Bronchial Pattern Cat
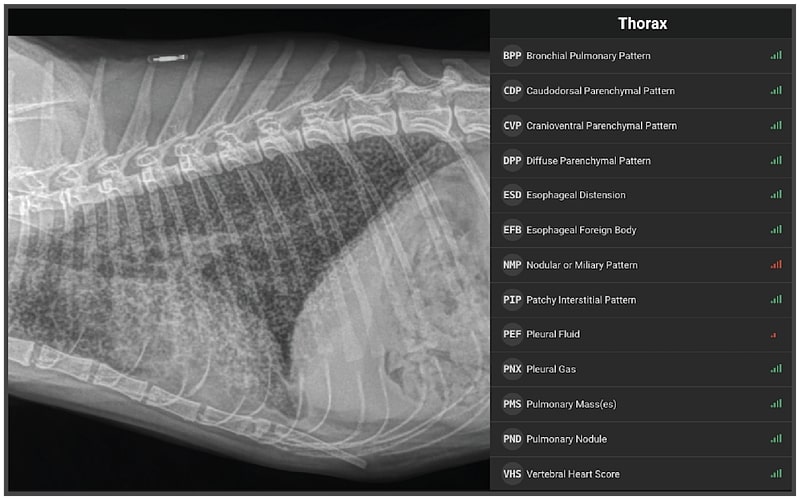
Bronchial Pattern Cat - Web feline bronchial asthma (allergic bronchitis) is a syndrome in cats with similarities to asthma in people. Web a bronchial pattern is most common; Symptoms of bronchitis in cats. Young cats and siamese and himalayan breeds are most affected. Bronchial pattern is caused by thickening and increased prominence of the bronchial walls, usually secondary to chronic inflammation. Web bronchitis in cats is a term that refers broadly to the inflammation of the bronchial tubes in your cat’s respiratory system. Feline asthma is associated with airway hyperresponsiveness, airflow obstruction, airway remodeling, and eosinophilic airway inflammation. Web mineralization of the bronchial skeleton and the lung parenchyma is often seen in the aging dog but rarely in the cat. Additionally, air trapping in cats with asthma may result in pulmonary hyperinflation and a flattened diaphragm. Web bronchial to bronchointerstitial pattern (figure 1): Feline asthma is associated with airway hyperresponsiveness, airflow obstruction, airway remodeling, and eosinophilic airway inflammation. R eluctance among dairy farmers to report h5n1 bird flu outbreaks within their herds or allow testing of their workers has made. Web feline bronchitis describes a group of common inflammatory airway diseases of cats that include feline asthma. Lower airway disease is classically associated. It is discussed later in this chapter as part of tracheobronchitis. When a cat breathes air in through its nose or mouth, the air travels down the trachea , which divides into the tubes known as the right and left bronchi , then into the smaller airways called bronchioles in the lungs. R eluctance among dairy farmers to report h5n1. Web bronchial to bronchointerstitial pattern (figure 1): Air trapping may also be evident (increased lucency and flattening of the diaphragm); Bronchial pattern is caused by thickening and increased prominence of the bronchial walls, usually secondary to chronic inflammation. This pattern comes closest to helping shed light on what disease the pet is suffering from. Web results of the present study. It is more likely to occur in cats already affected by respiratory disease or a disorder of the lungs or airways. The walls are thickened due to a combination of smooth muscle hypertrophy, mucus production, cellular infiltrate, and in come cases (feline asthma), bronchoconstriction. An interstitial pattern reflects increased opacity of the pulmonary interstitium. As well as sometimes right middle. Web a bronchial pattern is most common; In cats, only donuts are recognizable, as the bronchi are generally too small to create visible tram lines. With increasing disease severity or chronicity, atelectasis of the right middle lung lobe or left cranial lobe (caudal segment) and generalized lung overinflation. Web bronchitis in cats is a term that refers broadly to the. It may also extend into the lungs. Web b) bronchial patterns: 6,8 occasionally, pulmonary abscesses may be appreciated and resemble pulmonary neoplasia (figure 4). Web a bronchial pattern is diffuse thickening of the airway walls giving the appearance of thick lines and rings throughout the lungs. Symptoms of bronchitis in cats. Air trapping may also be evident (increased lucency and flattening of the diaphragm); Web a bronchial pattern is most common; Additionally, air trapping in cats with asthma may result in pulmonary hyperinflation and a flattened diaphragm. A bronchial pattern is characterized by “doughnuts” and “tramlines”; When a cat breathes air in through its nose or mouth, the air travels down. A bronchial pattern is characterized by “doughnuts” and “tramlines”; Web b) bronchial patterns: Kuehn, dvm, ms, dacvim, michigan veterinary specialists. This syndrome may also be referred to as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd). Web aspiration pneumonia (ap) and bronchopneumonia (bp) are poorly characterized diseases in cats that share clinical similarities to inflammatory airway disease (iad). Describe clinicopathologic, radiographic, and microbiologic features in cats with ap and bp and compare findings to those in cats with iad. Feline asthma is associated with airway hyperresponsiveness, airflow obstruction, airway remodeling, and eosinophilic airway inflammation. A well structured interstitial fishbone appearance of the lungs can be interpreted as mild fibrosis of the lungs in old cats. It may also. R eluctance among dairy farmers to report h5n1 bird flu outbreaks within their herds or allow testing of their workers has made. An interstitial pattern reflects increased opacity of the pulmonary interstitium. A well structured interstitial fishbone appearance of the lungs can be interpreted as mild fibrosis of the lungs in old cats. With increasing disease severity or chronicity, atelectasis. The inflammation of the bronchi causes the walls of the airways to become thickened and swollen, along with excessive mucus production, with secretions gathering in the airways. Bronchitis can have many underlying causes, including allergy. The walls are thickened due to a combination of smooth muscle hypertrophy, mucus production, cellular infiltrate, and in come cases (feline asthma), bronchoconstriction. Their airways are very small, so look in the periphery for donuts and especially on the v/d or d/v projection where they show up better. Symptoms of bronchitis in cats. Web bronchitis in cats is a term that refers broadly to the inflammation of the bronchial tubes in your cat’s respiratory system. Web feline bronchial asthma (allergic bronchitis) is a syndrome in cats with similarities to asthma in people. Web aspiration pneumonia (ap) and bronchopneumonia (bp) are poorly characterized diseases in cats that share clinical similarities to inflammatory airway disease (iad). Web the term feline bronchitis describes the coughing and/or wheezing that comes from inflammation in the lower airway. Web feline bronchial asthma (allergic bronchitis) is a syndrome in cats with similarities to asthma in people. Web the bronchial pattern is most common in cats with chronic lower airway disease. Describe clinicopathologic, radiographic, and microbiologic features in cats with ap and bp and compare findings to those in cats with iad. Bronchial pattern is caused by thickening and increased prominence of the bronchial walls, usually secondary to chronic inflammation. In cats, only donuts are recognizable, as the bronchi are generally too small to create visible tram lines. Web • radiographic changes in asthmatic cats often include a prominent bronchial pattern (tram lines and donuts) or a mixed pattern of bronchial, alveolar, or interstitial changes. This syndrome may also be referred to as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd).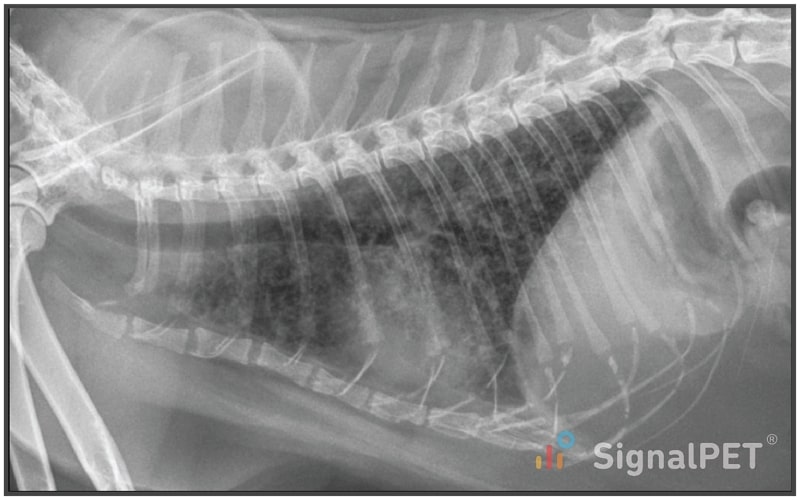
Radiology Case of the Week Feline Miliary Pulmonary Pattern

Perspectives in veterinary medicine Description and classification of

Lung; cat No. 1. Diffuse, severe bronchointerstitial pattern
Radiology Case of the Week Feline Miliary Pulmonary Pattern

Common Pulmonary Diseases in Cats Clinician's Brief

Plain lateral thoracic radiograph of the cat showing a mild bronchial

CT findings in two cats with broncholithiasis Patrick Byrne, James S

Figure 3 from Radiographic abnormalities in cats with feline bronchial
Right lateral radiograph of a sixmonthold cat infected with

Feline Asthma Clinician's Brief
A Bronchial Pattern Is Characterized By “Doughnuts” And “Tramlines”;
Air Trapping May Also Be Evident (Increased Lucency And Flattening Of The Diaphragm);
Kuehn, Dvm, Ms, Dacvim, Michigan Veterinary Specialists.
It Is More Likely To Occur In Cats Already Affected By Respiratory Disease Or A Disorder Of The Lungs Or Airways.
Related Post: