Ana Pattern Fine Speckled
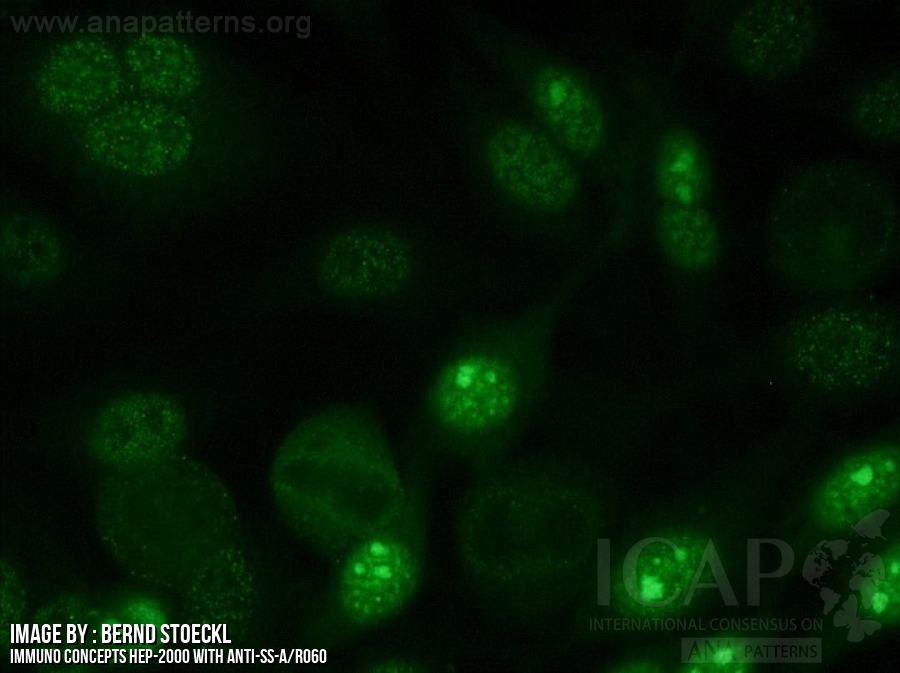
Ana Pattern Fine Speckled - Fine and coarse speckles of ana staining are seen throughout the nucleus. Web a positive ana test is usually reported as both a ratio (called a titer) and a pattern, such as smooth or speckled. A speckled staining pattern means fine, coarse speckles of ana are present throughout the nucleus. Mitotic cells (metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) have the chromatin mass not stained. A speckled pattern may indicate various diseases, including lupus and sjögren’s syndrome. Fine tiny speckles across all nucleoplasm. In contrast, antinuclear antibodies often attack your body's own. Titres are reported in ratios, most often 1:40, 1:80, 1:160, 1:320, and 1:640. Ana test results are most often reported in 2 parts: Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations, and clinical relevance. The nucleoli may be stained or not stained. In contrast, antinuclear antibodies often attack your body's own. Certain diseases are more likely to have certain patterns. Web a homogeneous/peripheral pattern reflects antibodies to histone/dsdna/chromatin, whereas many other specificities found in systemic rheumatic diseases show speckled patterns of various sizes and densities (fine speckled, large speckled, etc.). Ana test results are. A centromere staining pattern means the ana staining is present along the chromosomes. Fine tiny speckles across all nucleoplasm. Ana test results are most often reported in 2 parts: The level or titer and the pattern. Web the characteristic dense fine speckled (dfs) staining pattern of interphase cells is indicated by the red arrow and the strong chromosome staining of. Web indirect immunofluorescence (iif) is the most prevalent screening antinuclear antibody test for systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease (sard). Dfs70/ledgf is a transcription factor involved in cell survival and stress protection, and autoantibodies may inhibit its function. Web a homogeneous/peripheral pattern reflects antibodies to histone/dsdna/chromatin, whereas many other specificities found in systemic rheumatic diseases show speckled patterns of various sizes and. A speckled staining pattern means fine, coarse speckles of ana are present throughout the nucleus. Web indirect immunofluorescence (iif) is the most prevalent screening antinuclear antibody test for systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease (sard). Mitotic cells (metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) have the chromatin mass not stained. Ana test results are most often reported in 2 parts: Web although the dense fine. Ana pattern is most commonly speckled, followed by centromeric and less commonly nucleolar. Web indirect immunofluorescence (iif) is the most prevalent screening antinuclear antibody test for systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease (sard). Some, but not all labs will report a titre above 1:160 as positive. Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations, and clinical relevance. The. Fine and coarse speckles of ana staining are seen throughout the nucleus. Ana pattern is most commonly speckled, followed by centromeric and less commonly nucleolar. A speckled pattern may indicate various diseases, including lupus and sjögren’s syndrome. Dfs70/ledgf is a transcription factor involved in cell survival and stress protection, and autoantibodies may inhibit its function. Mitotic cells (metaphase, anaphase, and. Ana pattern is most commonly speckled, followed by centromeric and less commonly nucleolar. This pattern is more commonly associated with antibodies to extractable nuclear antigens. Dfs70/ledgf is a transcription factor involved in cell survival and stress protection, and autoantibodies may inhibit its function. Ana pattern is almost always. Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations,. Some, but not all labs will report a titre above 1:160 as positive. An ana test detects antinuclear antibodies (ana) in your blood. Web although the dense fine speckled (dfs) immunofluorescence staining pattern has been studied by various researchers in recent years, its clinical associations remain unspecified. Your immune system normally makes antibodies to help you fight infection. Dfs70/ledgf is. Titres are reported in ratios, most often 1:40, 1:80, 1:160, 1:320, and 1:640. Web a homogeneous/peripheral pattern reflects antibodies to histone/dsdna/chromatin, whereas many other specificities found in systemic rheumatic diseases show speckled patterns of various sizes and densities (fine speckled, large speckled, etc.). Ana pattern is almost always. The nucleoli may be stained or not stained. This pattern is more. Mitotic cells (metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) have the chromatin mass not stained. A centromere staining pattern means the ana staining is present along the chromosomes. Titres are reported in ratios, most often 1:40, 1:80, 1:160, 1:320, and 1:640. Chromatin is not observed in mitotic cells. Ana test results are most often reported in 2 parts: Web the characteristic dense fine speckled (dfs) staining pattern of interphase cells is indicated by the red arrow and the strong chromosome staining of metaphase cells by the blue arrow. Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations, and clinical relevance. Web indirect immunofluorescence (iif) is the most prevalent screening antinuclear antibody test for systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease (sard). This pattern is more commonly associated with antibodies to extractable nuclear antigens. Web scleroderma or systemic sclerosis: Certain diseases are more likely to have certain patterns. A centromere staining pattern means the ana staining is present along the chromosomes. This pattern can be associated with systemic lupus erythematosus, sjögren’s syndrome, systemic sclerosis, polymyositis, and rheumatoid arthritis. Dfs70/ledgf is a transcription factor involved in cell survival and stress protection, and autoantibodies may inhibit its function. A speckled staining pattern means fine, coarse speckles of ana are present throughout the nucleus. Mitotic cells (metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) have the chromatin mass not stained. In contrast, antinuclear antibodies often attack your body's own. Fine and coarse speckles of ana staining are seen throughout the nucleus. Chromatin is not observed in mitotic cells. The nucleoli may be stained or not stained. Ana pattern is most commonly speckled, followed by centromeric and less commonly nucleolar.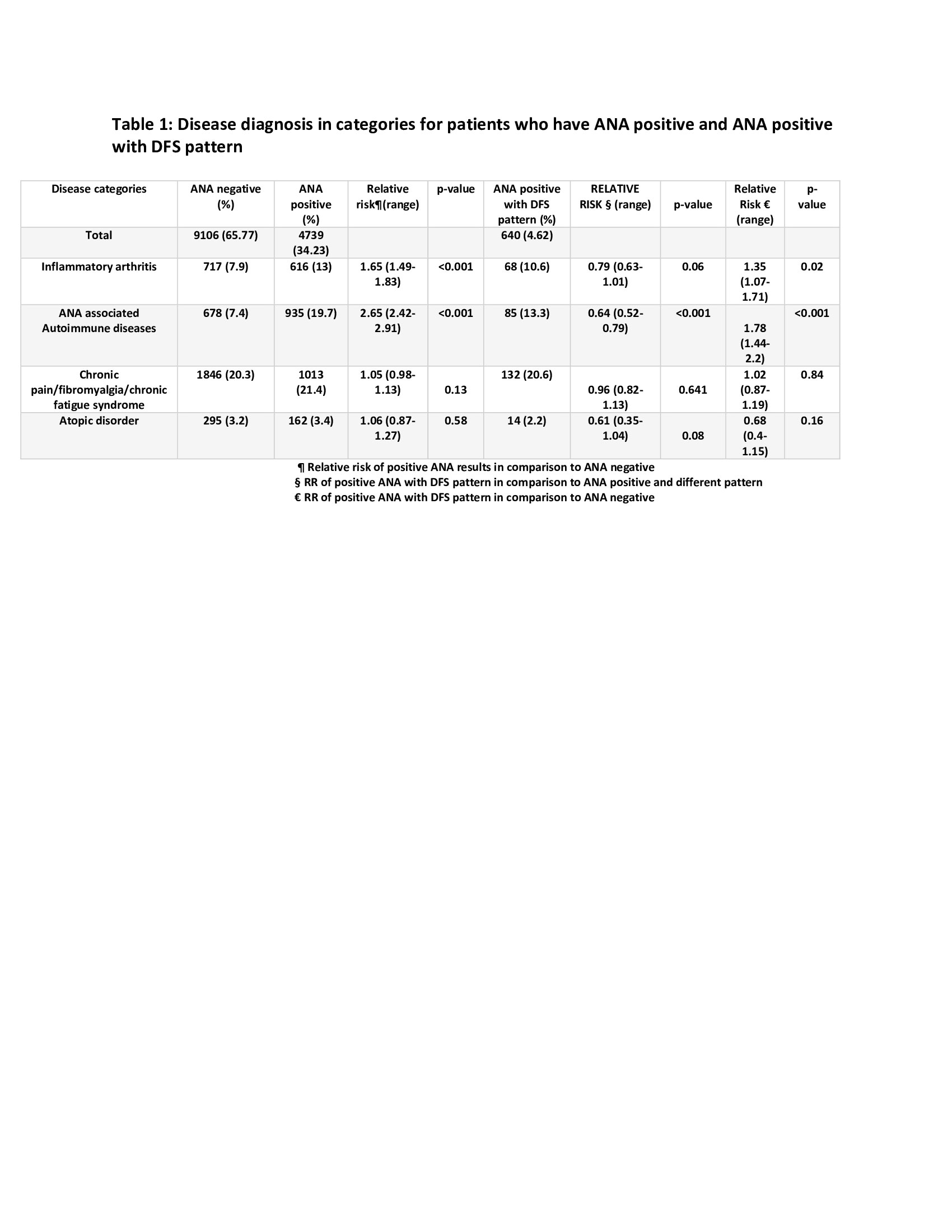
Clinical Correlation of Dense Fine Speckled (DFS) Pattern of ANA ACR

Fine speckled ANA, AC4 from homepage of International consensus of ANA

Ana With Speckled Pattern Chumado

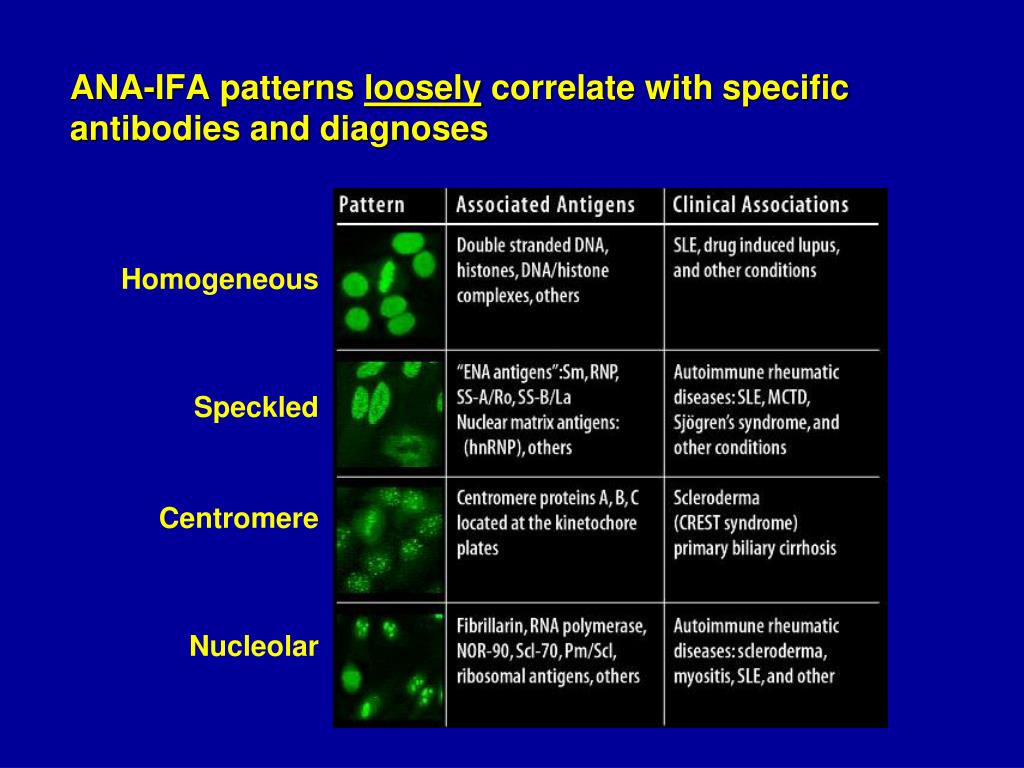
ANA Patterns

Positive Ana Speckled Pattern Chumado

International consensus on antinuclear antibody patterns definition of
Frontiers AntiNuclear Antibodies Patterns in Patients With Systemic
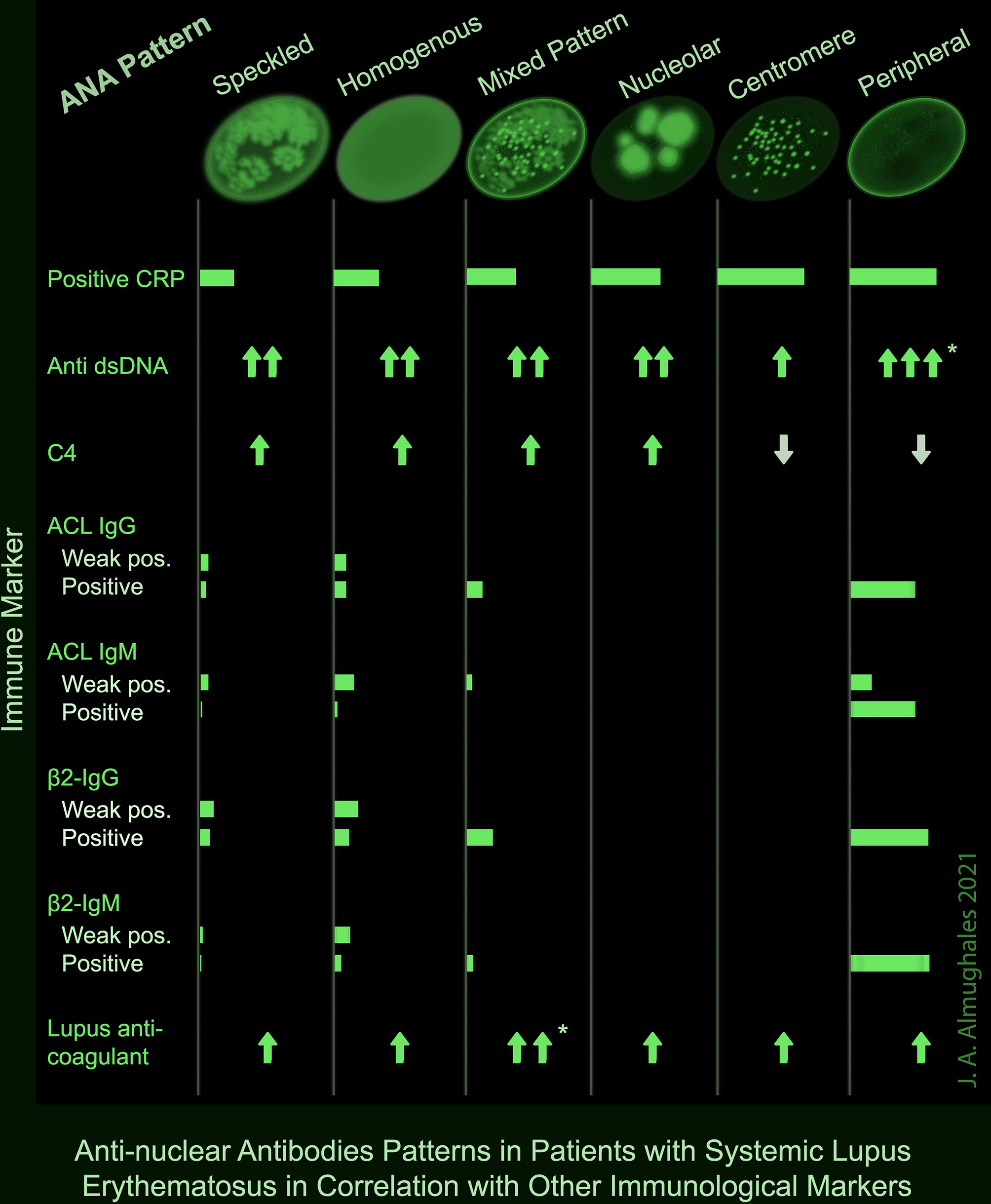
Antinuclear Factor (ANF), Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) and Its
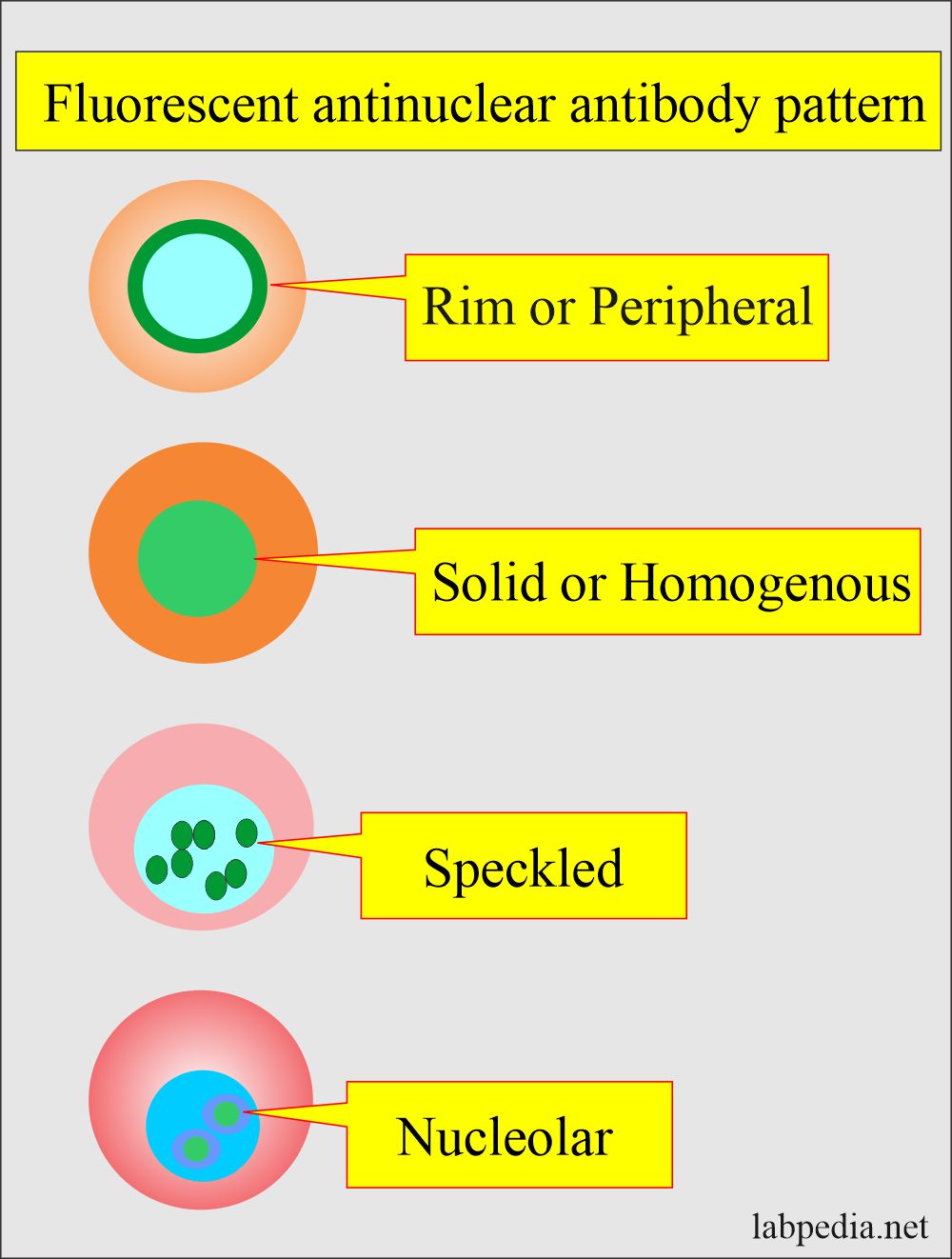
37+ Ana Pattern Nuclear Dense Fine Speckled FayneHjalte
Ana Titer 1 160 Speckled Pattern Chumado
Fine Tiny Speckles Across All Nucleoplasm.
Some, But Not All Labs Will Report A Titre Above 1:160 As Positive.
Also Known As Fine Granular, This Pattern Is Characterized By Fine, Tiny Speckles Emission Of Interphase Nuclei, With A Uniform Distribution.
Ana Pattern Is Almost Always.
Related Post: