Astrocytes Drawing
Astrocytes Drawing - Web astrocytes form a large network of glial cells that communicate with each other via gap junctions, ensuring coordinated execution of their activities across various regions of the cns. Web open access article. Web astrocytes are the most abundant cell type in the brain and are a crucial part of solving its mysteries. Astrocytes participate in all essential cns functions, including blood flow regulation, energy metabolism, ion and water homeostasis, immune defence, neurotransmission, and adult neurogenesis. Web astrocytes are complex cells morphologically, consisting of soma and processes, which form intricate branching processes. Astrocytes, like other glial subtypes, have been commonly thought of as mere support and maintenance cells. Web like neurons, astrocytes originate from radial glial cells, which, despite their uniform appearance, form different progenitor domains within the ventricles of the developing brain, and generate cell subtypes with distinct morphological, functional and positional identities. Web astrocytes provide structural and metabolic support of neuronal tissue, but may also be involved in shaping synaptic output. Web astrocytes, often called star cells, are the workhorses of the central nervous system. Web this important study investigated how astrocytes modulate synaptic transmission in specific basal ganglia circuits and found that striatal astrocytes differentially regulate neuronal activity. Similarly to other neuronal cells, astrocytes are comprised of synapses, or cell ends that allow for chemical and. Web astrocytes are the most abundant cell type in the brain and are a crucial part of solving its mysteries. Originally assumed to be passive supporting cells, astrocyte's functions are now recognized to include active modulation and information processing at the neural. This rapid expansion has exposed a pressing need for unifying. It has long, thin, unbranched processes. Web astrocytes are a subtype of glial cells that make up the majority of cells in the human central nervous system (cns). Learn more about how pressbooks supports open publishing practices. Web astrocytes provide structural and metabolic support of neuronal tissue, but may also. Astrocytes perform several key functions which include: Learn more about how pressbooks supports open publishing practices. Web the drawing depicts three distinct actions of astrocytes on the function of ca1 pyramidal neurons (pns). Web astrocytes provide structural and metabolic support of neuronal tissue, but may also be involved in shaping synaptic output. It has long, thin, unbranched processes. It has long, thin, unbranched processes. Astrocytes, like other glial subtypes, have been commonly thought of as mere support and maintenance cells. Originally assumed to be passive supporting cells, astrocyte's functions are now recognized to include active modulation and information processing at the neural synapse. This rapid expansion has exposed a pressing need for unifying. Web the drawing depicts three. Astrocytes are the most abundant cell type in the brain and are a crucial part of solving its mysteries. Draw a fibrous astrocyte in the white matter; Web an irregular, stellate shape. A | heterosynaptic depression of synapses between schaffer collaterals (scs) and pns —. Web research into the roles of astrocytes in neurology and psychiatry is accelerating and drawing. Web juan gaertner/science photo library/getty images. Draw a fibrous astrocyte in the white matter; Similarly to other neuronal cells, astrocytes are comprised of synapses, or cell ends that allow for chemical and. Web astrocytes form a large network of glial cells that communicate with each other via gap junctions, ensuring coordinated execution of their activities across various regions of the. Similarly to other neuronal cells, astrocytes are comprised of synapses, or cell ends that allow for chemical and. Web this important study investigated how astrocytes modulate synaptic transmission in specific basal ganglia circuits and found that striatal astrocytes differentially regulate neuronal activity. Web astrocytes are the most abundant cell type in the brain and are a crucial part of solving. It has long, thin, unbranched processes. Web open access article. Web research into the roles of astrocytes in neurology and psychiatry is accelerating and drawing in increasing numbers of researchers. Web astrocytes provide structural and metabolic support of neuronal tissue, but may also be involved in shaping synaptic output. Web astrocytes are the most abundant cell type in the brain. Web astrocytes are complex cells morphologically, consisting of soma and processes, which form intricate branching processes. Cajal, drawing from memory, has. Web astrocytes, often called star cells, are the workhorses of the central nervous system. Astrocytes perform several key functions which include: Originally assumed to be passive supporting cells, astrocyte’s functions are now recognized to include active modulation and information. Cajal, drawing from memory, has. Web want to create or adapt books like this? A | heterosynaptic depression of synapses between schaffer collaterals (scs) and pns —. Web astrocytes, often called star cells, are the workhorses of the central nervous system. Originally assumed to be passive supporting cells, astrocyte’s functions are now recognized to include active modulation and information processing. Astrocytes are the most abundant cell type in the brain and are a crucial part of solving its mysteries. Astrocytes, like other glial subtypes, have been commonly thought of as mere support and maintenance cells. Web juan gaertner/science photo library/getty images. Cajal, drawing from memory, has. Astrocytes perform several key functions which include: Web open access article. Originally assumed to be passive supporting cells, astrocyte's functions are now recognized to include active modulation and information processing at the neural synapse. Web this video describes the structure and function of astrocytes. Web astrocytes are the most abundant cell type in the brain and are a crucial part of solving its mysteries. Web like neurons, astrocytes originate from radial glial cells, which, despite their uniform appearance, form different progenitor domains within the ventricles of the developing brain, and generate cell subtypes with distinct morphological, functional and positional identities. By matt jensen.watch the next lesson: Draw a fibrous astrocyte in the white matter; Web the drawing depicts three distinct actions of astrocytes on the function of ca1 pyramidal neurons (pns). Similarly to other neuronal cells, astrocytes are comprised of synapses, or cell ends that allow for chemical and. Web an irregular, stellate shape. Web astrocytes provide structural and metabolic support of neuronal tissue, but may also be involved in shaping synaptic output.
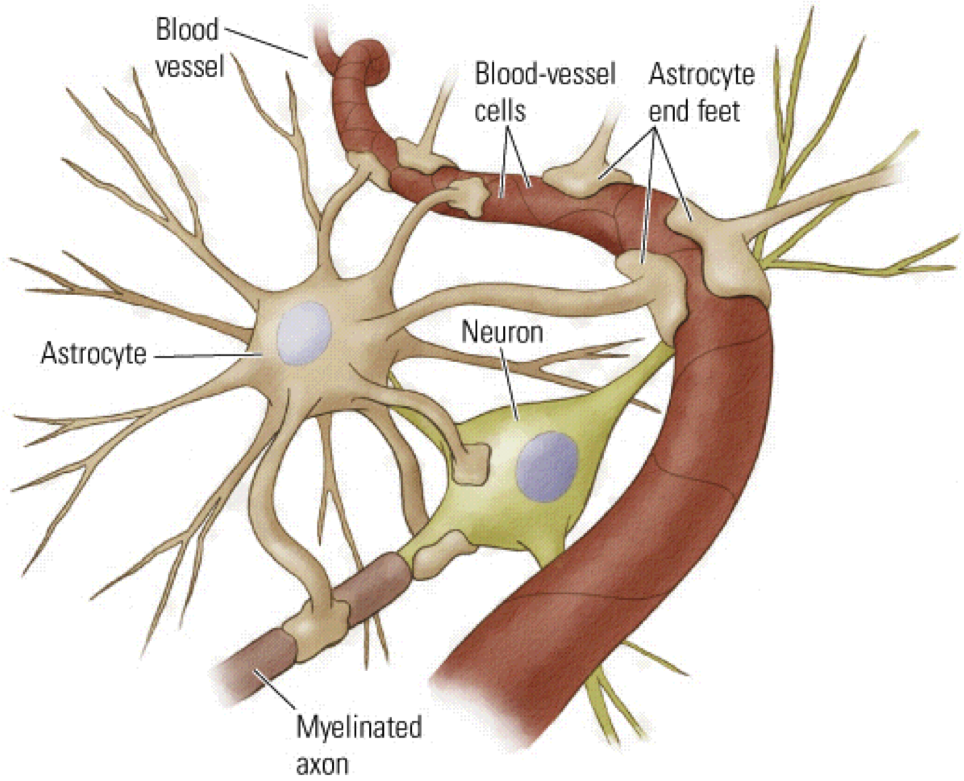
Astrocytes have close morphological and functional associations with
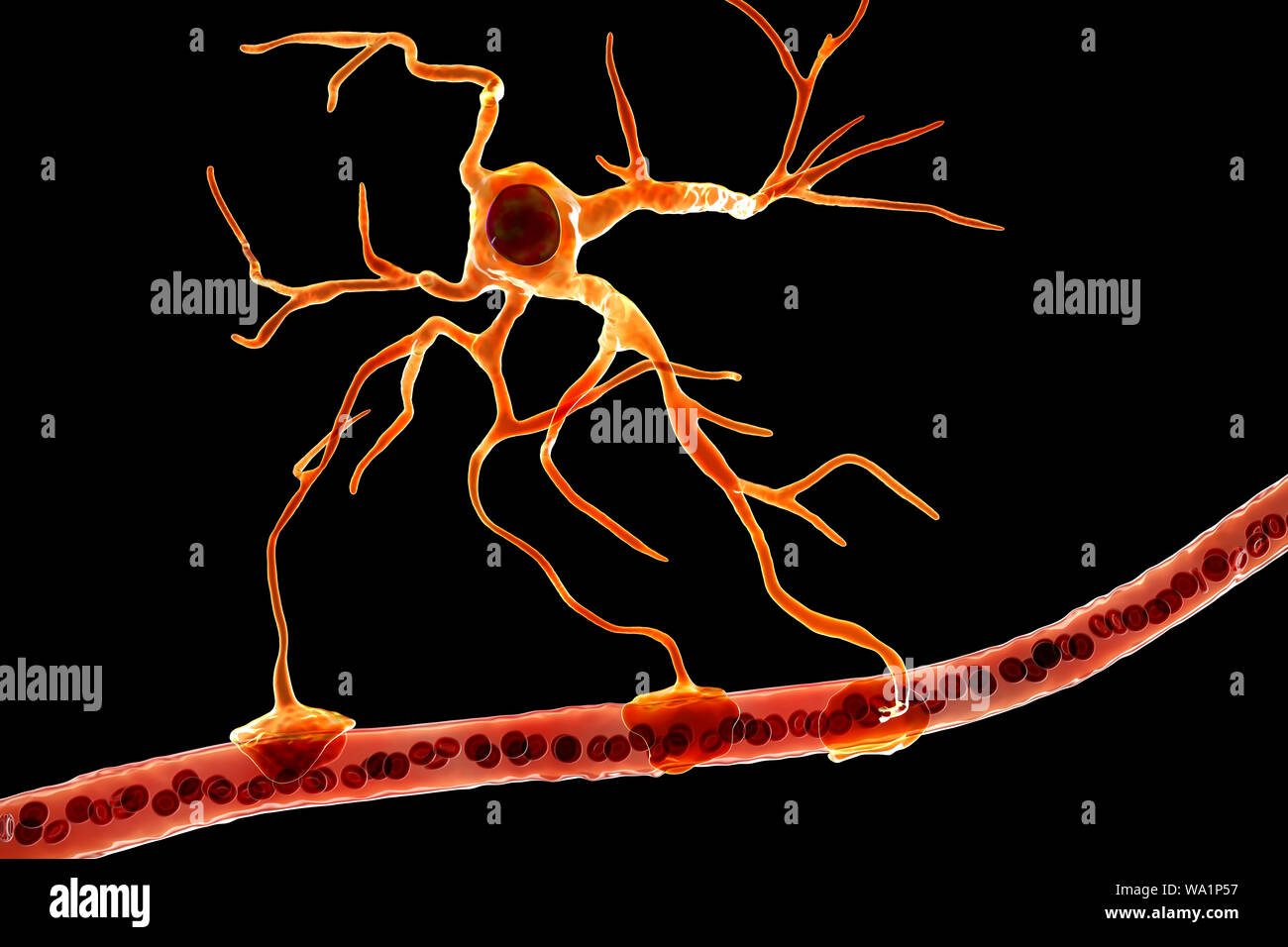
Astrocyte and blood vessel, computer illustration. Astrocytes, brain

Astrocyte morphology and subcellular compartments. General schematic
Astrocytes Display Unique Activity Patterns Neuroscience News

Astrocyte structure nerve cell infographics Vector Image

Nervous Tissue Anatomy and Physiology I

Astrocyte brain cells, confocal light micrograph Stock Image C045

Protoplasmic astrocytes, illustration Stock Image F029/9472
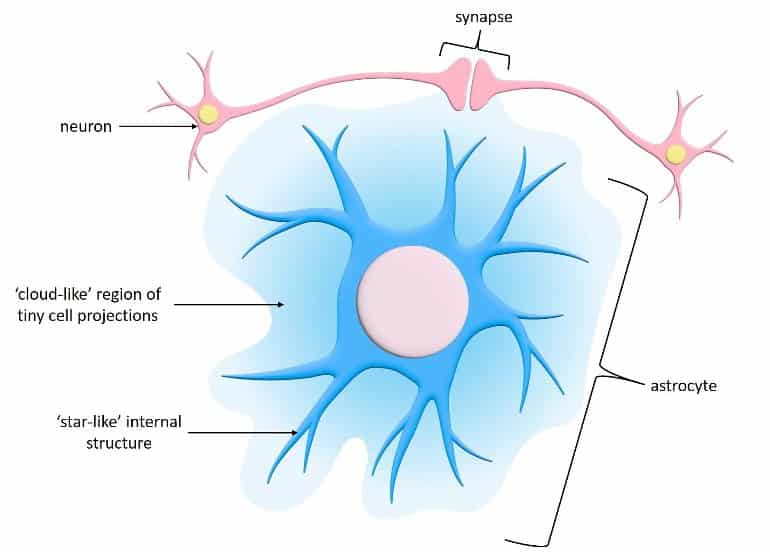
Astrocytes control synapse function
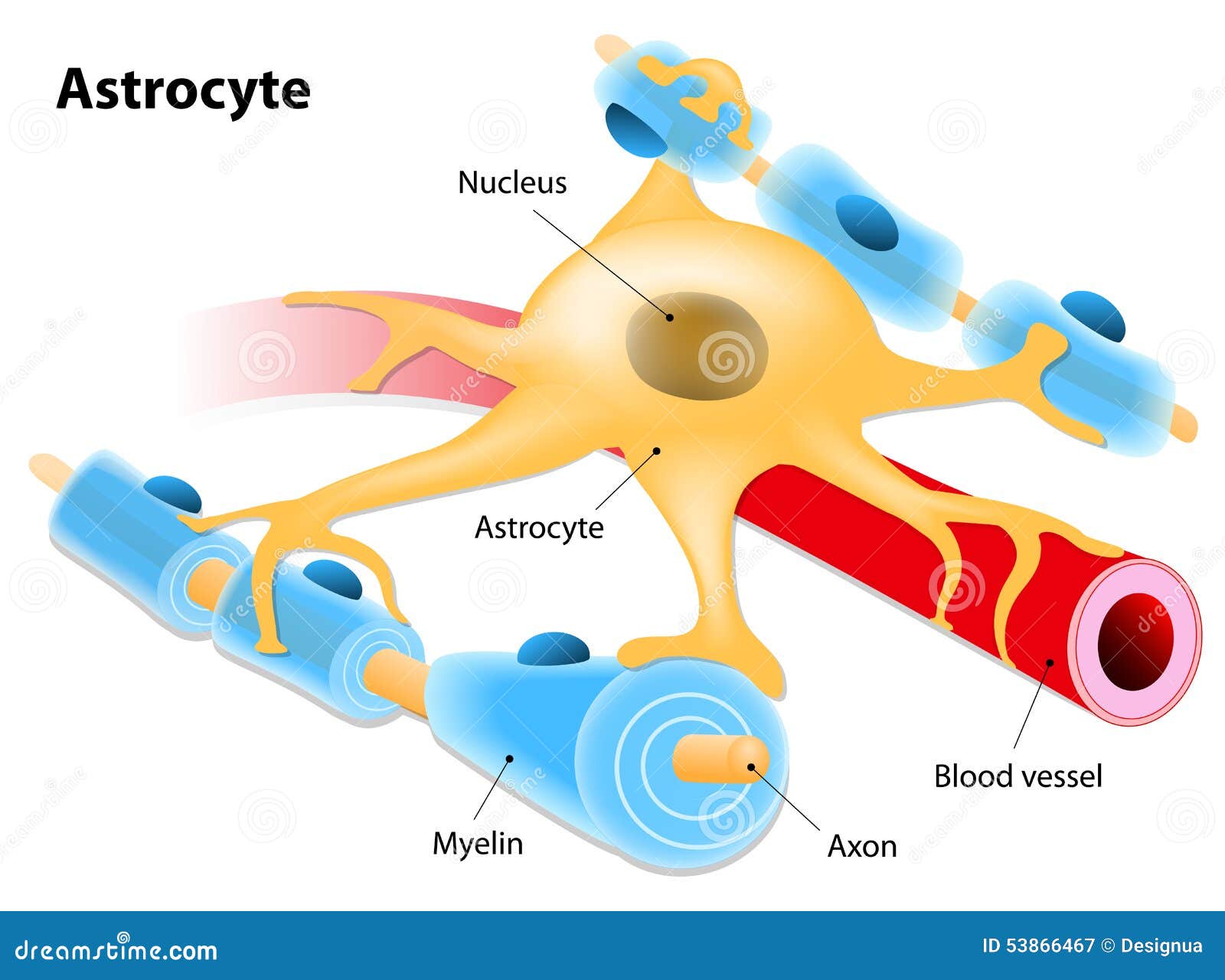
Astrocyte Stock Vector Image 53866467
It Has Long, Thin, Unbranched Processes.
Web Astrocytes Are A Subtype Of Glial Cells That Make Up The Majority Of Cells In The Human Central Nervous System (Cns).
Web Draw A Protoplasmic Astrocyte In The Gray Matter;
Web Astrocytes, Often Called Star Cells, Are The Workhorses Of The Central Nervous System.
Related Post: