Ana Pattern Nuclear Homogeneous
Ana Pattern Nuclear Homogeneous - Their presence in serum may indicate an autoimmune disease. A homogenous pattern can mean any autoimmune disease but more specifically, lupus or sjögren’s syndrome. Web the pattern of the ana test can give information about the type of autoimmune disease present and the appropriate treatment program. An autoimmune disorder causes your immune system to attack your own cells, tissues, and/or organs by mistake. If the test finds antinuclear antibodies in your blood, it may mean you have an autoimmune disorder. Web the classical nuclear patterns are speckled, homogeneous, nucleolar and centromere. A homogenous (diffuse) pattern appears as total nuclear fluorescence and is common in people with systemic lupus. Some, but not all labs will report a titre above 1:160 as positive. Mitotic cells (metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) have the chromatin mass intensely stained in a homogeneous hyaline fashion. Web an ana test looks for antinuclear antibodies in your blood. Web ana test results are most often reported in 2 parts: In contrast, antinuclear antibodies often attack your body's own. Patterns that are reported include, homogeneous, speckled, centromere, and others. The nucleoli maybe stained or not stained depending on cell substrate. Your immune system normally makes antibodies to help you fight infection. Anas are typically classified into two groups, antibodies to dna and histones and antibodies to nuclear material. Web the classical nuclear patterns are speckled, homogeneous, nucleolar and centromere. Web antinuclear antibodies (ana) refer to an autoantibody directed at material within the nucleus of a cell. Your immune system normally makes antibodies to help you fight infection. The nucleoli maybe stained. A homogenous staining pattern means the entire nucleus is stained with ana. Web the pattern of the ana test can give information about the type of autoimmune disease present and the appropriate treatment program. A speckled staining pattern means fine, coarse speckles of ana are present throughout the. Web antinuclear antibodies (ana) refer to an autoantibody directed at material within. Some, but not all labs will report a titre above 1:160 as positive. Web homogeneous and regular fluorescence across all nucleoplasm. Web the classical nuclear patterns are speckled, homogeneous, nucleolar and centromere. If the test finds antinuclear antibodies in your blood, it may mean you have an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, antinuclear antibodies often attack your body's own. If the test finds antinuclear antibodies in your blood, it may mean you have an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, antinuclear antibodies often attack your body's own. The level or titer and the pattern. Web the pattern of the ana test can give information about the type of autoimmune disease present and the appropriate treatment program. A speckled staining pattern means. Some, but not all labs will report a titre above 1:160 as positive. Titres are reported in ratios, most often 1:40, 1:80, 1:160, 1:320, and 1:640. It’s the most common type of staining pattern. Web an ana test detects antinuclear antibodies (ana) in your blood. Web the classical nuclear patterns are speckled, homogeneous, nucleolar and centromere. Web antinuclear antibodies (ana) refer to an autoantibody directed at material within the nucleus of a cell. Patterns that are reported include, homogeneous, speckled, centromere, and others. Mitotic cells (metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) have the chromatin mass intensely stained in a homogeneous hyaline fashion. Web an ana test detects antinuclear antibodies (ana) in your blood. Web ana test results are. Anas are typically classified into two groups, antibodies to dna and histones and antibodies to nuclear material. The nucleoli maybe stained or not stained depending on cell substrate. A homogenous staining pattern means the entire nucleus is stained with ana. Web the classical nuclear patterns are speckled, homogeneous, nucleolar and centromere. Patterns that are reported include, homogeneous, speckled, centromere, and. A homogenous (diffuse) pattern appears as total nuclear fluorescence and is common in people with systemic lupus. Anas are typically classified into two groups, antibodies to dna and histones and antibodies to nuclear material. Their presence in serum may indicate an autoimmune disease. The level or titer and the pattern. An autoimmune disorder causes your immune system to attack your. The nucleoli maybe stained or not stained depending on cell substrate. Your immune system normally makes antibodies to help you fight infection. Patterns that are reported include, homogeneous, speckled, centromere, and others. A homogenous pattern can mean any autoimmune disease but more specifically, lupus or sjögren’s syndrome. Web the classical nuclear patterns are speckled, homogeneous, nucleolar and centromere. A homogenous (diffuse) pattern appears as total nuclear fluorescence and is common in people with systemic lupus. A homogenous staining pattern means the entire nucleus is stained with ana. The nucleoli maybe stained or not stained depending on cell substrate. The level or titer and the pattern. Anas are typically classified into two groups, antibodies to dna and histones and antibodies to nuclear material. Web ana test results are most often reported in 2 parts: It’s the most common type of staining pattern. Web an ana test looks for antinuclear antibodies in your blood. Web antinuclear antibodies (ana) refer to an autoantibody directed at material within the nucleus of a cell. A homogenous pattern can mean any autoimmune disease but more specifically, lupus or sjögren’s syndrome. Their presence in serum may indicate an autoimmune disease. Web homogeneous and regular fluorescence across all nucleoplasm. In contrast, antinuclear antibodies often attack your body's own. Web the pattern of the ana test can give information about the type of autoimmune disease present and the appropriate treatment program. An autoimmune disorder causes your immune system to attack your own cells, tissues, and/or organs by mistake. Mitotic cells (metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) have the chromatin mass intensely stained in a homogeneous hyaline fashion.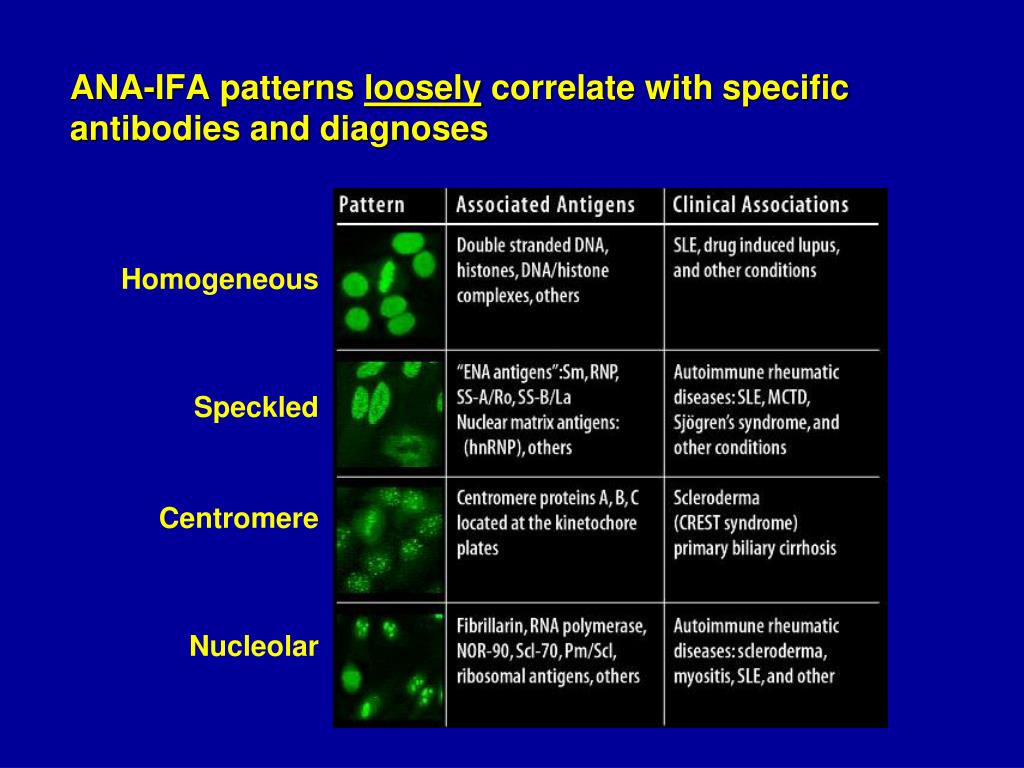
Homogeneous Ana Pattern Pagswa

ANA (Antinuclear antibody) with (Homogeneous immunofluorescence

ANA Patterns

ANA Patterns

Examples of diverse salivary ANA patterns in 47 salivaANApositive SLE
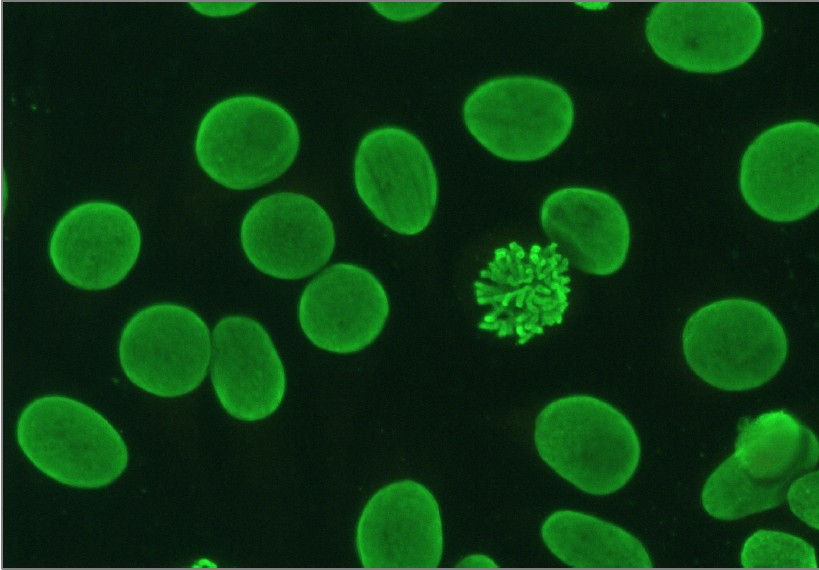
Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) homogeneous pattern positive control

ANA Patterns

Common ANA patterns by IIF a, negative sample; b, homogeneous; c
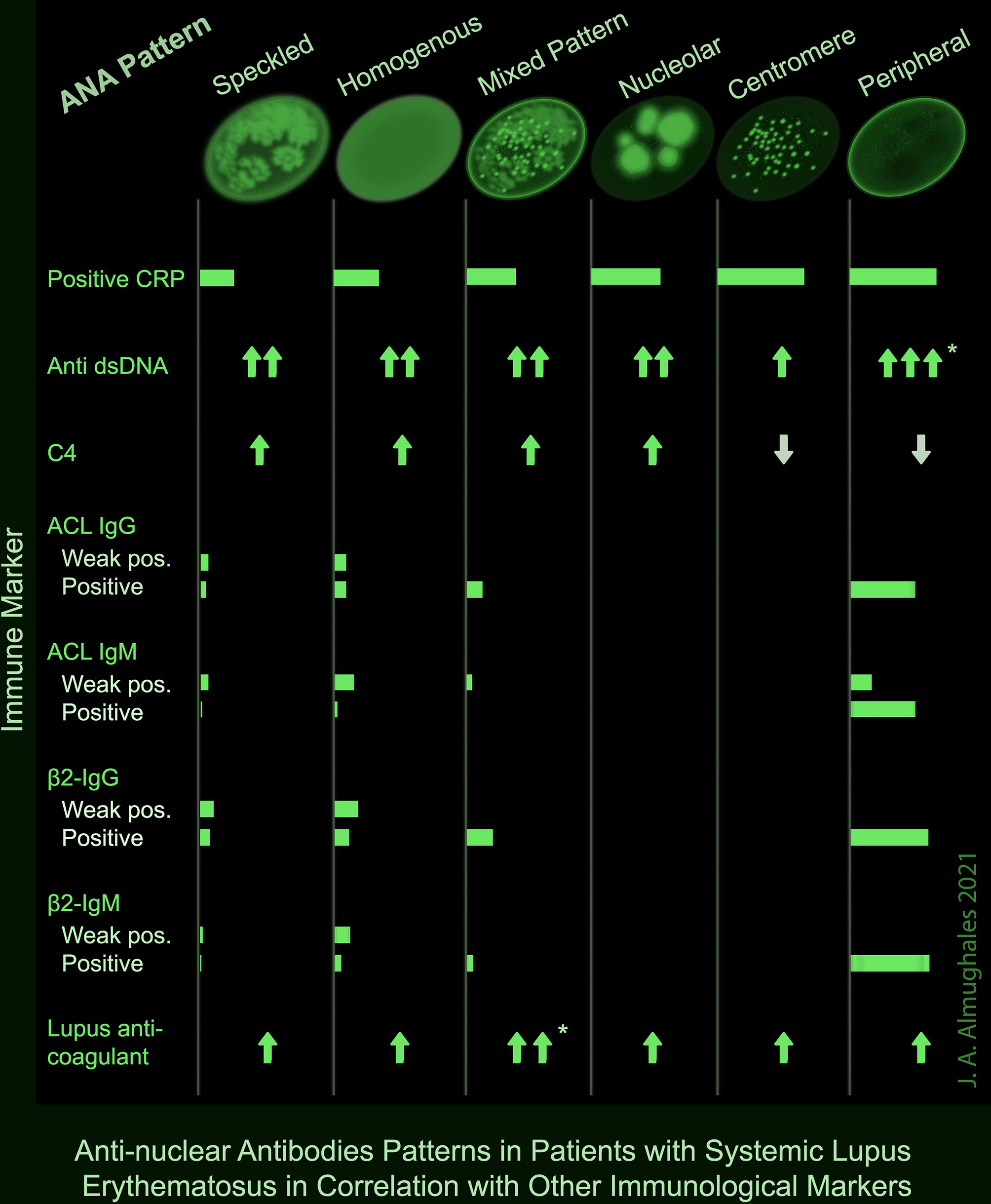
Frontiers AntiNuclear Antibodies Patterns in Patients With Systemic
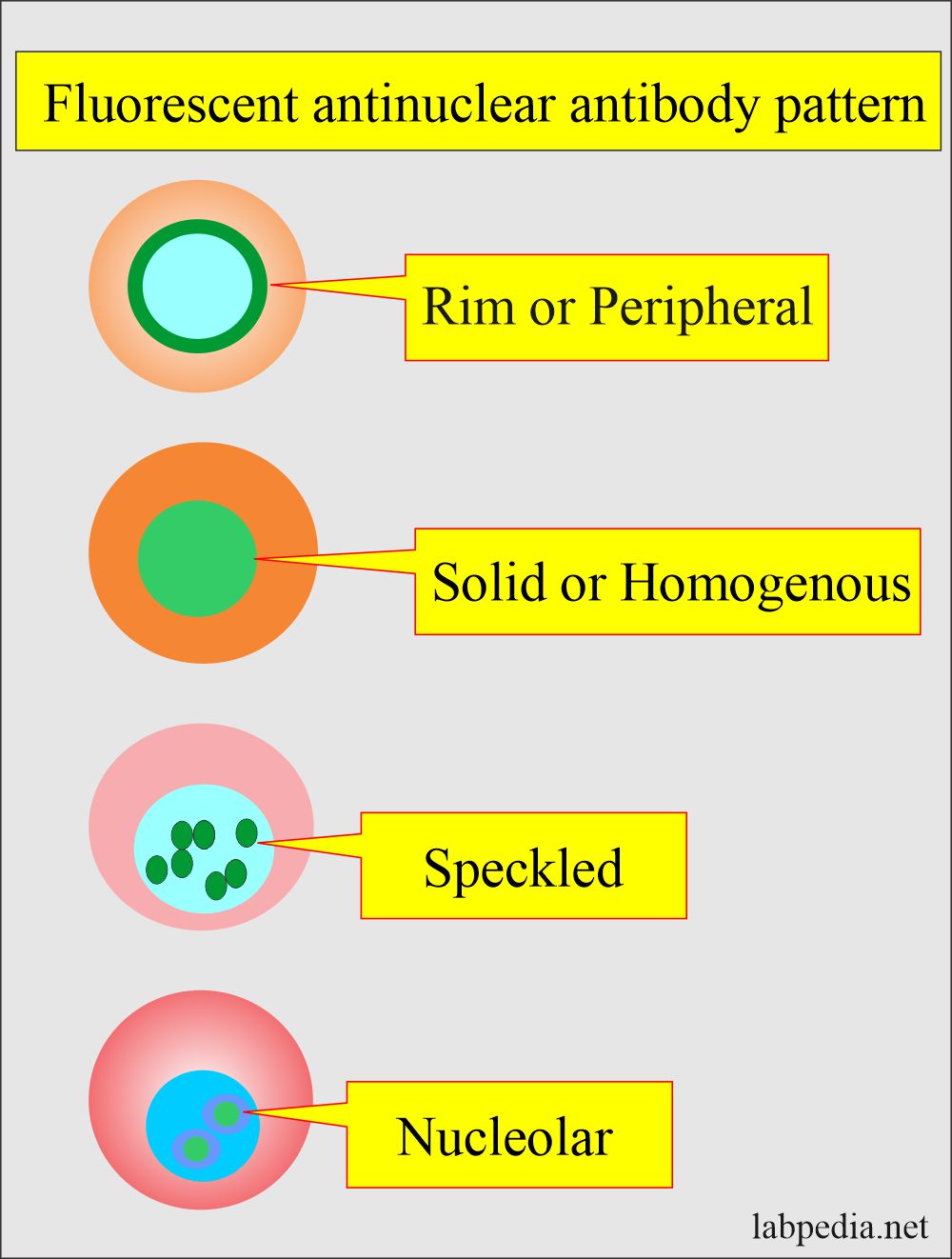
Antinuclear Factor (ANF), Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) and Its
Titres Are Reported In Ratios, Most Often 1:40, 1:80, 1:160, 1:320, And 1:640.
A Speckled Staining Pattern Means Fine, Coarse Speckles Of Ana Are Present Throughout The.
Some, But Not All Labs Will Report A Titre Above 1:160 As Positive.
Patterns That Are Reported Include, Homogeneous, Speckled, Centromere, And Others.
Related Post: