Atrophic Pattern Predominantly Parabasal Cells
Atrophic Pattern Predominantly Parabasal Cells - Hsil can also arise in a background of atrophy (fig. Web the occurrence of vaginal atrophy during menopause is associated with declining estrogen levels that cause structural and functional changes in vaginal tissue, including atrophy of vaginal. Web a pap smear is used to screen for cervical cancer. The condition also includes urinary tract problems such as urinary tract infections (utis) and urinary incontinence. Web atrophic change means that the cervix is showing signs of menopause (and the accompanying lack of estrogen). Get the best care from a doctor who knows you. Cells have high n/c ratio but uniform chromatin. External genitalia should be examined for. The health care professional first places a speculum inside the vagina. While evaluating the cytomorphologic features of a pap smear from the cervix or vagina, it is important to know the normal cytomorphology, benign reactive conditions, and epithelial changes due to. Naked nuclei (small cells) may be seen. In women older than age 30, the pap test may be combined with a test for human papillomavirus (hpv) — a common sexually transmitted infection that can cause cervical cancer. Vaginal atrophy occurs most often after menopause. Vaginal atrophy in menopause shows increased parabasal cells on cytology. Web so basically, most women will. Web a pap smear is used to screen for cervical cancer. Depending on the level of estrogen deficiency, superficial and intermediate cells may be seen or can be virtually absent in severely atrophic smears. The existence of precursor lesions for invasive cervical cancer has been recognized for more than 50 years. While evaluating the cytomorphologic features of a pap smear. Vaginal atrophy occurs most often after menopause. How is a pap test done? Web furthermore, recognizing the parabasal cells in the menopausal smears, either singly or as syncytial aggregates, is important to avoid overdiagnosis of squamous intraepithelial lesions. The pap smear is usually done in conjunction with a pelvic exam. This results in itching, burning and pain during sex, among. Abundant neutrophils (>100 per ×400 field) are also significantly correlated ( p =.01). The pap smear is usually done in conjunction with a pelvic exam. Pseudokeratinized cells (pink to orangophilic cytoplasm) are due to degeneration. Web atrophic pattern histologic findings demonstrate decreased superficial squamous cells, increased parabasal cells, decreased lactobacilli. Naked nuclei (small cells) may be seen. Atrophic pattern predominantly parabasal cells. External genitalia should be examined for. Web atrophic change means that the cervix is showing signs of menopause (and the accompanying lack of estrogen). Web the occurrence of vaginal atrophy during menopause is associated with declining estrogen levels that cause structural and functional changes in vaginal tissue, including atrophy of vaginal. Web pap test is. Vaginal atrophy (atrophic vaginitis) is thinning, drying and inflammation of the vaginal walls that may occur when your body has less estrogen. Our understanding of the pathobiology and behavior of cervical cancer precursors has evolved considerably over the past five decades. Get the best care from a doctor who knows you. In women older than age 30, the pap test. The existence of precursor lesions for invasive cervical cancer has been recognized for more than 50 years. Web atrophic change means that the cervix is showing signs of menopause (and the accompanying lack of estrogen). Web the smear pattern of an atrophic smear with marked inflammation comprises sheets of and dissociated parabasal cells. Web atrophic pattern histologic findings demonstrate decreased. 1) the result of the pap test itself; Often, inflammation with patchy erythema, petechiae and increased friability may be present. Cells have high n/c ratio but uniform chromatin. This results in itching, burning and pain during sex, among other symptoms. Loss of fragile cytoplasm of the thin atrophic and relatively dry epithelium leads to plenty bare nuclei throughout the smear. The pap smear is usually done in conjunction with a pelvic exam. Abundant neutrophils (>100 per ×400 field) are also significantly correlated ( p =.01). Pseudokeratinized cells (pink to orangophilic cytoplasm) are due to degeneration. Cells have high n/c ratio but uniform chromatin. Web atrophic pattern histologic findings demonstrate decreased superficial squamous cells, increased parabasal cells, decreased lactobacilli. External genitalia should be examined for. In atrophic smears, parabasal and some basal cells are the characteristic cell types. Here the pathologist noted cells that were growing or repairing themselves, which is a normal. Web atrophic pattern histologic findings demonstrate decreased superficial squamous cells, increased parabasal cells, decreased lactobacilli. Pseudokeratinized cells (pink to orangophilic cytoplasm) are due to degeneration. Web atrophic epithelium appears pale, smooth and shiny. Abundant neutrophils (>100 per ×400 field) are also significantly correlated ( p =.01). The hpv testing makes the recommendation we give you about how to follow up on your pap result more accurate. Hsil can also arise in a background of atrophy (fig. 1) the result of the pap test itself; This results in itching, burning and pain during sex, among other symptoms. The health care professional first places a speculum inside the vagina. Conclusions.—exact concordance to atrophic vaginitis is less than 90%. Web the occurrence of vaginal atrophy during menopause is associated with declining estrogen levels that cause structural and functional changes in vaginal tissue, including atrophy of vaginal. Web furthermore, recognizing the parabasal cells in the menopausal smears, either singly or as syncytial aggregates, is important to avoid overdiagnosis of squamous intraepithelial lesions. While evaluating the cytomorphologic features of a pap smear from the cervix or vagina, it is important to know the normal cytomorphology, benign reactive conditions, and epithelial changes due to. Depending on the level of estrogen deficiency, superficial and intermediate cells may be seen or can be virtually absent in severely atrophic smears. Web a pap test is a procedure used to collect cells from the cervix (lower part of the uterus) so they can be looked at closely in a lab under a microscope. Web pap test is an important screening test for cervical cancer. Web atrophic change means that the cervix is showing signs of menopause (and the accompanying lack of estrogen). The condition also includes urinary tract problems such as urinary tract infections (utis) and urinary incontinence.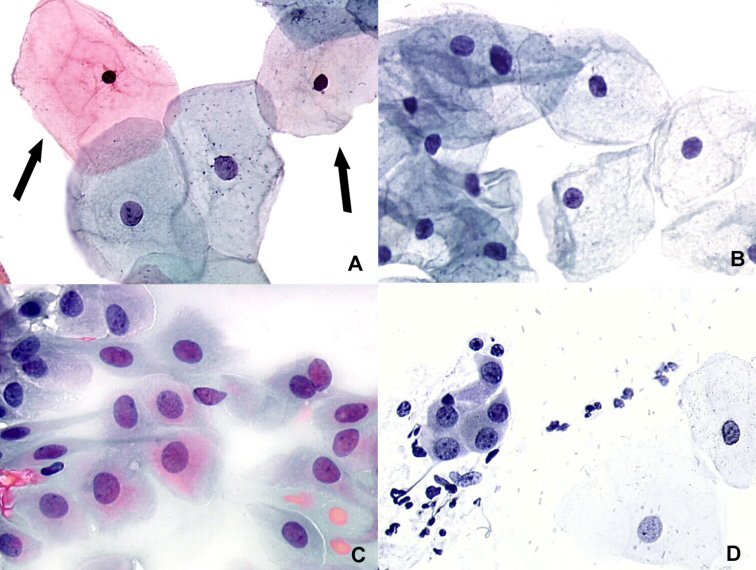
Pathology Outlines Parabasal cells

Parabasal cells in pap smear with postpartum Ad , ad, cells

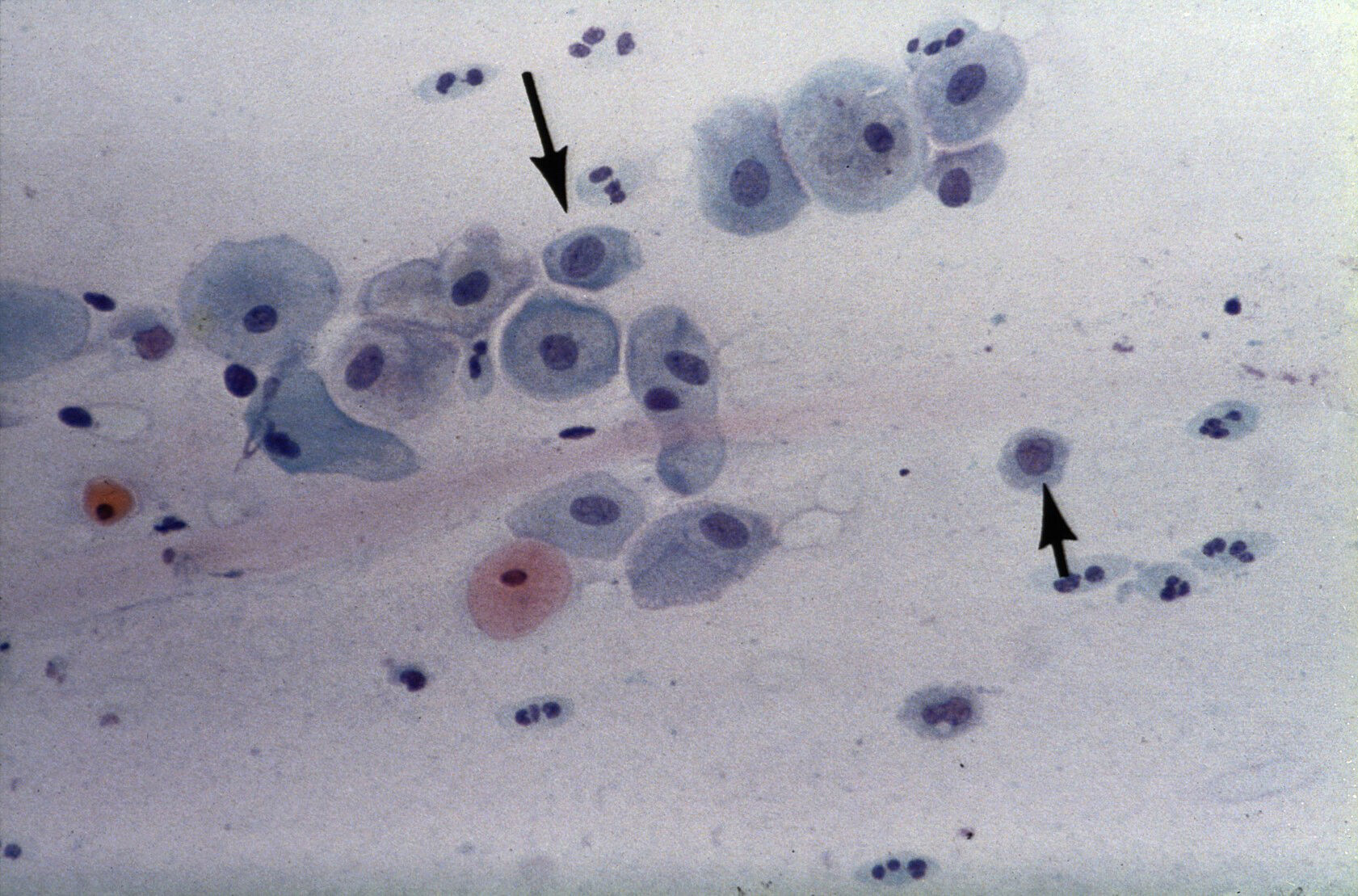
− Atrophy associated with inflammation A) parabasal squamous epithelial
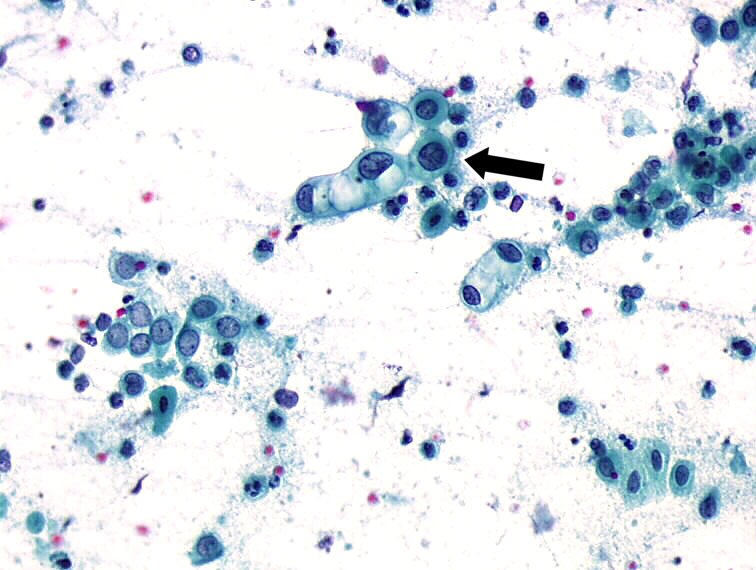
Cytopathology of the uterine cervix digital atlas

− Atrophy associated with inflammation A) parabasal squamous epithelial

− Atrophy associated with inflammation A) parabasal squamous epithelial
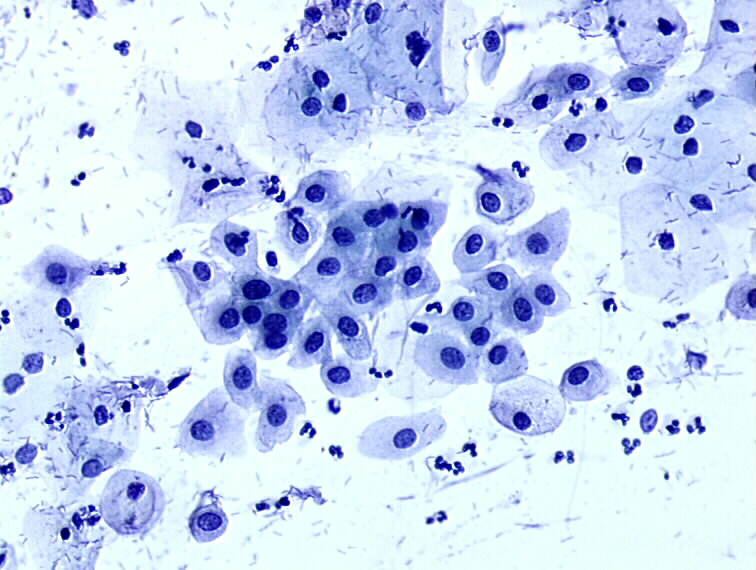
Cytopathology of the uterine cervix digital atlas
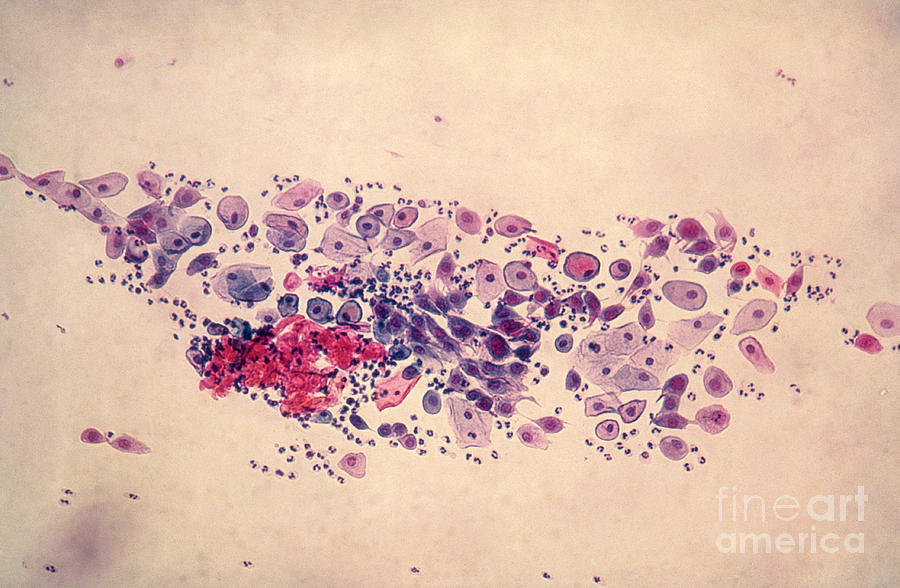
Pap Smear, Parabasal Cells Photograph by Science Source
Parabasal cells Collection

Histopathology and cytopathology of the uterine cervix digital atlas
Web So Basically, Most Women Will Get Two Pieces Of Information:
Web The Smear Pattern Of An Atrophic Smear With Marked Inflammation Comprises Sheets Of And Dissociated Parabasal Cells.
However, There Are Normal To Low Numbers Of Neutrophils.
When To See A Doctor.
Related Post: