Ana Pattern Nuclear Homogenous
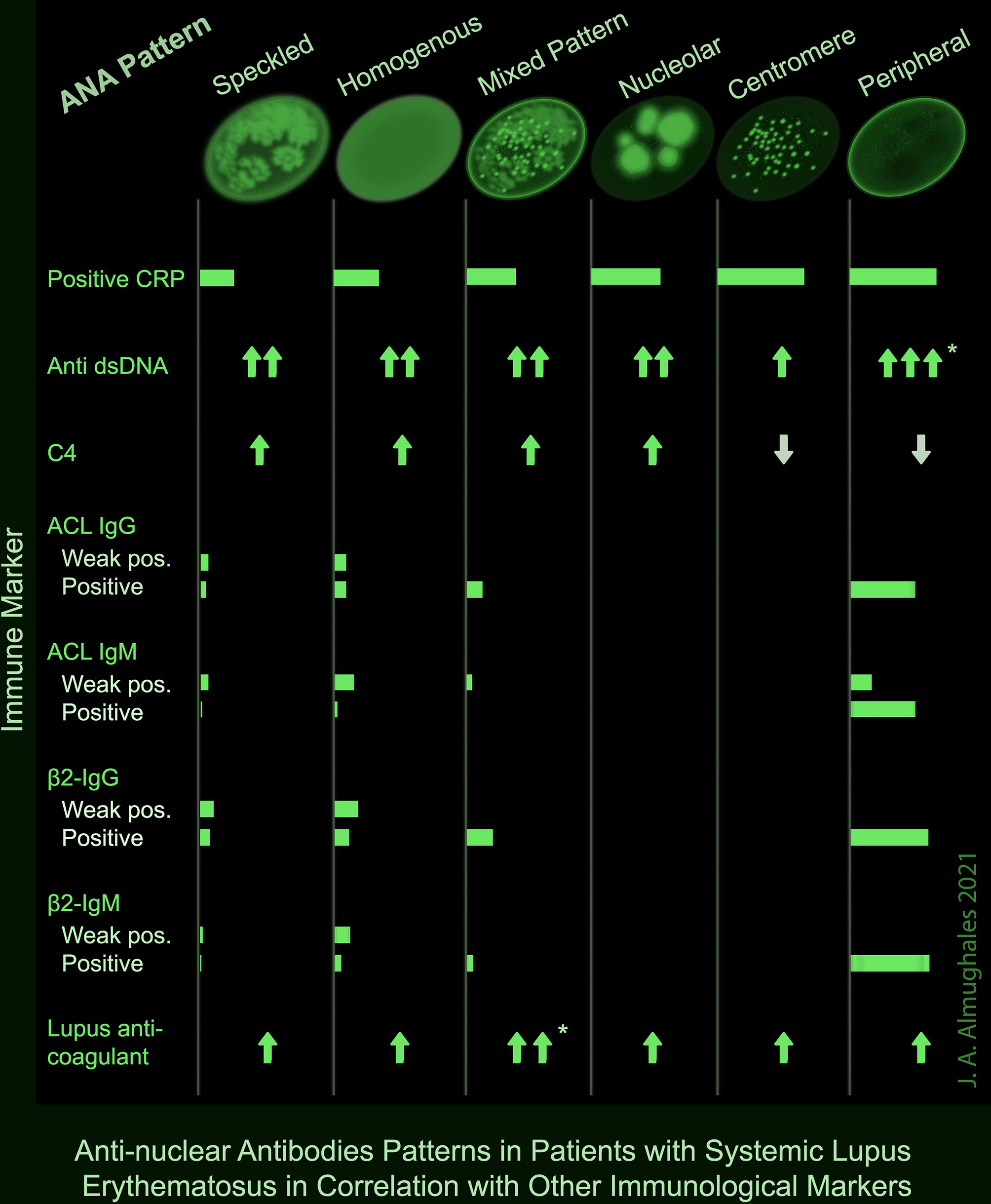
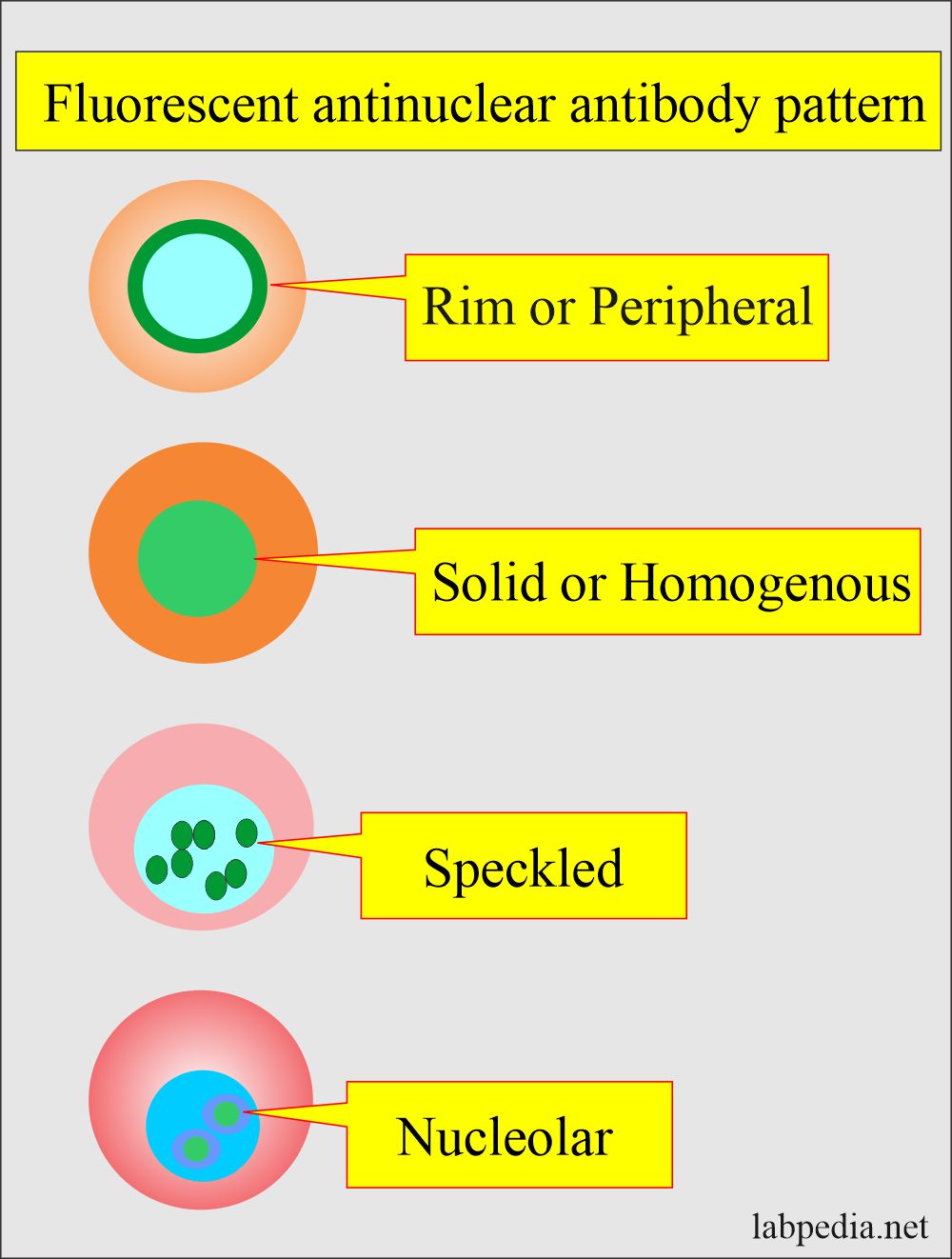
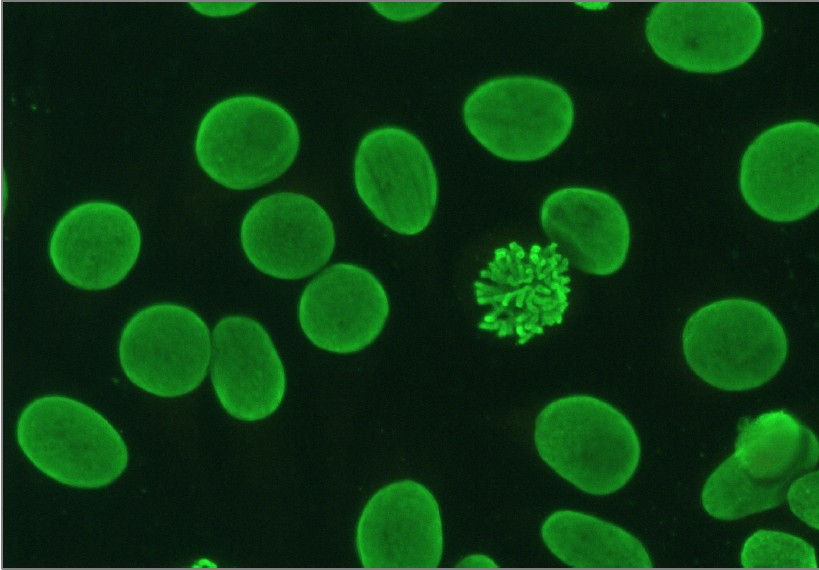
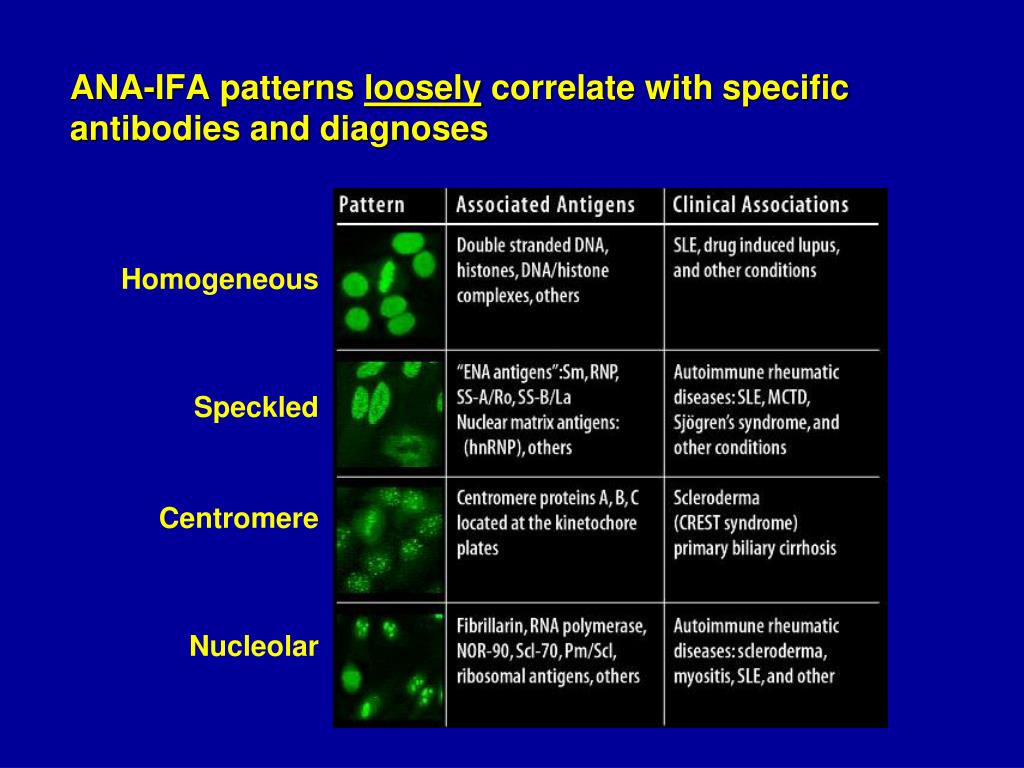
Ana Pattern Nuclear Homogenous - How the test is performed. An autoimmune disorder causes your immune system to attack your own cells, tissues, and/or organs by mistake. Antibodies that attack healthy proteins within the cell nucleus are called antinuclear antibodies (anas). Updated on october 14, 2022. In contrast, antinuclear antibodies often attack your body's own tissues — specifically targeting each cell's nucleus. A peripheral pattern indicates that fluorescence occurs at the edges of the nucleus in a shaggy appearance; Homogenous staining can result from antibodies to dna and histones. What does a positive ana blood test. This is the ana antibody panel. Doctors may order an ana test if you have signs or symptoms of an autoimmune. How the test is performed. This is the ana antibody panel. Web homogeneous and regular fluorescence across all nucleoplasm. Web the classical nuclear patterns are speckled, homogeneous, nucleolar and centromere. If your doctor thinks you might have lupus, they may ask you to take blood tests to check for antibodies in your blood. Web the most frequently observed ana patterns were the speckled (52.1%) and homogeneous (35.2%) patterns, while other patterns were rare representing less than 7% of the patients each. Homogenous staining can result from antibodies to dna and histones. The significance of ana pattern. The patterns seen are as follows: Web staining patterns include: Blood is drawn from a vein. Their presence in serum may indicate an autoimmune disease. Web the classical nuclear patterns are speckled, homogeneous, nucleolar and centromere. A homogenous staining pattern means the entire nucleus is stained with ana. A speckled pattern is also found in lupus. A peripheral pattern indicates that fluorescence occurs at the edges of the nucleus in a shaggy appearance; The nucleoli maybe stained or not stained depending on cell substrate. Homogenous staining can result from antibodies to dna and histones. Web homogenous and/or nuclear rim (peripheral) pattern correlates with antibody to native dna and deoxynucleoprotein and bears correlation with sle, sle activity,. The significance of ana pattern. The patterns seen are as follows: Web the antinuclear antibody test looks for antibodies that bind to a part of the cell called the nucleus. Web the most frequently observed ana patterns were the speckled (52.1%) and homogeneous (35.2%) patterns, while other patterns were rare representing less than 7% of the patients each. Ana titers. An autoimmune disorder causes your immune system to attack your own cells, tissues, and/or organs by mistake. When active, usually a homogenous pattern on ana or less commonly speckled, rim, or nucleolar when present in. In contrast, antinuclear antibodies often attack your body's own tissues — specifically targeting each cell's nucleus. Mitotic cells (metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) have the chromatin. Web the antinuclear antibody test looks for antibodies that bind to a part of the cell called the nucleus. If the test finds antinuclear antibodies in your blood, it may mean you have an autoimmune disorder. An ana test detects antinuclear antibodies (ana) in your blood. Mitotic cells (metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) have the chromatin mass intensely stained in a. Doctors may order an ana test if you have signs or symptoms of an autoimmune. When active, usually a homogenous pattern on ana or less commonly speckled, rim, or nucleolar when present in. Homogenous (diffuse) pattern suggests sle or. It’s the most common type of staining pattern. The nucleoli maybe stained or not stained depending on cell substrate. An autoimmune disorder causes your immune system to attack your own cells, tissues, and/or organs by mistake. Understanding the ana blood test (antinuclear antibody test) by carol eustice. What does a positive ana blood test. Web an ana test looks for antinuclear antibodies in your blood. Doctors may order an ana test if you have signs or symptoms of an. This is the ana antibody panel. Web a positive nuclear staining result will usually come back with a more detailed staining pattern, such as speckled (fig. A titer (a measure of how much ana is in the blood) and a pattern (where the ana was detected in the cells). Anas are typically classified into two groups, antibodies to dna and. A peripheral pattern indicates that fluorescence occurs at the edges of the nucleus in a shaggy appearance; These patterns were recently defined by the international consensus on ana patterns (icap) ( 2 ). Mitotic cells (metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) have the chromatin mass intensely stained in a homogeneous hyaline fashion. Web the ana staining patterns are loosely associated with underlying autoimmune diseases. Web the classical nuclear patterns are speckled, homogeneous, nucleolar and centromere. What is the ana test? If your doctor thinks you might have lupus, they may ask you to take blood tests to check for antibodies in your blood. Homogenous staining can result from antibodies to dna and histones. Web the most frequently observed ana patterns were the speckled (52.1%) and homogeneous (35.2%) patterns, while other patterns were rare representing less than 7% of the patients each. Web homogenous and/or nuclear rim (peripheral) pattern correlates with antibody to native dna and deoxynucleoprotein and bears correlation with sle, sle activity, and lupus nephritis. Homogenous (diffuse) pattern suggests sle or. Your immune system normally makes antibodies to help you fight infection. Web a homogenous (diffuse) pattern appears as total nuclear fluorescence and is common in people with systemic lupus. Web in iif, ana can display different nuclear patterns depending on the targeted antigen. A speckled pattern is also found in lupus. Ana titers were highest in patients with mixed pattern followed by the speckled pattern.
Biochemistry, Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA) StatPearls NCBI Bookshelf

Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA) test and their patterns ANA test What

Common ANA patterns by IIF a, negative sample; b, homogeneous; c
Frontiers AntiNuclear Antibodies Patterns in Patients With Systemic

ANA Patterns
Antinuclear Factor (ANF), Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) and Its
Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) homogeneous pattern positive control

Ana With Speckled Pattern Chumado
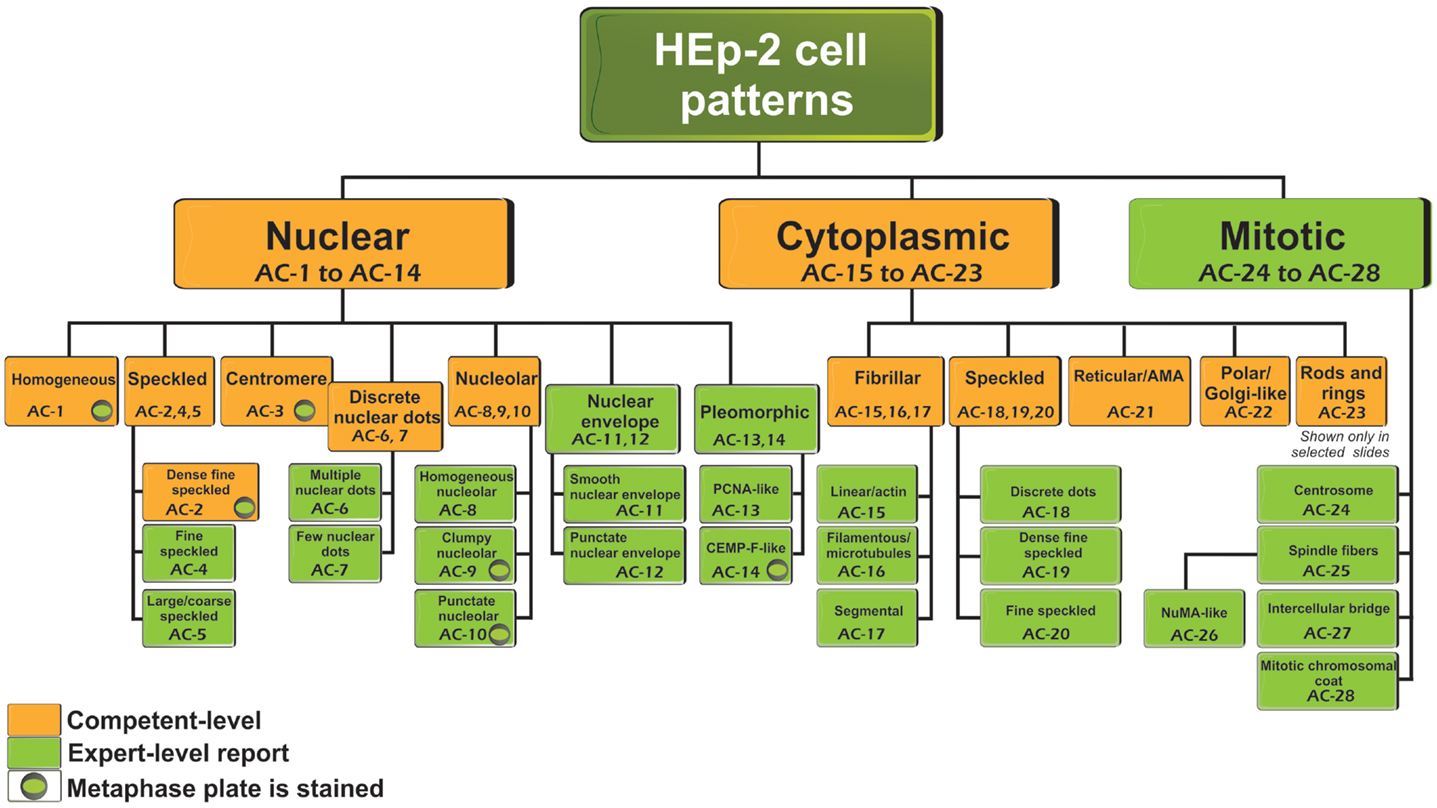
Frontiers Report of the First International Consensus on Standardized
Homogeneous Ana Pattern Pagswa
How The Test Is Performed.
The Nucleoli Maybe Stained Or Not Stained Depending On Cell Substrate.
Web Homogeneous And Regular Fluorescence Across All Nucleoplasm.
If The Test Is Positive, A Panel Of Tests May Be Done To Identify Specific Antibodies.
Related Post: