Burst Suppression Pattern
Burst Suppression Pattern - The percent of the record/epoch that is attenuated or suppressed (fig. Web eeg findings consistently associated with a poor outcome when seen 24 hours after an arrest are isoelectric eeg, low voltage eeg, and burst suppression (specifically burst suppression with identical bursts), as well as the absence of eeg reactivity. The bursts may be sharp waves, spikes, or slow waves. This can range from 1% to 99%. If <1%, it is considered continuous. Titrating to a desired pattern is difficult, and eegs may change with stable infusions. Web its pattern is easily recognizable—a burst, a suppression of activity, and a repeat. The pattern is found in patients with inactivated brain states, such as from general anesthesia, coma, or hypothermia. Attenuation percent or suppression percent: Web a particularly ominous background is the “burst suppression” background, which (as the name suggests) describes an eeg that alternates between periods of complete suppression interspersed with “bursts” of eeg activity. Web burst suppression is a pattern of brain activity where the electroencephalogram (eeg) is intermittently interrupted by “suppressions,” i.e., periods of reduced voltage (fig. Web burst suppression pattern: Attenuation percent or suppression percent: Web burst suppression is a pattern of brain activity where the electroencephalogram (eeg) is intermittently interrupted by “suppressions,” i.e., periods of reduced voltage (figure 1). The latter. The pattern is found in patients with inactivated brain states, such as from general anesthesia, coma, or hypothermia. Web burst suppression is a pattern of brain activity where the electroencephalogram (eeg) is intermittently interrupted by “suppressions,” i.e., periods of reduced voltage (fig. 5 isoelectric eeg and low voltage eeg are patterns well known to neurologists and have long. Web its. It is characteristic of an inactivated brain and is commonly observ. Web burst suppression is a pattern of brain activity where the electroencephalogram (eeg) is intermittently interrupted by “suppressions,” i.e., periods of reduced voltage (fig. Web burst suppression is a pattern of brain activity where the electroencephalogram (eeg) is intermittently interrupted by “suppressions,” i.e., periods of reduced voltage (figure 1).. Titrating to a desired pattern is difficult, and eegs may change with stable infusions. Burst suppression is characterized by brief bursts of electrographic activity. Often bursts disappear, fully suppressing the eeg. The bursts may be sharp waves, spikes, or slow waves. This can range from 1% to 99%. Often bursts disappear, fully suppressing the eeg. Web for nearly continuous, discontinuous, and burst attenuation/burst suppression patterns, specify: The pattern is found in patients with inactivated brain states, such as from general anesthesia, coma, or hypothermia. Attenuation percent or suppression percent: If <1%, it is considered continuous. Titrating to a desired pattern is difficult, and eegs may change with stable infusions. Web for nearly continuous, discontinuous, and burst attenuation/burst suppression patterns, specify: Web burst suppression is a pattern of brain activity where the electroencephalogram (eeg) is intermittently interrupted by “suppressions,” i.e., periods of reduced voltage (fig. The pattern is found in patients with inactivated brain states, such. Burst suppression is characterized by brief bursts of electrographic activity. The bursts are seen intermittently in a background of isoelectric eeg. The latter are the result of cortical hyperexcitability, as demonstrated by intracellular recordings in. Web eeg findings consistently associated with a poor outcome when seen 24 hours after an arrest are isoelectric eeg, low voltage eeg, and burst suppression. The percent of the record/epoch that is attenuated or suppressed (fig. 5 isoelectric eeg and low voltage eeg are patterns well known to neurologists and have long. Often bursts disappear, fully suppressing the eeg. If <1%, it is considered continuous. Burst suppression is characterized by brief bursts of electrographic activity. If <1%, it is considered continuous. Titrating to a desired pattern is difficult, and eegs may change with stable infusions. The latter are the result of cortical hyperexcitability, as demonstrated by intracellular recordings in. Burst suppression is characterized by brief bursts of electrographic activity. Web its pattern is easily recognizable—a burst, a suppression of activity, and a repeat. This can range from 1% to 99%. Web its pattern is easily recognizable—a burst, a suppression of activity, and a repeat. Web for nearly continuous, discontinuous, and burst attenuation/burst suppression patterns, specify: Web a particularly ominous background is the “burst suppression” background, which (as the name suggests) describes an eeg that alternates between periods of complete suppression interspersed with “bursts”. This can range from 1% to 99%. If <1%, it is considered continuous. The pattern is found in patients with inactivated brain states, such as from general anesthesia, coma, or hypothermia. Attenuation percent or suppression percent: Web its pattern is easily recognizable—a burst, a suppression of activity, and a repeat. Web burst suppression pattern: The percent of the record/epoch that is attenuated or suppressed (fig. Web burst suppression is a pattern of brain activity where the electroencephalogram (eeg) is intermittently interrupted by “suppressions,” i.e., periods of reduced voltage (figure 1). 5 isoelectric eeg and low voltage eeg are patterns well known to neurologists and have long. Web burst suppression is a pattern of brain activity where the electroencephalogram (eeg) is intermittently interrupted by “suppressions,” i.e., periods of reduced voltage (fig. It is characteristic of an inactivated brain and is commonly observ. Web a particularly ominous background is the “burst suppression” background, which (as the name suggests) describes an eeg that alternates between periods of complete suppression interspersed with “bursts” of eeg activity. Titrating to a desired pattern is difficult, and eegs may change with stable infusions. Web eeg findings consistently associated with a poor outcome when seen 24 hours after an arrest are isoelectric eeg, low voltage eeg, and burst suppression (specifically burst suppression with identical bursts), as well as the absence of eeg reactivity. The bursts are seen intermittently in a background of isoelectric eeg. The latter are the result of cortical hyperexcitability, as demonstrated by intracellular recordings in.
(A) The synchronous and asymmetric burst suppression pattern in a

Electroencephalogram patterns in critical care A primer for acute care

EEG pattern of burst suppression. Download Scientific Diagram
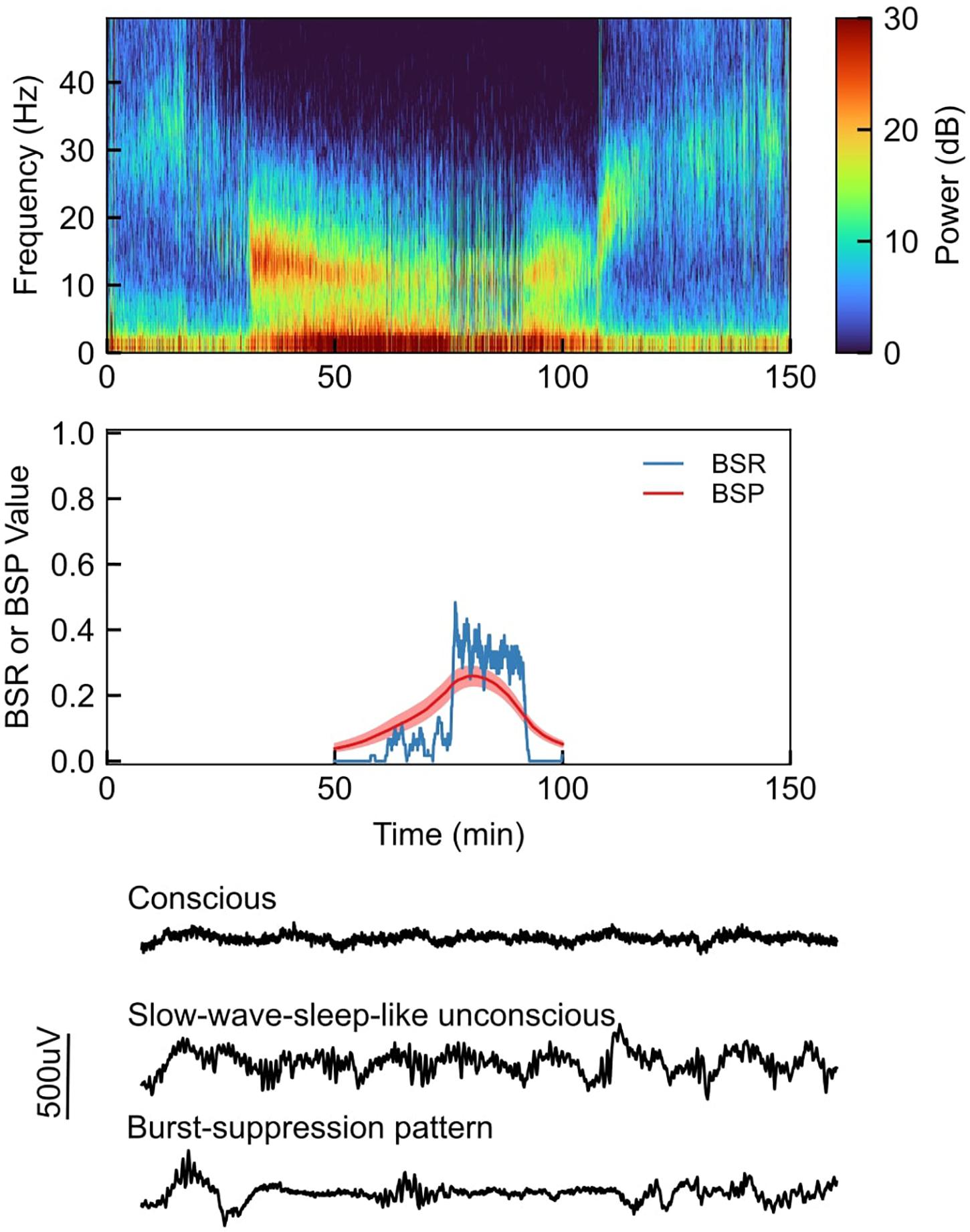
Frontiers Etiology of Burst Suppression EEG Patterns

burst suppression

Burst Suppression Pattern Video YouTube

QEEG and raw EEG of a burst suppression pattern. a The qEEG panels show

Figure 59. [Burstsuppression coma pattern following anoxicischemic

Figure 1 from The BurstSuppression Electroencephalogram Semantic Scholar

burst suppression
Often Bursts Disappear, Fully Suppressing The Eeg.
Web For Nearly Continuous, Discontinuous, And Burst Attenuation/Burst Suppression Patterns, Specify:
Burst Suppression Is Characterized By Brief Bursts Of Electrographic Activity.
The Bursts May Be Sharp Waves, Spikes, Or Slow Waves.
Related Post: