Cervical Facet Referral Pattern
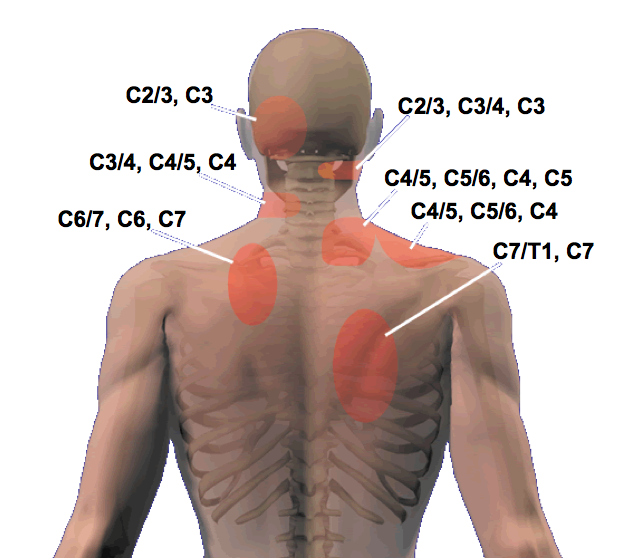
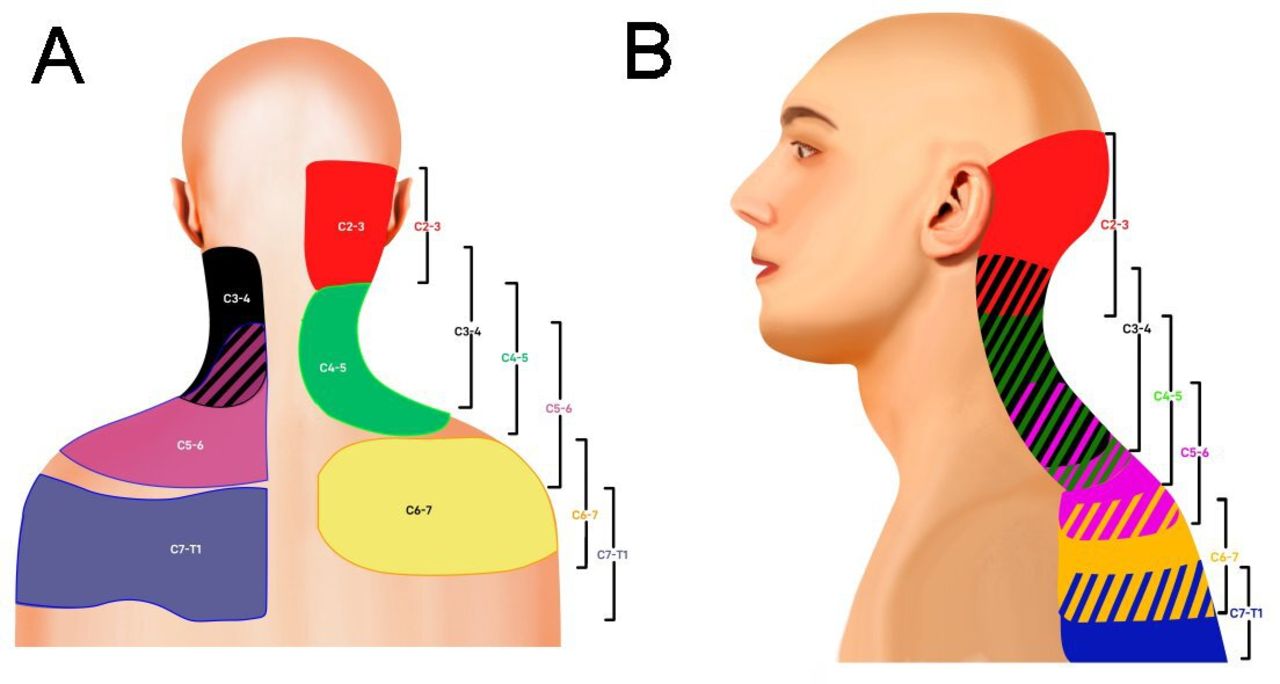
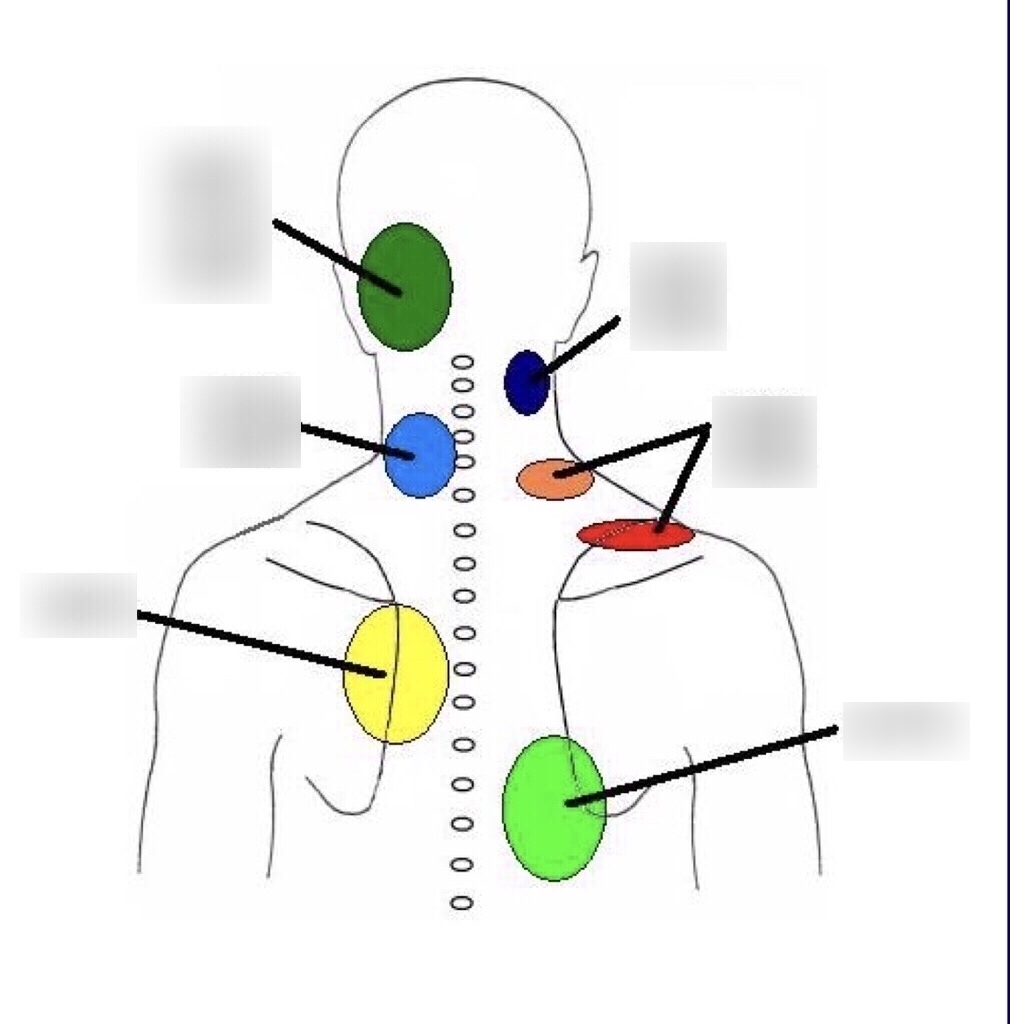
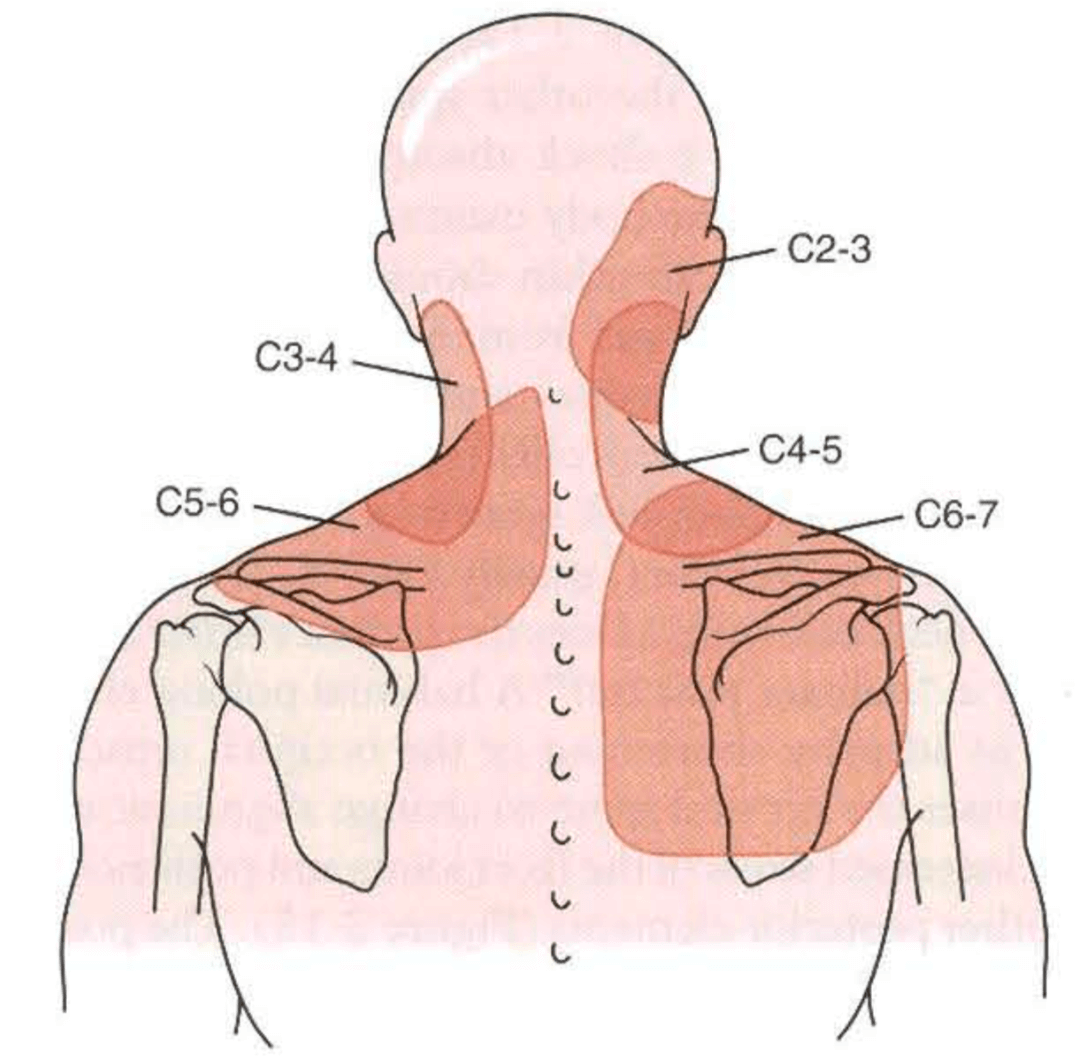
Cervical Facet Referral Pattern - • there are no effective correlations between clinical symptoms, physical examination and degenerative spinal changes. Web in a study of 5 such subjects, joint pain referral patterns were mapped out. (b) main referred pain distributions for the zygapophysial joints from c0/c1 to c7/t1 and the dorsal rami c3 to c7. Web in addition, the lower, rather than upper, cervical facet joints are also difficult to palpate due to muscles. Striped areas (hash marks) represent overlapping cervical facet joint pain maps. Web the pain is usually unilateral and radiates in a facet joint referral pattern. Web referral pain patterns arising from the cervical facet joints have been described using noxious stimulation of the joints in asymptomatic subjects that was subsequently validated with diagnostic blocks. Predict success of cervical mbb or rfa. Regional anesthesia and pain medicine 47. (a) diagram of cervical zygapophysial joint pain distribution in volunteers. • diagnostic positive facet joint block can. Web in addition, the lower, rather than upper, cervical facet joints are also difficult to palpate due to muscles. The most commonly affected cervical spine levels are c5, c6 and c7. Unlike the thoracic and lumbar facet joints, referral pain pattern and cobb angle rather than tenderness on the facetal area is helpful. (a) diagram of cervical zygapophysial joint pain distribution in volunteers. (b) main referred pain distributions for the zygapophysial joints from c0/c1 to c7/t1 and the dorsal rami c3 to c7. Pain usually increases with extension ('closing down' of the joint) and reduces with flexion ('opening' of the joint). Web the pain is usually unilateral and radiates in a facet joint. Regional anesthesia and pain medicine 47. Web in addition, the lower, rather than upper, cervical facet joints are also difficult to palpate due to muscles. Web referral patterns for cervical facet joint pains, as described by various investigators [17, 19, 20]. Web cervical facet syndrome, also known as cervical facet joint pain, is a condition that occurs when the facet. Web referral pain patterns arising from the cervical facet joints have been described using noxious stimulation of the joints in asymptomatic subjects that was subsequently validated with diagnostic blocks. Web consensus practice guidelines on interventions for cervical spine (facet) joint pain from a multispecialty international working group. Web in addition, the lower, rather than upper, cervical facet joints are also. Predict success of cervical mbb or rfa. Web referral patterns for cervical facet joint pains, as described by various investigators [17, 19, 20]. Unlike the thoracic and lumbar facet joints, referral pain pattern and cobb angle rather than tenderness on the facetal area is helpful in suggesting cervical facet joint pain. Match pain distribution with pain referral patterns. Web referral. Web consensus practice guidelines on interventions for cervical spine (facet) joint pain from a multispecialty international working group. Regional anesthesia and pain medicine 47. (b) main referred pain distributions for the zygapophysial joints from c0/c1 to c7/t1 and the dorsal rami c3 to c7. Web cervical facet syndrome, also known as cervical facet joint pain, is a condition that occurs. The most commonly affected cervical spine levels are c5, c6 and c7. Web in a study of 5 such subjects, joint pain referral patterns were mapped out. Web referral pain patterns arising from the cervical facet joints have been described using noxious stimulation of the joints in asymptomatic subjects that was subsequently validated with diagnostic blocks. Web consensus practice guidelines. Unlike the thoracic and lumbar facet joints, referral pain pattern and cobb angle rather than tenderness on the facetal area is helpful in suggesting cervical facet joint pain. • diagnostic positive facet joint block can. Match pain distribution with pain referral patterns. + response to facet interventions: (a) diagram of cervical zygapophysial joint pain distribution in volunteers. • diagnostic positive facet joint block can. Web referral pain patterns arising from the cervical facet joints have been described using noxious stimulation of the joints in asymptomatic subjects that was subsequently validated with diagnostic blocks. Web referral patterns for cervical facet joint pains, as described by various investigators [17, 19, 20]. Striped areas (hash marks) represent overlapping cervical facet. Web • facet arthrosis is the most frequent form of facet pathology. Identify tender areas under fluoroscopy. Web referral pain patterns arising from the cervical facet joints have been described using noxious stimulation of the joints in asymptomatic subjects that was subsequently validated with diagnostic blocks. Web in a study of 5 such subjects, joint pain referral patterns were mapped. + response to facet interventions: Pain usually increases with extension ('closing down' of the joint) and reduces with flexion ('opening' of the joint). (a) diagram of cervical zygapophysial joint pain distribution in volunteers. Striped areas (hash marks) represent overlapping cervical facet joint pain maps. Unlike the thoracic and lumbar facet joints, referral pain pattern and cobb angle rather than tenderness on the facetal area is helpful in suggesting cervical facet joint pain. (b) main referred pain distributions for the zygapophysial joints from c0/c1 to c7/t1 and the dorsal rami c3 to c7. Web cervical facet syndrome, also known as cervical facet joint pain, is a condition that occurs when the facet joints in the cervical spine become inflamed or damaged. The facet joints are small joints located between the neck vertebrae, which help to provide stability and facilitate movement. Web referral patterns for cervical facet joint pains, as described by various investigators [17, 19, 20]. Web consensus practice guidelines on interventions for cervical spine (facet) joint pain from a multispecialty international working group. Identify tender areas under fluoroscopy. • diagnostic positive facet joint block can. Web guide diagnostic block segments: Web • facet arthrosis is the most frequent form of facet pathology. Match pain distribution with pain referral patterns. Web referral pain patterns arising from the cervical facet joints have been described using noxious stimulation of the joints in asymptomatic subjects that was subsequently validated with diagnostic blocks.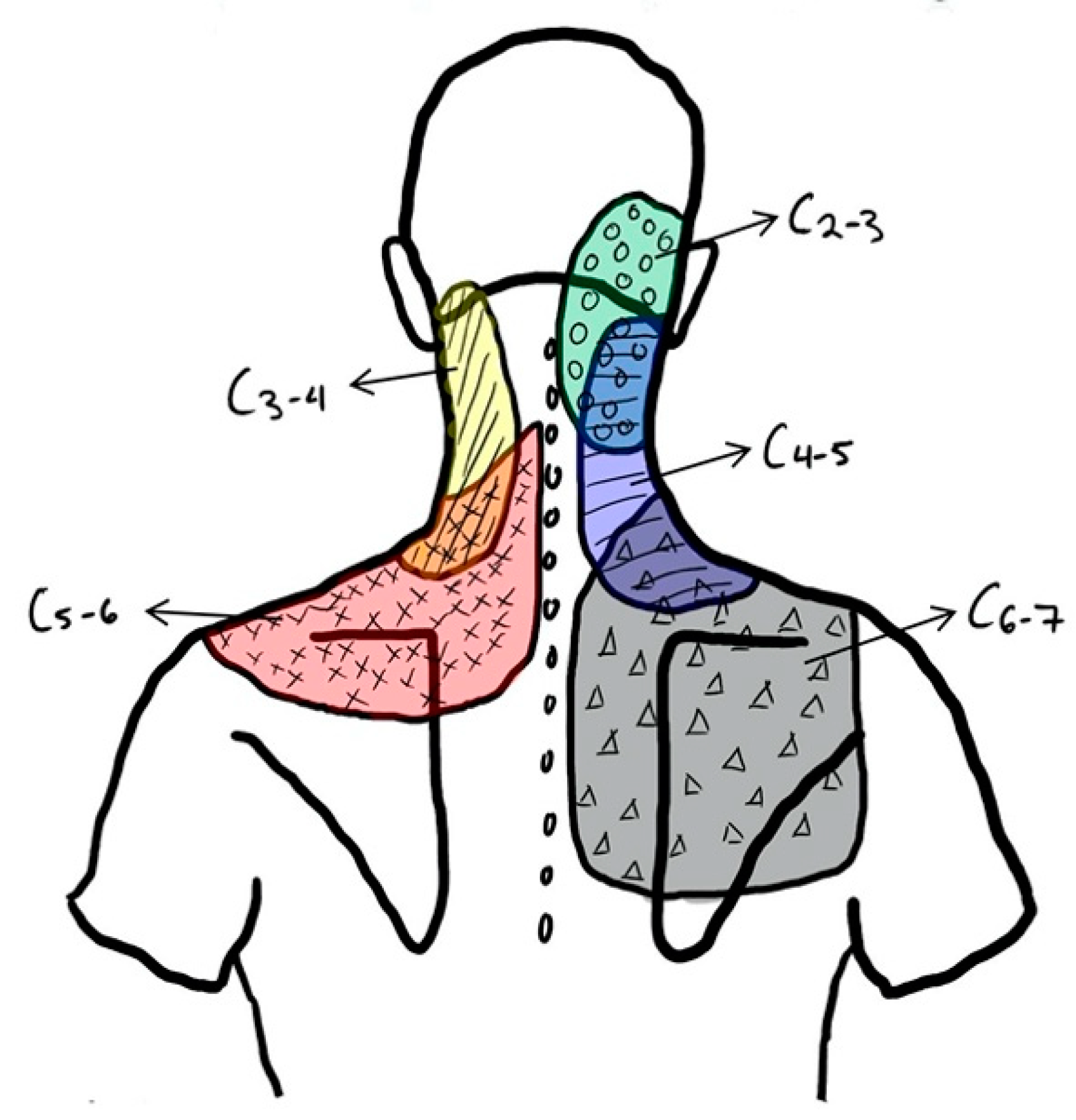
IJERPH Free FullText Medial Branch Blocks for Diagnosis of Facet
Cloward sign & Cervical Referral Patterns Modern Manual Therapy Blog
Consensus practice guidelines on interventions for cervical spine

Facet Joint Pain
Cervical Facet Joint Referral Patterns Diagram Quizlet
Neck pain treatment Manor Chiropractic

Ultrasoundguided scapulothoracic bursa injection Download Scientific

Cervical Facet Referral Patterns Bead Pattern (Free)

Illustration of distribution pattern related to facet joint pain

Evidence based pain referral patterns Download Scientific Diagram
• There Are No Effective Correlations Between Clinical Symptoms, Physical Examination And Degenerative Spinal Changes.
Predict Success Of Cervical Mbb Or Rfa.
Web The Pain Is Usually Unilateral And Radiates In A Facet Joint Referral Pattern.
The Most Commonly Affected Cervical Spine Levels Are C5, C6 And C7.
Related Post: