Ana Fine Speckled Pattern
Ana Fine Speckled Pattern - Web scleroderma or systemic sclerosis: It’s the most common type of staining pattern. Ana pattern is most commonly speckled, followed by centromeric and less commonly nucleolar. The nucleoli may be stained or not stained. Fine and coarse speckles of ana staining are seen throughout the nucleus. A homogenous pattern can mean. Web the presence of ana with a homogeneous & speckled (hs) pattern was significantly associated with the absence of cancer ( < 0.01). Web for example, a positive dense fine speckled pattern as a result of ana iif test followed with confirmed single reactivity to dfs70 antigen indicates that the presence of the. Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations, and clinical relevance. Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations, and clinical relevance. A homogenous pattern can mean. The level or titer and the pattern. Web a homogeneous/peripheral pattern reflects antibodies to histone/dsdna/chromatin, whereas many other specificities found in systemic rheumatic diseases show speckled. Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations, and clinical relevance. Web the characteristic dense fine speckled (dfs) staining pattern of interphase cells is indicated. Fine tiny speckles across all nucleoplasm. The nucleoli may be stained or not stained. This pattern is more commonly associated with antibodies to extractable nuclear. Web the presence of ana with a homogeneous & speckled (hs) pattern was significantly associated with the absence of cancer ( < 0.01). Web scleroderma or systemic sclerosis: Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations, and clinical relevance. This pattern is more commonly associated with antibodies to extractable nuclear. Patients with a hs pattern were found. And if the ana test is positive, your blood can be tested for the presence of particular. Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets,. Web a health care provider may request that a patient have a test for antinuclear antibodies (ana) as part of an evaluation for possible autoimmune disease. Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations, and clinical relevance. The level or titer and the pattern. Web for example, a positive dense fine speckled pattern as a result. A homogenous staining pattern means the entire nucleus is stained with ana. Mitotic cells (metaphase, anaphase, and. Ana pattern is most commonly speckled, followed by centromeric and less commonly nucleolar. Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations, and clinical relevance. And if the ana test is positive, your blood can be tested for the presence. Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations, and clinical relevance. Fine and coarse speckles of ana staining are seen throughout the nucleus. Web indirect immunofluorescence (iif) is the most prevalent screening antinuclear antibody test for systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease (sard). Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations, and clinical relevance.. A homogenous staining pattern means the entire nucleus is stained with ana. Web antinuclear antibody panel (ana test) uses. Titres are reported in ratios, most often 1:40, 1:80, 1:160, 1:320, and 1:640. The level or titer and the pattern. Web the presence of ana with a homogeneous & speckled (hs) pattern was significantly associated with the absence of cancer (. Web the presence of ana with a homogeneous & speckled (hs) pattern was significantly associated with the absence of cancer ( < 0.01). Web for example, a positive dense fine speckled pattern as a result of ana iif test followed with confirmed single reactivity to dfs70 antigen indicates that the presence of the. And if the ana test is positive,. Ana pattern is most commonly speckled, followed by centromeric and less commonly nucleolar. Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations, and clinical relevance. Web for example, a positive dense fine speckled pattern as a result of ana iif test followed with confirmed single reactivity to dfs70 antigen indicates that the presence of the. Fine and. The level or titer and the pattern. Web a homogeneous/peripheral pattern reflects antibodies to histone/dsdna/chromatin, whereas many other specificities found in systemic rheumatic diseases show speckled. Fine tiny speckles across all nucleoplasm. Web while an ana test can't confirm a specific diagnosis, it can rule out some diseases. A homogenous pattern can mean. Dense fine speckled (dfs) pattern in antinuclear antibody (ana) test using indirect. Ana pattern is most commonly speckled, followed by centromeric and less commonly nucleolar. Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations, and clinical relevance. Web scleroderma or systemic sclerosis: Web a health care provider may request that a patient have a test for antinuclear antibodies (ana) as part of an evaluation for possible autoimmune disease. This pattern is more commonly associated with antibodies to extractable nuclear. And if the ana test is positive, your blood can be tested for the presence of particular. Certain iif patterns have known. Mitotic cells (metaphase, anaphase, and. Web while an ana test can't confirm a specific diagnosis, it can rule out some diseases. Fine tiny speckles across all nucleoplasm. Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations, and clinical relevance. Web indirect immunofluorescence (iif) is the most prevalent screening antinuclear antibody test for systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease (sard). Web for example, a positive dense fine speckled pattern as a result of ana iif test followed with confirmed single reactivity to dfs70 antigen indicates that the presence of the. Titres are reported in ratios, most often 1:40, 1:80, 1:160, 1:320, and 1:640. Fine and coarse speckles of ana staining are seen throughout the nucleus.
Figure 3 from The Clinical Significance of the Dense Fine Speckled

Ana With Speckled Pattern Chumado
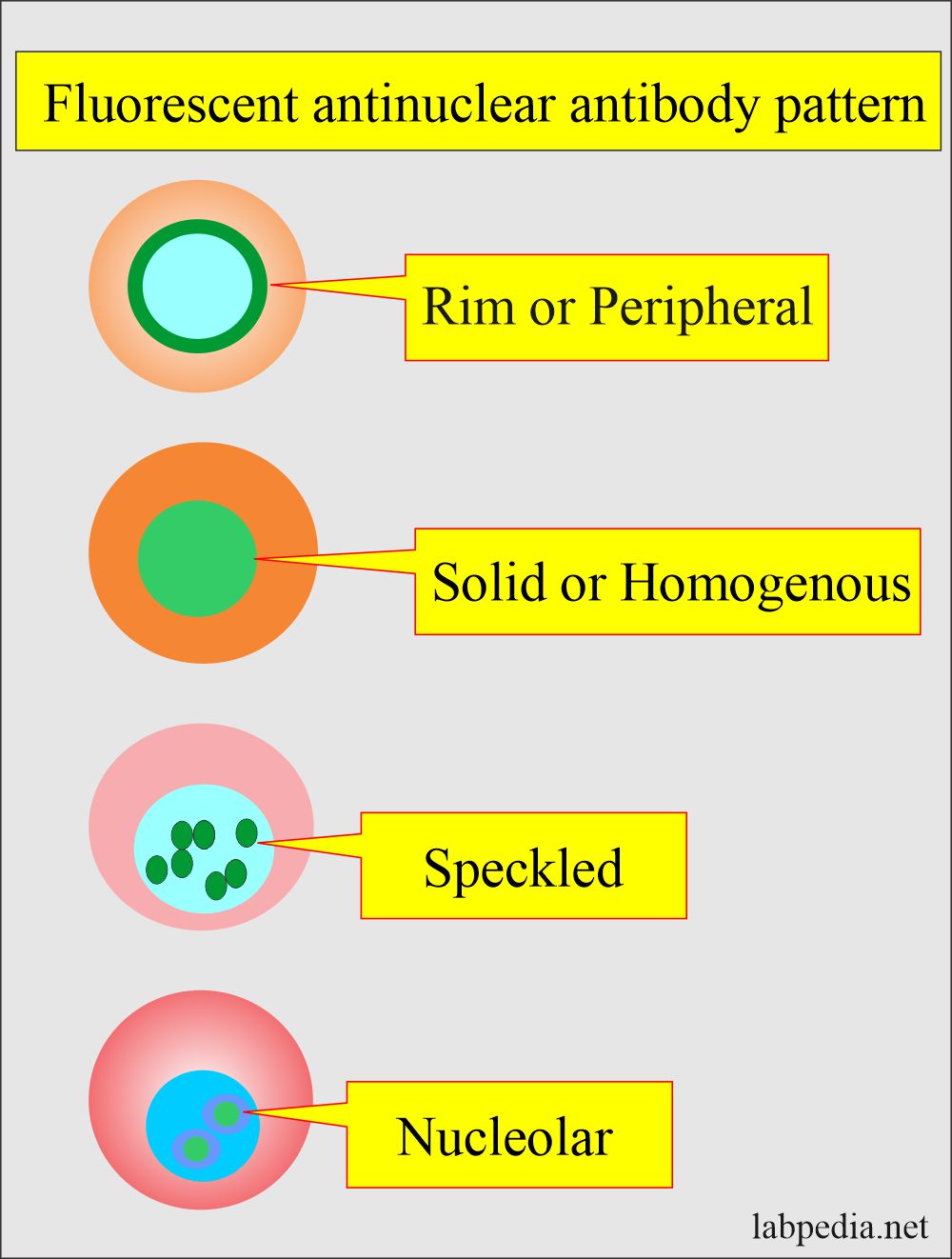
Antinuclear Factor (ANF), Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) and Its

Positive Ana Speckled Pattern Chumado
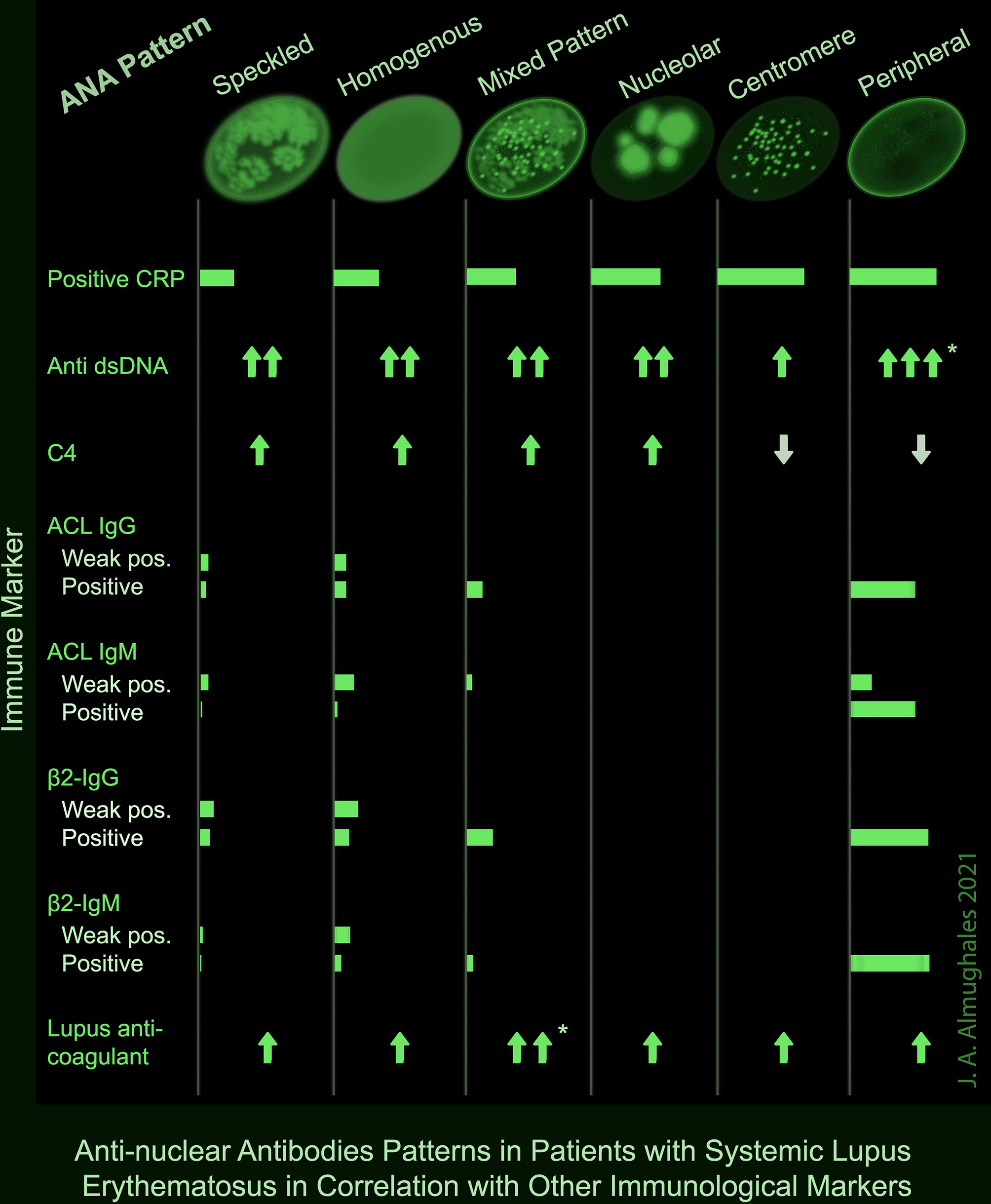
Frontiers AntiNuclear Antibodies Patterns in Patients With Systemic

Common ANA patterns by IIF a, negative sample; b, homogeneous; c
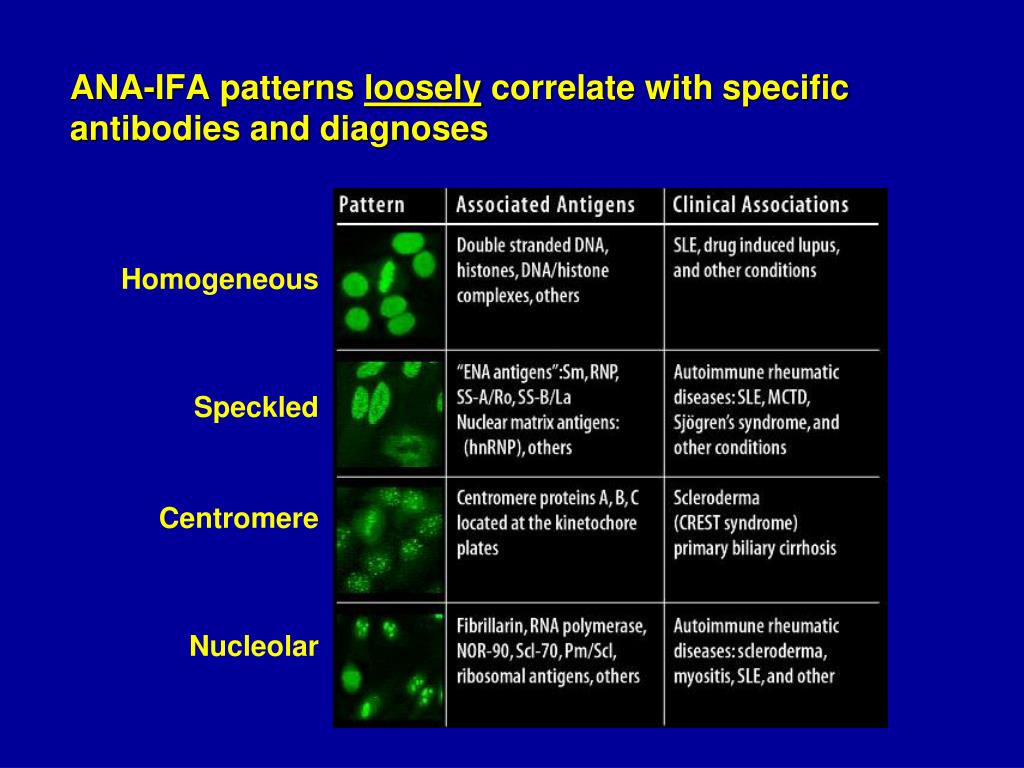
Ana Titer 1 160 Speckled Pattern Chumado

Ana Test Patterns

ANA Patterns
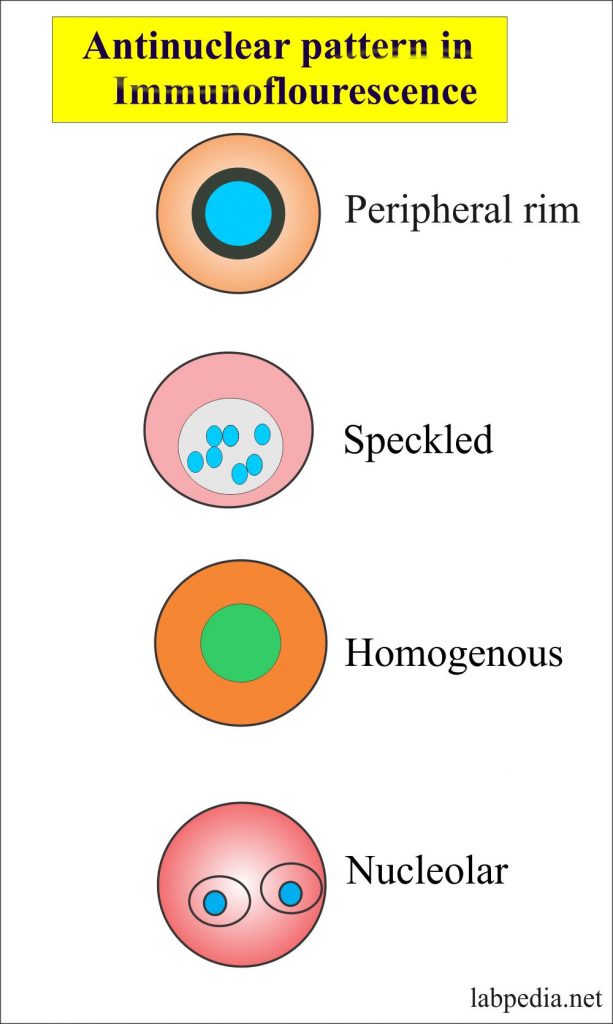
Positive Ana Speckled Pattern Chumado
This New Study Reports The Experience Of 4 Expert Laboratories On Ac.
A Homogenous Pattern Can Mean.
It’s The Most Common Type Of Staining Pattern.
Antibodies That Attack Healthy Proteins Within The Cell Nucleus Are Called Antinuclear.
Related Post: