Cholestatic Pattern Of Liver Injury
Cholestatic Pattern Of Liver Injury - Cholestasis can be due to a functional impairment of the hepatocytes. Web an ultrasound can be useful in determining whether there is an intrahepatic or extrahepatic cause of cholestatic pattern of liver injury. 2 generated a resourceful spatiotemporal atlas deconstructing processes upon. 1 based on national health and nutrition examination survey iii data, approximately 7.9% of the. Characterized by intracytoplasmic bile (hepatocanalicular cholestasis) and changes of chronic cholestasis. An autoimmune mechanism can present. The aim of this study was to document the predicted ranges of. Web this article reviews the latest guidelines for primary biliary cholangitis (pbc) and primary sclerosing cholangitis (psc), two common cholestatic disorders. Find out the possible causes, tests,. Web cholestatic hepatocellular injury: Web cholestatic drug‐induced liver injury (dili) can be a diagnostic challenge due to a large differential diagnosis, variability in clinical presentation, and lack of serologic biomarkers. Web cholestasis is defined as stagnation, or at least a marked reduction, in bile secretion and flow. Web this article reviews the latest guidelines for primary biliary cholangitis (pbc) and primary sclerosing cholangitis (psc),. Elevation of alp and bilirubin levels often indicate a cholestatic pattern. Cholestatic liver disease results from insufficient bile synthesis, secretion and/or flow through the biliary tract. Cholestasis can be due to a functional impairment of the hepatocytes. Characterized by intracytoplasmic bile (hepatocanalicular cholestasis) and changes of chronic cholestasis. Web abnormal liver tests are a common occurrence in the united states. We recommend udca (a1), same. Web when both sets of enzymes are elevated, distinguishing between the two patterns of liver disease can be difficult. Web obstruction of bile secretion results in cholestatic liver injury. Web r factor for liver injury. What do we know and how should we proceed. Find out the possible causes, tests,. Web current literature supports statin induced liver injury presenting in either hepatocellular or cholestatic patterns, though with the former being the prevailing. Web this article reviews the latest guidelines for primary biliary cholangitis (pbc) and primary sclerosing cholangitis (psc), two common cholestatic disorders. Web cholestatic drug‐induced liver injury (dili) can be a diagnostic challenge. Web current literature supports statin induced liver injury presenting in either hepatocellular or cholestatic patterns, though with the former being the prevailing. Web r factor for liver injury. Web cholestasis is defined as stagnation, or at least a marked reduction, in bile secretion and flow. Cholestasis can be due to a functional impairment of the hepatocytes. Web cholestatic hepatocellular injury: Web cholestasis is defined as stagnation, or at least a marked reduction, in bile secretion and flow. Web cholestasis describes impairment in bile formation or flow which can manifest clinically with fatigue, pruritus, and jaundice. Web there are 3 main patterns of cholestatic liver injury seen in dili (fig. Web an ultrasound can be useful in determining whether there is. Web when both sets of enzymes are elevated, distinguishing between the two patterns of liver disease can be difficult. Web injury or obstruction at any point along biliary flow can lead to cholestasis. Web cholestasis describes impairment in bile formation or flow which can manifest clinically with fatigue, pruritus, and jaundice. Most typically seen in biliary disease (primary sclerosing cholangitis,. Most typically seen in biliary disease (primary sclerosing cholangitis, primary. Web when both sets of enzymes are elevated, distinguishing between the two patterns of liver disease can be difficult. Web an ultrasound can be useful in determining whether there is an intrahepatic or extrahepatic cause of cholestatic pattern of liver injury. Web this article reviews the latest guidelines for primary. Cholestatic liver disease results from insufficient bile synthesis, secretion and/or flow through the biliary tract. Web this article reviews the latest guidelines for primary biliary cholangitis (pbc) and primary sclerosing cholangitis (psc), two common cholestatic disorders. Web there are 3 main patterns of cholestatic liver injury seen in dili (fig. We recommend udca (a1), same. Web an ultrasound can be. Cholestasis can be due to a functional impairment of the hepatocytes. Web cholestasis describes impairment in bile formation or flow which can manifest clinically with fatigue, pruritus, and jaundice. 1 based on national health and nutrition examination survey iii data, approximately 7.9% of the. Alp can be elevated in the presence of liver or bone disease,. We recommend udca (a1),. Most typically seen in biliary disease (primary sclerosing cholangitis, primary. Web the three abnormal patterns that can be detected in liver function tests include the hepatocellular pattern, cholestatic pattern, and isolated hyperbilirubinemia. Common presenting features include fatigue, pruritus, and. Characterized by intracytoplasmic bile (hepatocanalicular cholestasis) and changes of chronic cholestasis. Elevation of alp and bilirubin levels often indicate a cholestatic pattern. Web cholestatic hepatocellular injury: 1 based on national health and nutrition examination survey iii data, approximately 7.9% of the. Cholestasis can be due to a functional impairment of the hepatocytes. Web cholestasis is defined as stagnation, or at least a marked reduction, in bile secretion and flow. Cholestatic liver disease results from insufficient bile synthesis, secretion and/or flow through the biliary tract. Web r factor for liver injury. Web this article reviews the latest guidelines for primary biliary cholangitis (pbc) and primary sclerosing cholangitis (psc), two common cholestatic disorders. Web current literature supports statin induced liver injury presenting in either hepatocellular or cholestatic patterns, though with the former being the prevailing. Web there are 3 main patterns of cholestatic liver injury seen in dili (fig. Alp can be elevated in the presence of liver or bone disease,. Differentiates cholestatic from hepatocellular liver injury, recommended by acg guidelines.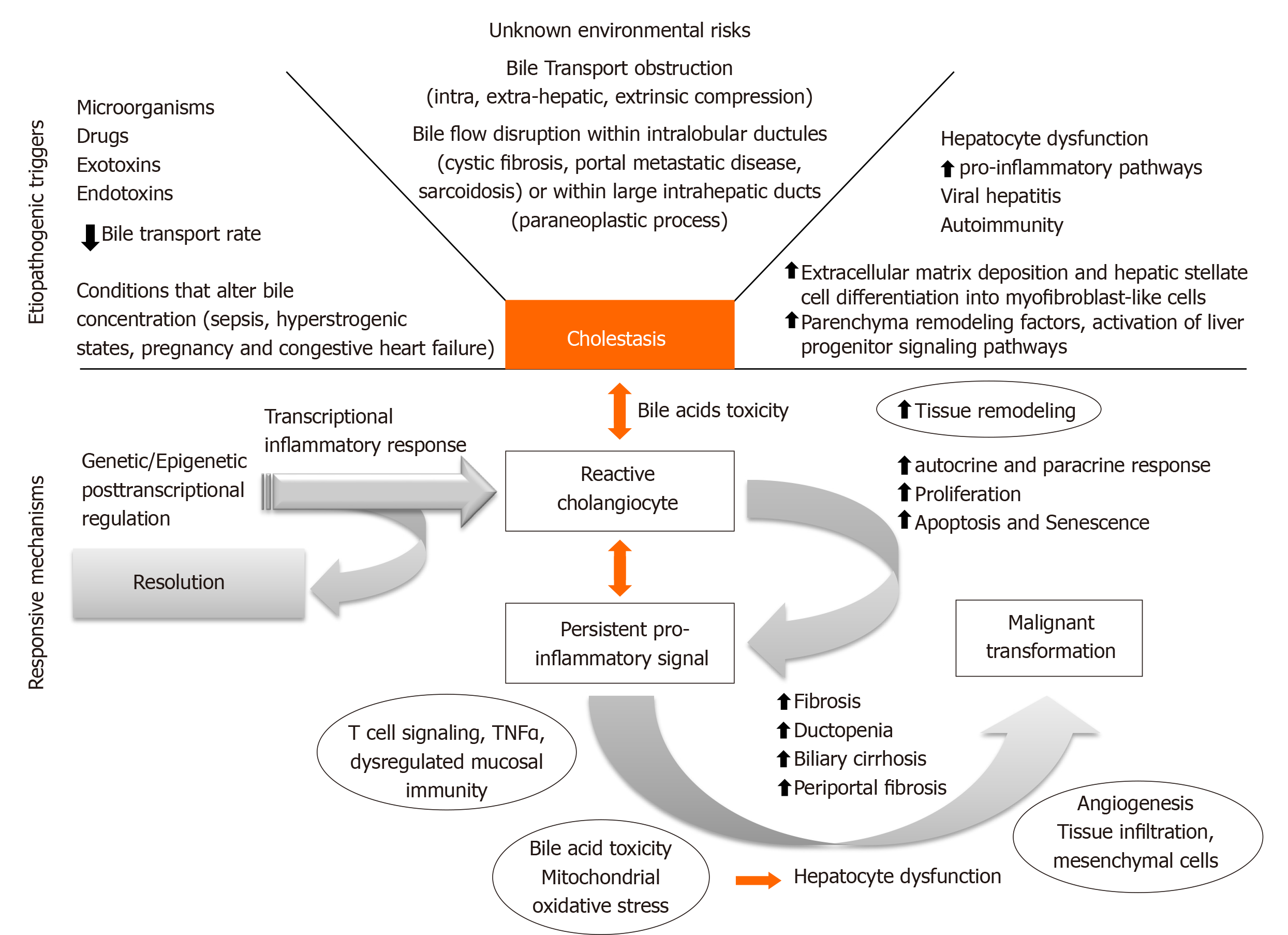
Review Pathogenesis of cholestatic liver diseases

Cholestatic liver diseases new targets, new therapies Priscila

Figure 1 from Diagnostic and therapeutic approach to cholestatic liver
DrugInduced Cholestatic Liver Injury Basicmedical Key
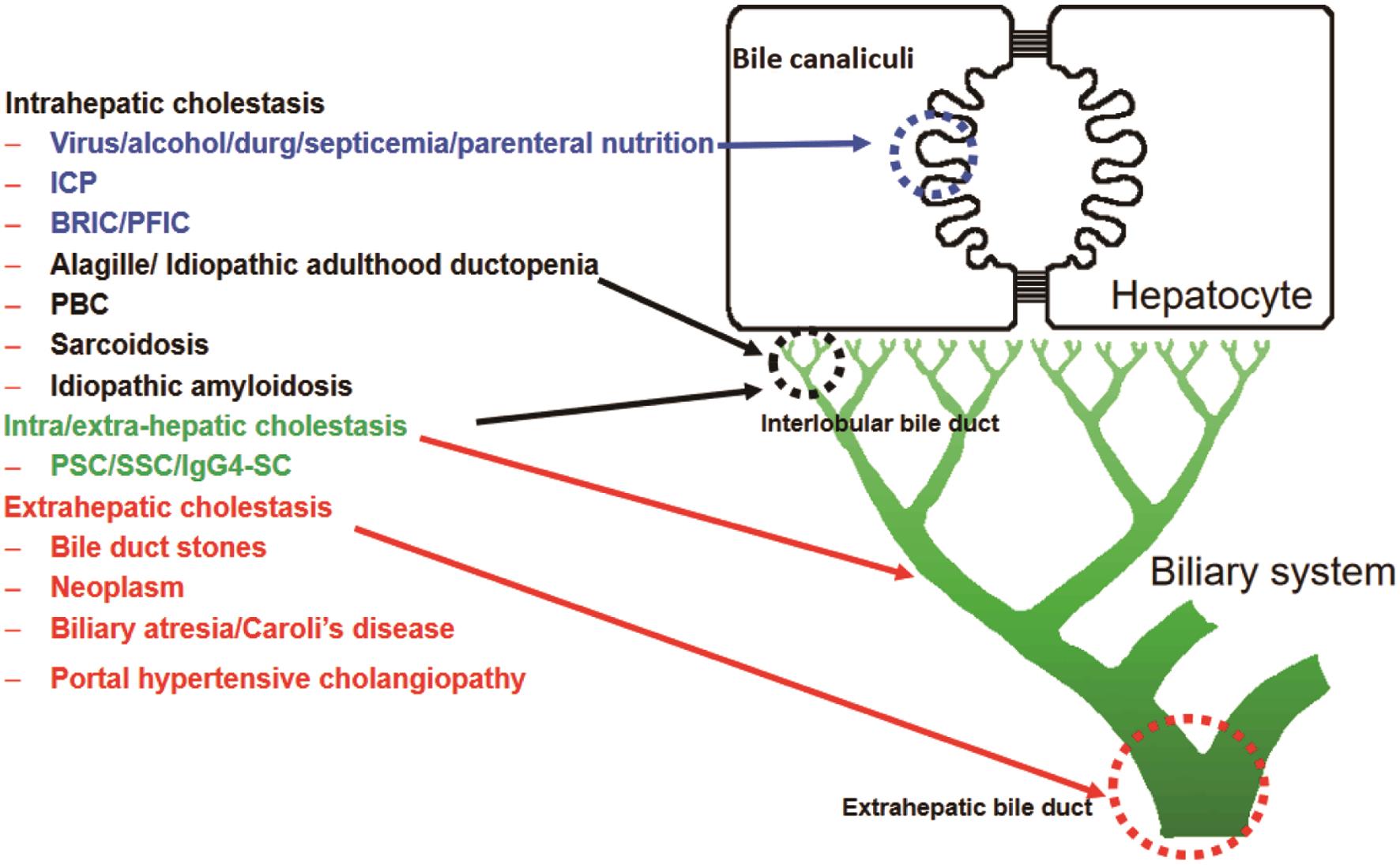
to JCTH

Cholestasis Liver and Gallbladder Disorders MSD Manual Consumer Version
DrugInduced Cholestatic Liver Injury Basicmedical Key

Liver cholestasis causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment & pathology

Liver Histology Clinics in Liver Disease
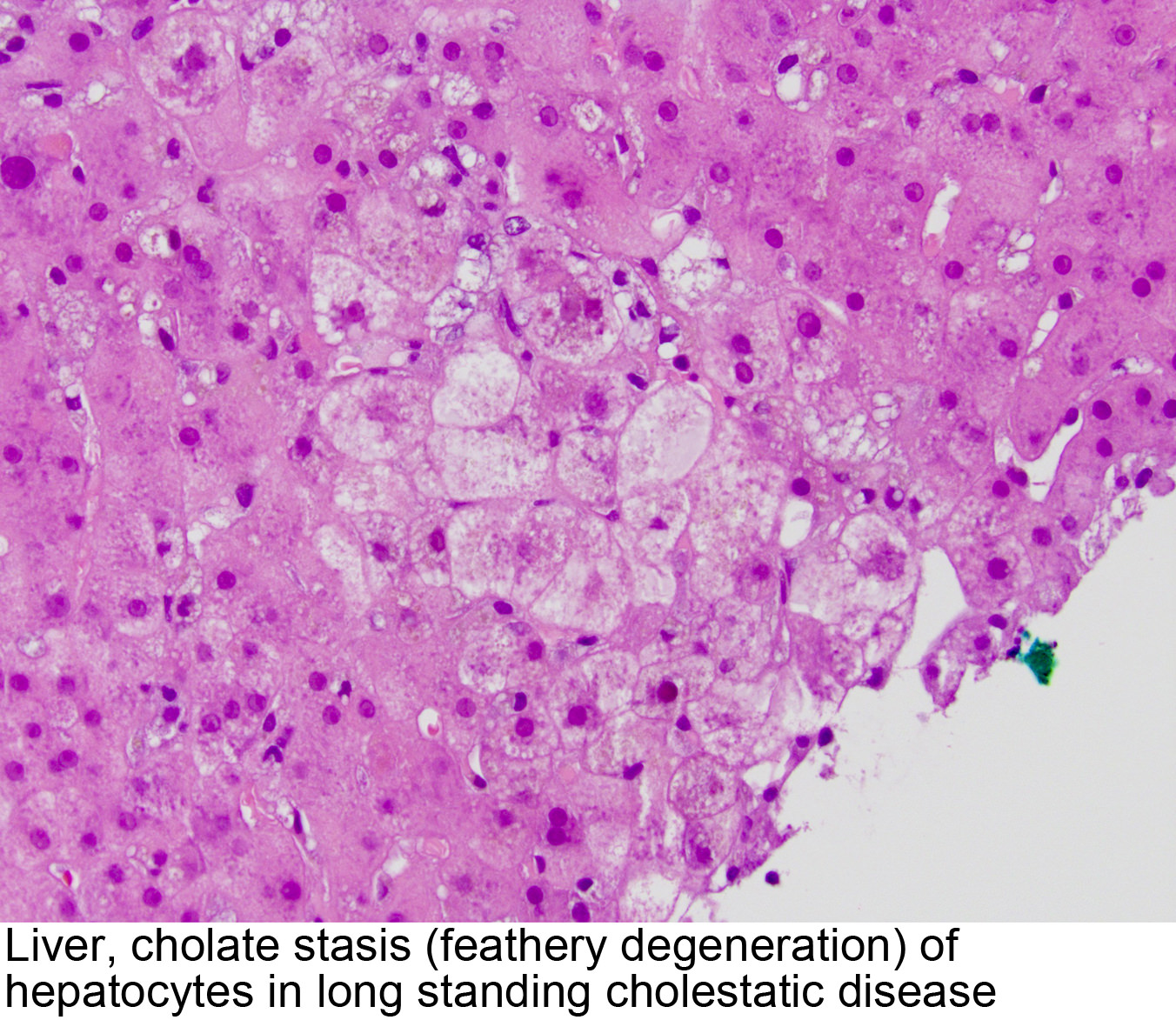
Pathology Outlines Cholestasis
Web Cholestasis Describes Impairment In Bile Formation Or Flow Which Can Manifest Clinically With Fatigue, Pruritus, And Jaundice.
2 Generated A Resourceful Spatiotemporal Atlas Deconstructing Processes Upon.
Tissue Injury And Inflammation, Repair, And Fibrosis Are Fundamental.
Web When Both Sets Of Enzymes Are Elevated, Distinguishing Between The Two Patterns Of Liver Disease Can Be Difficult.
Related Post: