochemical pattern to that of cholestasis (eg, amyloidosis, fatty liver, and lymphoma). This review focuses on the principal causes of cholestasis and the features associated with each condition. Web c holestasis describes impairment in bile formation or ow that can. Web the three abnormal patterns that. Generally not associated with cholestasis. Web when both sets of enzymes are elevated, distinguishing between the two patterns of liver disease can be difficult. Web cholestasis that has progressed to cirrhosis and portal hypertension can be associated with the same physical findings as those seen in patients with hepatocellular or. Decrease in bile flow due to hepatocellular dysfunction or biliary. Web differentiates cholestatic from hepatocellular liver injury, recommended by acg guidelines. Web when both sets of enzymes are elevated, distinguishing between the two patterns of liver disease can be difficult. This review focuses on the principal causes of cholestasis and the features associated with each condition. Decrease in bile flow due to hepatocellular dysfunction or biliary obstruction. Sometimes serum levels. The pattern occurs when there is a disproportionate elevation in alkaline. Web the three abnormal patterns that can be detected in liver function tests include the hepatocellular pattern, cholestatic pattern, and isolated hyperbilirubinemia. Web definition / general. Aminotransferases (ast, alt) generally associated with hepatocellular damage. Use the first lab values (alt and alp) indicating acute liver injury to calculate the. Web the cholestatic pattern of liver function test abnormalities indicates biliary obstruction. Overall analysis of liver function tests (lft) transaminitis: Web c holestasis describes impairment in bile formation or ow that can. Web an infiltrative disorder of the liver may be associated with a very similar biochemical pattern to that of cholestasis (eg, amyloidosis, fatty liver, and lymphoma). Generally not. Sometimes serum levels of aminotransferases may be very high (>1000 iu/l) and fluctuate despite obvious cholestasis—this pattern is typical of biliary obstruction caused by. Web cholestasis that has progressed to cirrhosis and portal hypertension can be associated with the same physical findings as those seen in patients with hepatocellular or. Hepatocellular, autoimmune, cholestatic, and infiltrative (table 1). The aim of. Alt is more specific for liver damage than ast. Web hepatocellular liver injury is characterized by elevations in serum alanine (alt) and aspartate (ast) aminotransferases while cholestasis is associated with elevated serum. This review focuses on the principal causes of cholestasis and the features associated with each condition. Compared to hepatocellular injury, mixed pattern of dili is. Overall analysis of. Compared to hepatocellular injury, mixed pattern of dili is. Web the cholestatic pattern of liver function test abnormalities indicates biliary obstruction. Manifest clinically with fatigue, pruritus, and jaundice.1 the differential diagnosis of. Web hepatocellular liver injury is characterized by elevations in serum alanine (alt) and aspartate (ast) aminotransferases while cholestasis is associated with elevated serum. Alt is more specific for. The predominant laboratory abnormality defines the pattern of. Web the three abnormal patterns that can be detected in liver function tests include the hepatocellular pattern, cholestatic pattern, and isolated hyperbilirubinemia. Web when both sets of enzymes are elevated, distinguishing between the two patterns of liver disease can be difficult. Microscopically visible bile, usually in. Alt is more specific for liver damage than ast. Decrease in bile flow due to hepatocellular dysfunction or biliary obstruction. Overall analysis of liver function tests (lft) transaminitis: Web hepatocellular injury and death, with the accompanying inflammatory response, provoke symptoms of fatigue and weakness, and account, in part, for the characteristic. Aminotransferases (ast, alt) generally associated with hepatocellular damage. Web the cholestatic pattern of liver function test abnormalities indicates biliary obstruction. Use the first lab values (alt and alp) indicating acute liver injury to calculate the r factor. The pattern occurs when there is a disproportionate elevation in alkaline. Web using a schematic approach that classifies enzyme alterations as predominantly hepatocellular or predominantly cholestatic, we review abnormal. Web differentiates cholestatic from hepatocellular liver injury, recommended by acg guidelines. Web c holestasis describes impairment in bile formation or ow that can. Hepatocellular, autoimmune, cholestatic, and infiltrative (table 1).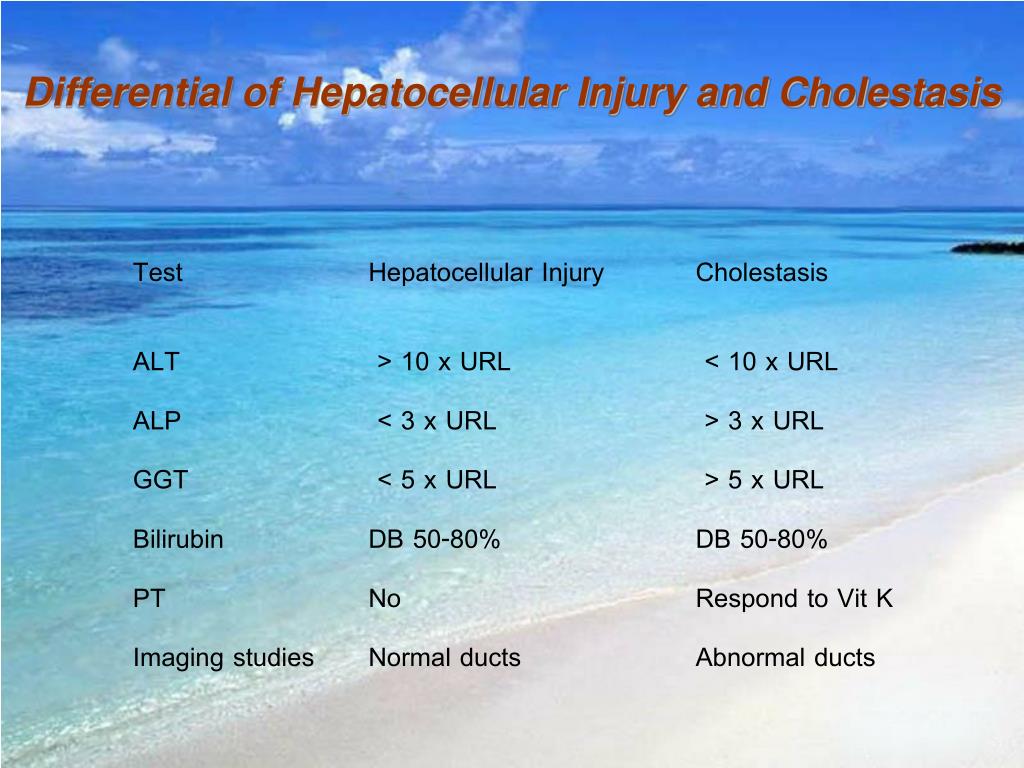
PPT Liver Function Test s PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID

Liver (2)

Pin on Infographics

Summary of enzymes patterns in liver disease summary table Download Table

LFTs explained Emergency Medicine Kenya Foundation

Liver Failure Case

Liver Enzymes (hepatic vs cholestatic patterns) Sketchy Medicine
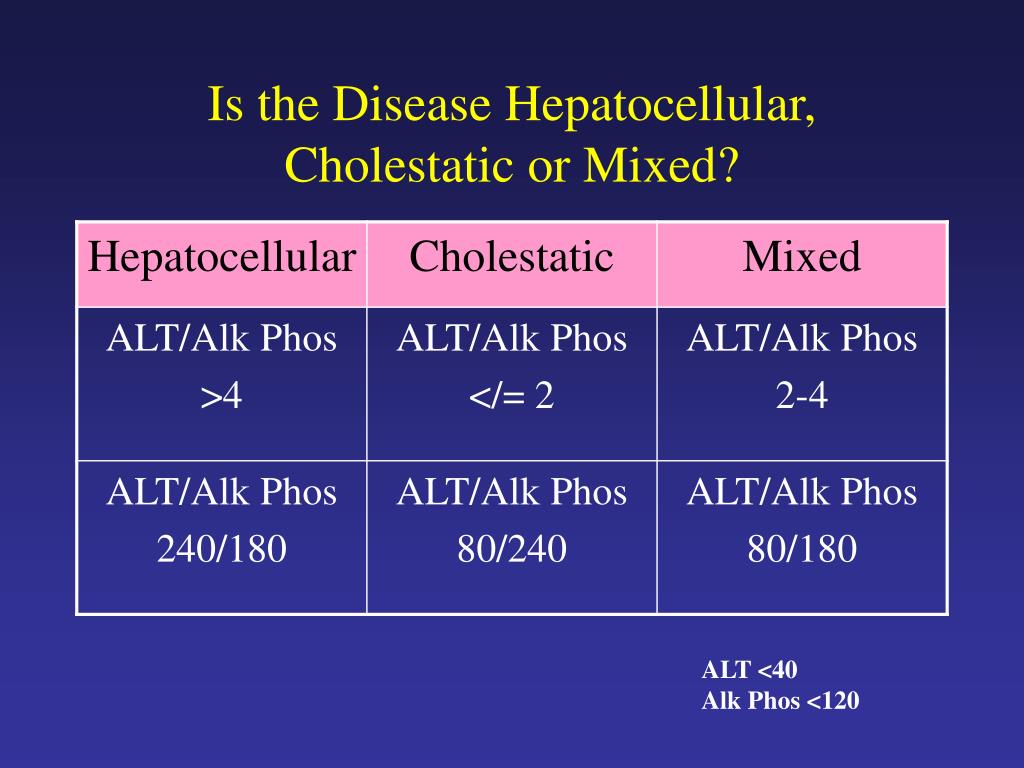
PPT Work up of the Asymptomatic Patient with Liver Enzyme

Laboratory Associations with Hepatocellular and Cholestatic Patterns of

PPT Abnormal LFTs PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID139175
Web Cholestasis That Has Progressed To Cirrhosis And Portal Hypertension Can Be Associated With The Same Physical Findings As Those Seen In Patients With Hepatocellular Or.
This Review Focuses On The Principal Causes Of Cholestasis And The Features Associated With Each Condition.
Web There Are Four Major Types Of Liver Injury:
Sometimes Serum Levels Of Aminotransferases May Be Very High (>1000 Iu/L) And Fluctuate Despite Obvious Cholestasis—This Pattern Is Typical Of Biliary Obstruction Caused By.
Related Post: