Ana Pattern 1 Homogeneous
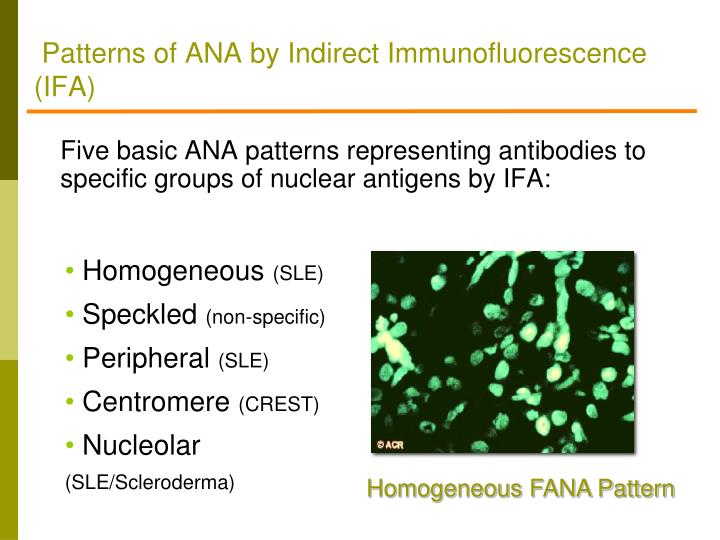
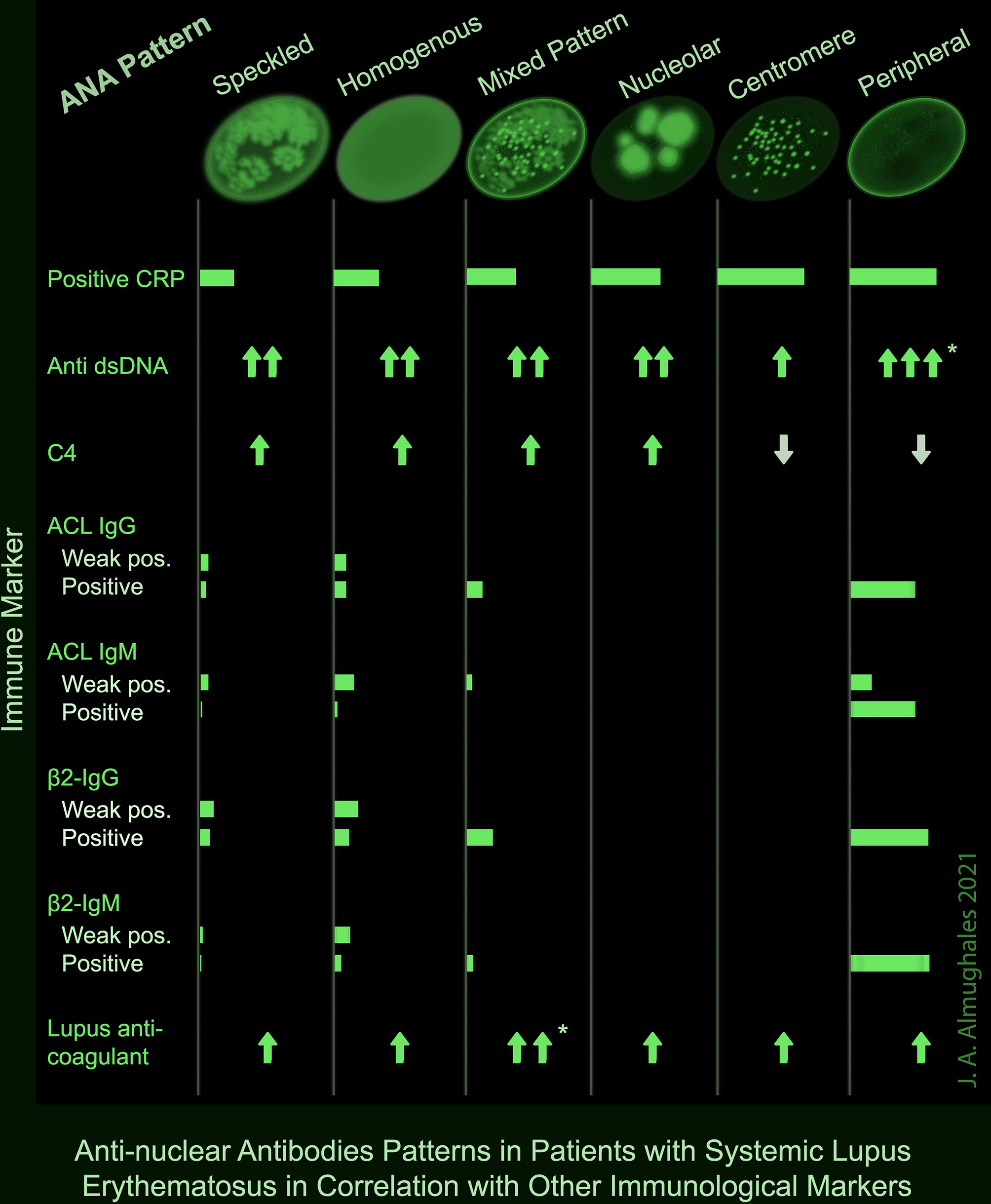
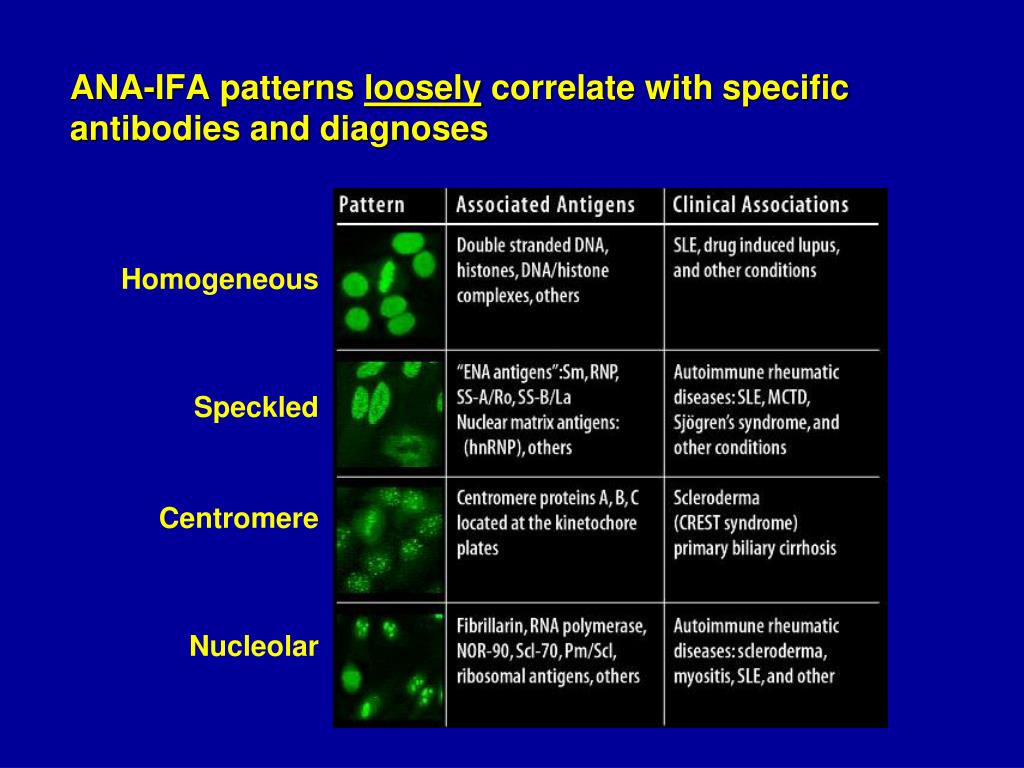
Ana Pattern 1 Homogeneous - Web ana test results are most often reported in 2 parts: Common ana patterns and their associated systemic rheumatic diseases; Web antinuclear antibody (ana) autoantibodies, or antibodies produced by the immune system that attack the body’s own cells, are a hallmark of lupus. Web the pattern refers to how the ana sample is detected visually, using different kinds of staining techniques: Web each pattern is assigned an alphanumeric ac code (anticell). Ana pattern associated rheumatic disease; Homogeneous and regular fluorescence across all nucleoplasm. The nucleoli maybe stained or not stained depending on cell substrate. The level or titer and the pattern. Ana is usually measured as 0 to 4+ or as a titer (the number of times a blood sample can be diluted and still be positive). The intensity of fluorescence depends on the titer of antibodies in the serum. Web ana titers and patterns can vary between laboratory testing sites due to variations in the methodology used. Common ana patterns and their associated systemic rheumatic diseases; Ana titers were highest in patients with mixed pattern followed by the speckled pattern. Total nuclear fluorescence due to an. Total nuclear fluorescence due to an antibody directed against dna or histone proteins. Web is the ana pattern suggestive of a specific disease? Positive results are further diluted to a titre of 1:160, 1:320 and a final titre of 1:640. Ana is usually measured as 0 to 4+ or as a titer (the number of times a blood sample can. Ana is usually measured as 0 to 4+ or as a titer (the number of times a blood sample can be diluted and still be positive). Web is the ana pattern suggestive of a specific disease? Your immune system normally makes antibodies to help you fight infection. The pattern refers to the distribution of staining produced by autoantibodies reacting with. If the test finds antinuclear antibodies in your blood, it may mean you have an autoimmune disorder. For this test, we use a. While these patterns are not specific to any one illness, certain illnesses can more frequently be associated with one pattern or another. Samples are initially diluted to a 1 in 80 dilution (titre 1:80). Web the presence. The patient in case 1 has no end organ involvement of her lupus, yet her ana titer is > 1:1280. Web the presence of ana with a homogeneous & speckled (hs) pattern was significantly associated with the absence of cancer (p < 0.01). Web homogenous and/or nuclear rim (peripheral) pattern correlates with antibody to native dna and deoxynucleoprotein and bears. Titres are reported in ratios, most often 1:40, 1:80, 1:160, 1:320, and 1:640. If the test finds antinuclear antibodies in your blood, it may mean you have an autoimmune disorder. Patterns that are reported include, homogeneous, speckled, centromere, and others. Uniform staining across all nucleoplasm is seen in this pattern. Common ana patterns and their associated systemic rheumatic diseases; Web ana titers and patterns can vary between laboratory testing sites due to variations in the methodology used. Web each pattern is assigned an alphanumeric ac code (anticell). Web homogenous and/or nuclear rim (peripheral) pattern correlates with antibody to native dna and deoxynucleoprotein and bears correlation with sle, sle activity, and lupus nephritis. Web the most frequently observed ana patterns. Web homogeneous nuclear pattern. Ana pattern associated rheumatic disease; The level or titer and the pattern. Uniform staining across all nucleoplasm is seen in this pattern. Some, but not all labs will report a titre above 1:160 as positive. Homogeneous — staining is even in the entire nucleus and is commonly found in people with sle and discoid lupus erythematosus (dle). Common ana patterns and their associated systemic rheumatic diseases; Interphase cells show homogeneous nuclear staining while mitotic cells show staining of the condensed chromosome regions. It is cases such as these that have piqued the interest of rheumatologists. Web positive results are reported as 1) the immunofluorescence pattern (eg homogenous, speckled etc) and 2) the titre to indicate if this is a high positive or low positive ana result. Interphase cells show homogeneous nuclear staining while mitotic cells show staining of the condensed chromosome regions. Web testing reveals a 1:40 antinuclear antibody (ana) titer and a weakly positive. An ana test detects antinuclear antibodies (ana) in your blood. Web each pattern is assigned an alphanumeric ac code (anticell). Titres are reported in ratios, most often 1:40, 1:80, 1:160, 1:320, and 1:640. The level or titer and the pattern. Web homogeneous nuclear pattern. The commonly recognized patterns include: Web the presence of ana with a homogeneous & speckled (hs) pattern was significantly associated with the absence of cancer (p < 0.01). An autoimmune disorder causes your immune system to attack your own cells, tissues, and/or organs by mistake. Total nuclear fluorescence due to an antibody directed against dna or histone proteins. Web ana titers and patterns can vary between laboratory testing sites due to variations in the methodology used. Samples are initially diluted to a 1 in 80 dilution (titre 1:80). Common ana patterns and their associated systemic rheumatic diseases; While these patterns are not specific to any one illness, certain illnesses can more frequently be associated with one pattern or another. Ana pattern associated rheumatic disease; If the test finds antinuclear antibodies in your blood, it may mean you have an autoimmune disorder. Web the most frequently observed ana patterns were the speckled (52.1%) and homogeneous (35.2%) patterns, while other patterns were rare representing less than 7% of the patients each.
Biochemistry, Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA) StatPearls NCBI Bookshelf

Ana Pattern Homogeneous Chumado

DFS70 antibodies biomarkers for the exclusion of ANAassociated
PPT Rheumatology Update Pearls for Primary Care PowerPoint
Frontiers AntiNuclear Antibodies Patterns in Patients With Systemic

ANA Patterns

6. IFA pattern Homogeneous ANA pattern YouTube
Homogeneous Ana Pattern Pagswa
Antinuclear Factor (ANF), Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) and Its

ANA Patterns
Interphase Cells Show Homogeneous Nuclear Staining While Mitotic Cells Show Staining Of The Condensed Chromosome Regions.
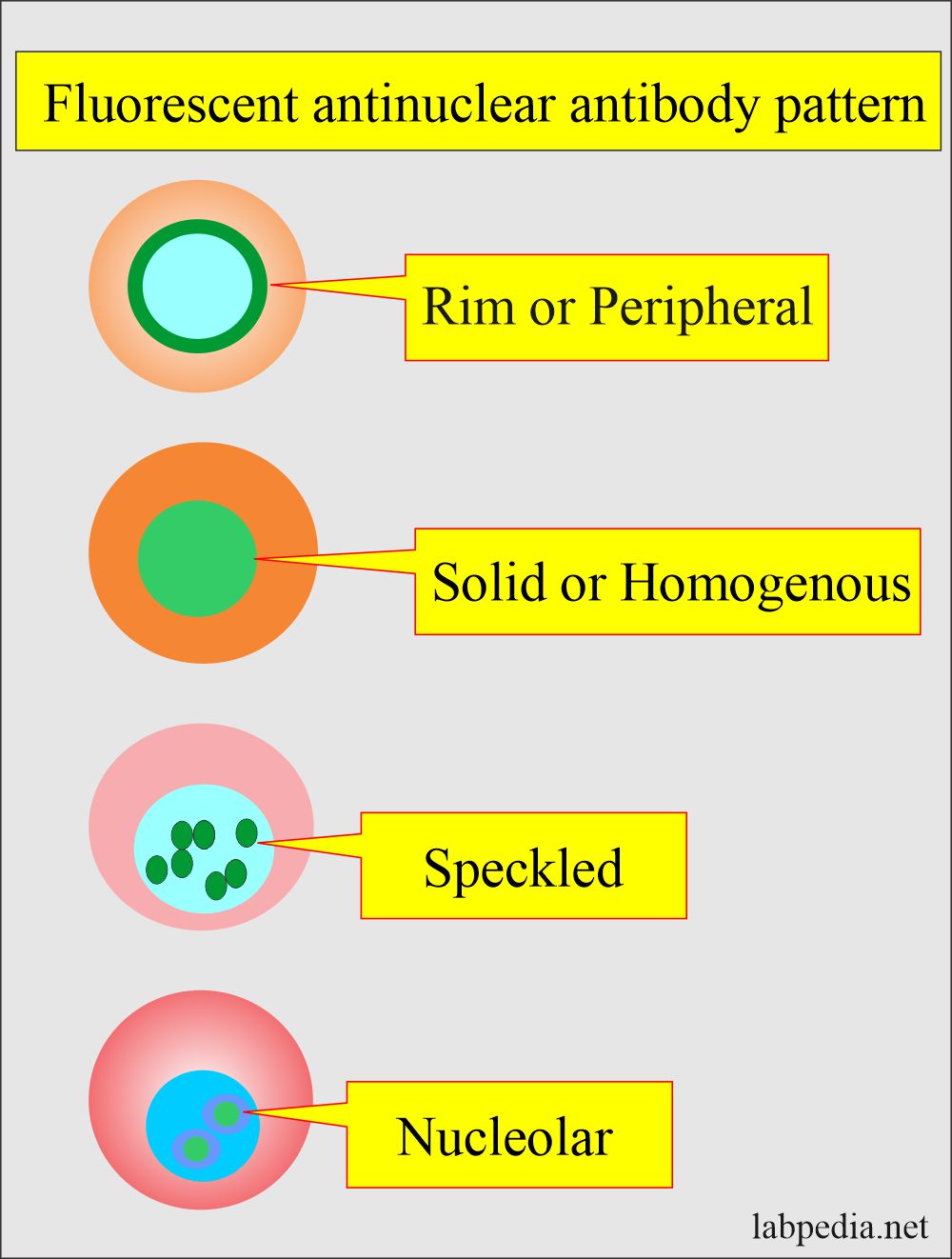
Uniform Staining Across All Nucleoplasm Is Seen In This Pattern.
Positive Results Are Further Diluted To A Titre Of 1:160, 1:320 And A Final Titre Of 1:640.
Homogeneous — Staining Is Even In The Entire Nucleus And Is Commonly Found In People With Sle And Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (Dle).
Related Post: