Auxiliary View In Engineering Drawing
Auxiliary View In Engineering Drawing - It is a view looking directly at the inclined surface in a direction. Show the true size of. Web to project an auxiliary top view on aip, draw projections from a 1’ and b 1’ perpendicular to x 1y 1 line, and on them step off 1a 1=3a and 2b 1=4b from the x 1y 1 line. 32k views 1 year ago engineering drawing. This video is mainly about auxiliary view. It is typically used in technical drawings and. This exercise takes you through the steps required to construct an. Web create auxiliary section views. An auxiliary view is an orthographic view on a plane that is not one of the principal planes of projection. You can think of an auxiliary view as a specialty view that is sometimes. After studying the material in this chapter, you should be able to: Create an auxiliary view from orthographic views. Web an auxiliary view is used to show the true size and shape of an inclined or oblique surface that can not be otherwise seen from any of the six principal views discussed in the previous chapter. It is a view. Recall that in a multiview drawing of an object with an inclined surface, in one multiview the inclined surface is seen on edge, whereas in the. Construct depth, height, or width auxiliary views. 32k views 1 year ago engineering drawing. Web to project an auxiliary top view on aip, draw projections from a 1’ and b 1’ perpendicular to x. Orthographic projection, axonometric projection, sectional. It is a view looking directly at the inclined surface in a direction. This exercise takes you through the steps required to construct an. Web draw primary auxiliary views representing the true shapes of surfaces that are perpendicular to one of the reference planes and inclined to the other two. Recall that in a multiview. The horizontal lines (parallel lines) are drawn with a 30°. Orthographic projection, axonometric projection, sectional. An auxiliary view is similar to a projected view, but it is unfolded normal to a reference. Show the true size of. Curves in auxiliary views are also presented. Web to sketch an auxiliary view, you begin with orthographic. It is typically used in technical drawings and. After studying the material in this chapter, you should be able to: An auxiliary view is an orthographic view on a plane that is not one of the principal planes of projection. Construct depth, height, or width auxiliary views. Show the true size of. Recall that in a multiview drawing of an object with an inclined surface, in one multiview the inclined surface is seen on edge, whereas in the. An auxiliary view is similar to a projected view, but it is unfolded normal to a reference. Web an auxiliary view is an orthographic view that is projected into. This video is mainly about auxiliary view. Web an auxiliary view is a projection on an auxiliary plane that is parallel to an inclined (slanting) surface. It is typically used in technical drawings and. • any view obtained by a. After studying the material in this chapter, you should be able to: Web an auxiliary view is a 2d representation of a 3d object that provides additional information about the object's shape and features. Web an auxiliary view is a projection on an auxiliary plane that is parallel to an inclined (slanting) surface. Plot curves in auxiliary views. After studying the material in this chapter, you should be able to: Recall that. Web we will now discuss various types of engineering drawings or cad drawing views including: Web to project an auxiliary top view on aip, draw projections from a 1’ and b 1’ perpendicular to x 1y 1 line, and on them step off 1a 1=3a and 2b 1=4b from the x 1y 1 line. Views of the object and add. Web we will now discuss various types of engineering drawings or cad drawing views including: An auxiliary view is an orthographic view on a plane that is not one of the principal planes of projection. Recall that in a multiview drawing of an object with an inclined surface, in one multiview the inclined surface is seen on edge, whereas in. Views of the object and add projection lines perpendicular (90 ) to the slanted surface, adding a reference. The horizontal lines (parallel lines) are drawn with a 30°. Web we will now discuss various types of engineering drawings or cad drawing views including: Plot curves in auxiliary views. It is a view looking directly at the inclined surface in a direction. This video is mainly about auxiliary view. Web an auxiliary view is a projection on an auxiliary plane that is parallel to an inclined (slanting) surface. These views are typically used when an object contains. An auxiliary view is similar to a projected view, but it is unfolded normal to a reference. Recall that in a multiview drawing of an object with an inclined surface, in one multiview the inclined surface is seen on edge, whereas in the. Web to project an auxiliary top view on aip, draw projections from a 1’ and b 1’ perpendicular to x 1y 1 line, and on them step off 1a 1=3a and 2b 1=4b from the x 1y 1 line. Create an auxiliary view from orthographic views. Construct depth, height, or width auxiliary views. After studying the material in this chapter, you should be able to: You can think of an auxiliary view as a specialty view that is sometimes. An auxiliary view is an orthographic view on a plane that is not one of the principal planes of projection.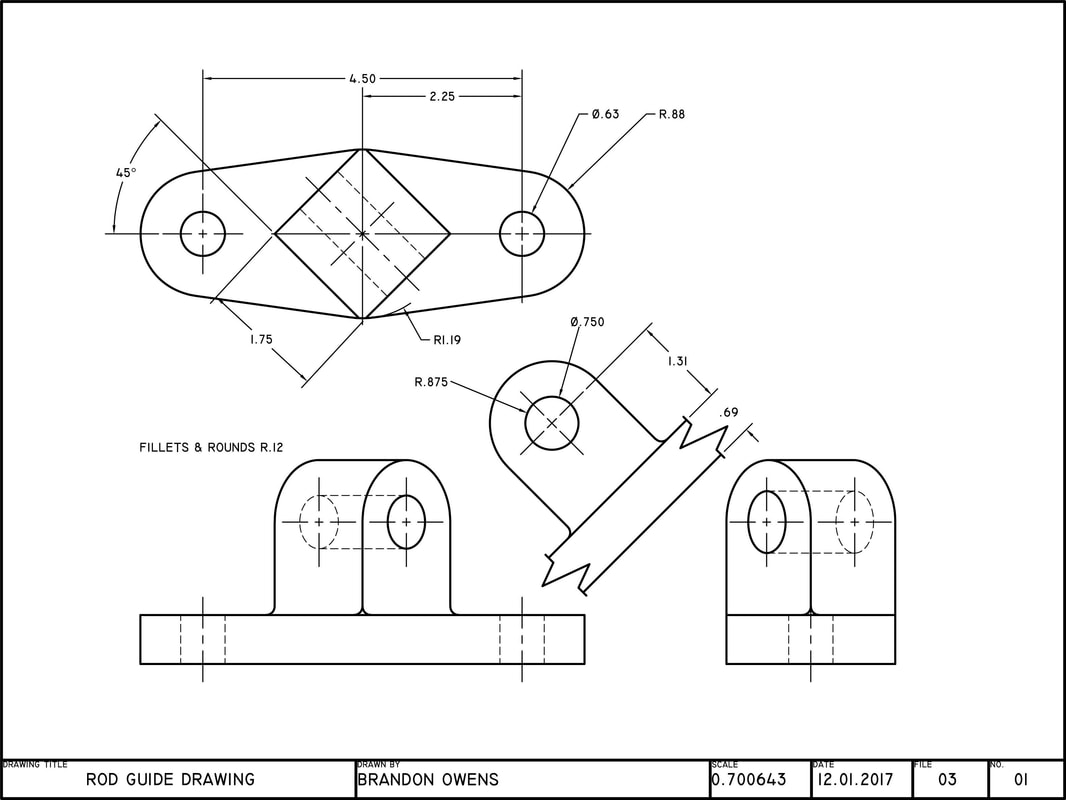
AUXILIARY DRAWINGS BRANDON OWENS' PORTFOLIO
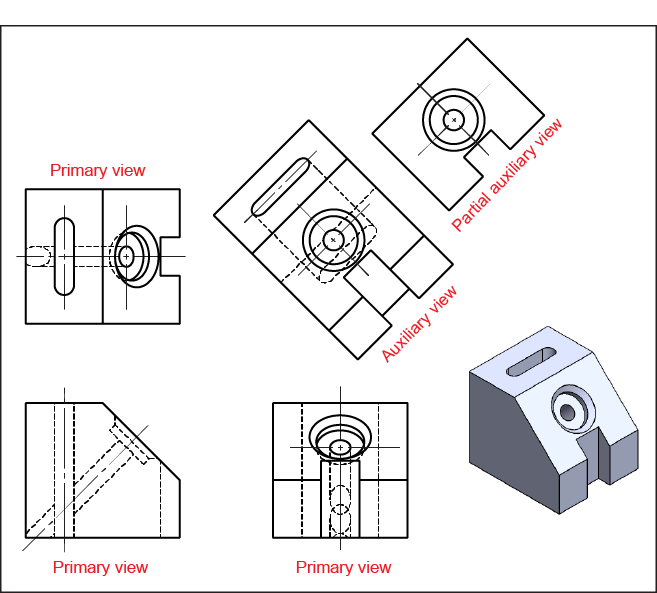
Introduction to Engineering Drawings
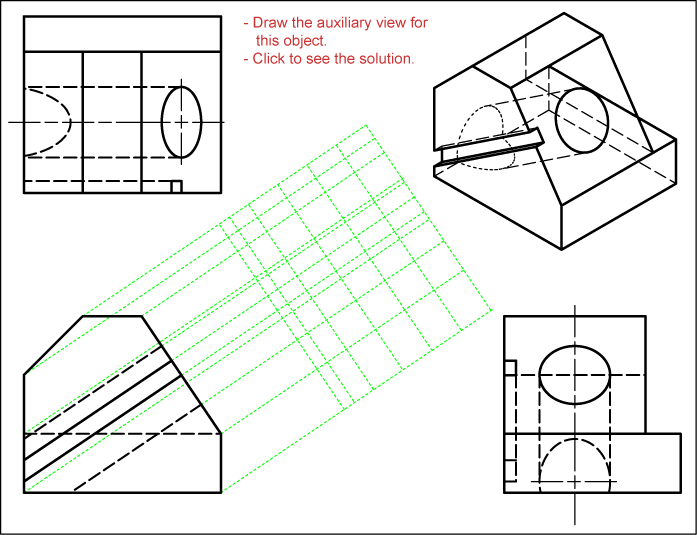
How To Draw An Auxiliary View Sockthanks29

Drawing Auxiliary view Engineering Design YouTube

Drawing 04_01 Primary Auxiliary View YouTube

AUXILIARY VIEW IN ENGINEERING DRAWING YouTube
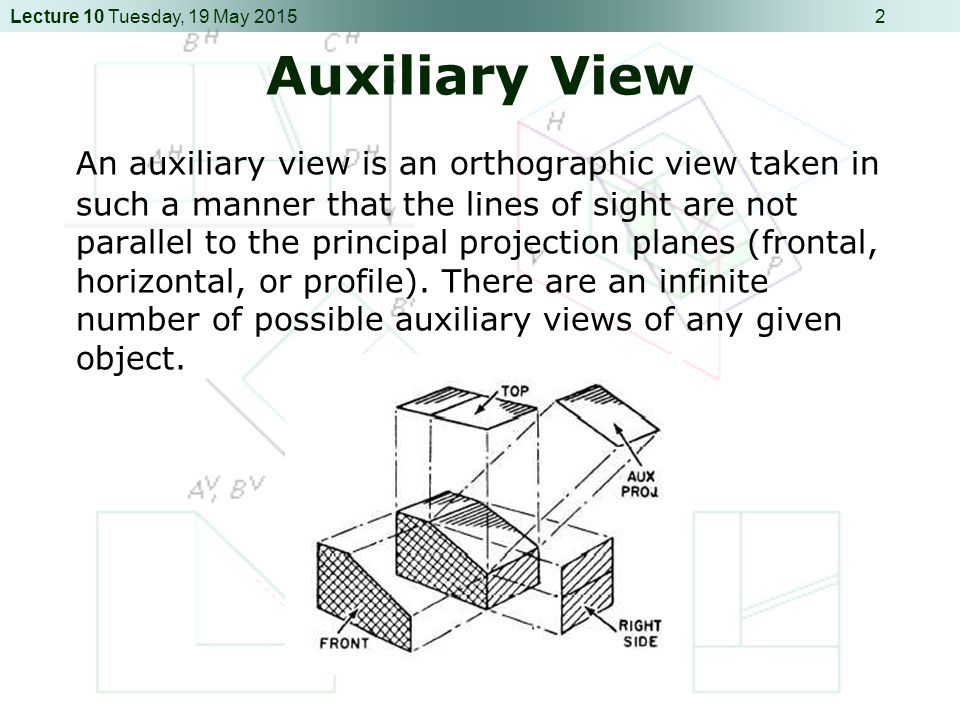
Auxiliary Views FREEMAN'S TECH ED SITE
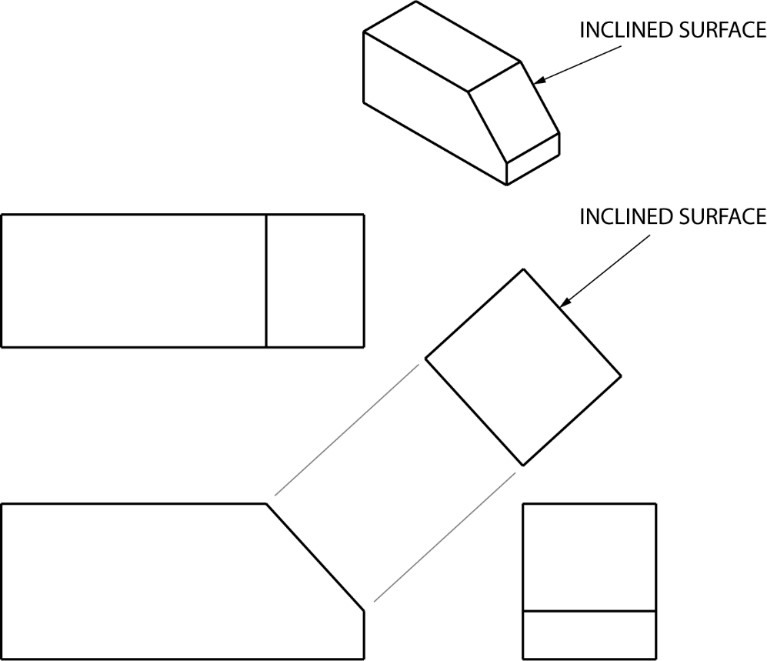
Auxiliary Views Basic Blueprint Reading

Auxiliary view in engineering drawing YouTube

Auxiliary Views//Engineering Drawing //Engineering Graphics YouTube
Web Create Auxiliary Section Views.
Orthographic Projection, Axonometric Projection, Sectional.
Web Draw Primary Auxiliary Views Representing The True Shapes Of Surfaces That Are Perpendicular To One Of The Reference Planes And Inclined To The Other Two.
Web An Auxiliary View Is Used To Show The True Size And Shape Of An Inclined Or Oblique Surface That Can Not Be Otherwise Seen From Any Of The Six Principal Views Discussed In The Previous Chapter.
Related Post: