Ana 1 640 Speckled Pattern
Ana 1 640 Speckled Pattern - Web positive results are reported as 1) the immunofluorescence pattern (eg homogenous, speckled etc) and 2) the titre to indicate if this is a high positive or low positive ana. Web the most frequently observed ana patterns were the speckled (52.1%) and homogeneous (35.2%) patterns, while other patterns were rare representing less. Thus, a titer of 1:640 shows a greater. Web we consider 1:640 a border point. Web most patients had reticular (51.0%) or speckled (46.4%) cytoplasmic ana patterns, while very few patients had fibrillar ana pattern (2.0%). Some, but not all labs will report a titre above 1:160 as positive. Ana pattern is most commonly speckled, followed by centromeric and less commonly nucleolar. This pattern is more commonly associated with antibodies to extractable nuclear. Web a positive nuclear staining result will usually come back with a more detailed staining pattern, such as speckled (fig. Patterns that are reported include, homogeneous, speckled, centromere, and others. Web a health care provider may request that a patient have a test for antinuclear antibodies (ana) as part of an evaluation for possible autoimmune disease. Common ana patterns and their associated systemic rheumatic diseases; What is the ana test, and why was it ordered? Craig et al4 found an ana titer of at least 1:64 in 15% of healthy. Autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis, graves' disease, hashimoto's thyroiditis, hepatitis c, hiv infection. Below 1:640 that we have less confidence that it is meaningful and more benign. Web a health care provider may request that a patient have a test for antinuclear antibodies (ana) as part of an evaluation for possible autoimmune disease. Demonstrated that 19% of patients with this. A speckled pattern may indicate various diseases,. Ana pattern is most commonly speckled, followed by centromeric and less commonly nucleolar. The titer gives information about how many times the lab technician diluted the blood plasma to get a. Web fluorescence pattern clinical significance* nuclear: Web a positive nuclear staining result will usually come back with a more detailed staining pattern,. Web a health care provider may request that a patient have a test for antinuclear antibodies (ana) as part of an evaluation for possible autoimmune disease. Web the most frequently observed ana patterns were the speckled (52.1%) and homogeneous (35.2%) patterns, while other patterns were rare representing less. Common ana patterns and their associated systemic rheumatic diseases; Some, but not. Web the most frequently observed ana patterns were the speckled (52.1%) and homogeneous (35.2%) patterns, while other patterns were rare representing less. Web fluorescence pattern clinical significance* nuclear: A speckled staining pattern means fine, coarse speckles of ana are present throughout the nucleus. Web usually, the results of the ana test are reported in titers and patterns. Demonstrated that 19%. Thus, a titer of 1:640 shows a greater. Ana pattern is most commonly speckled, followed by centromeric and less commonly nucleolar. Web most patients had reticular (51.0%) or speckled (46.4%) cytoplasmic ana patterns, while very few patients had fibrillar ana pattern (2.0%). Web a positive nuclear staining result will usually come back with a more detailed staining pattern, such as. Demonstrated that 19% of patients with this disease had positive ana at a level of 1 : Ana pattern associated rheumatic disease; Web the study by higashi et al. Patterns that are reported include, homogeneous, speckled, centromere, and others. A speckled pattern may indicate various diseases,. Web the analysis was performed for the most prevalent ana patterns (speckled, homogeneous, nucleolar and centromere) and only monospecific nuclear patterns were. Web a health care provider may request that a patient have a test for antinuclear antibodies (ana) as part of an evaluation for possible autoimmune disease. Web the titer shows how many times the patient's serum was diluted. Web the titer shows how many times the patient's serum was diluted before the antibodies could no longer be detected. In addition, it was demonstrated. Thus, a titer of 1:640 shows a greater. Web we consider 1:640 a border point. Some, but not all labs will report a titre above 1:160 as positive. Thus, a titer of 1:640 shows a greater. Demonstrated that 19% of patients with this disease had positive ana at a level of 1 : Higher than that we have more confidence that. Web a 1:640 titre has a likelihood ratio of 19, meaning that samples from patients with sle are 19 times more likely to give a positive test. Web the titer shows how many times the patient's serum was diluted before the antibodies could no longer be detected. Thus, a titer of 1:640 shows a greater. Web fluorescence pattern clinical significance* nuclear: Web a health care provider may request that a patient have a test for antinuclear antibodies (ana) as part of an evaluation for possible autoimmune disease. Higher than that we have more confidence that. Web most patients had reticular (51.0%) or speckled (46.4%) cytoplasmic ana patterns, while very few patients had fibrillar ana pattern (2.0%). In addition, it was demonstrated. Web the most frequently observed ana patterns were the speckled (52.1%) and homogeneous (35.2%) patterns, while other patterns were rare representing less. Ana pattern associated rheumatic disease; Titres are reported in ratios, most often 1:40, 1:80, 1:160, 1:320, and 1:640. Demonstrated that 19% of patients with this disease had positive ana at a level of 1 : Ana pattern is most commonly speckled, followed by centromeric and less commonly nucleolar. Fine and coarse speckles of ana staining are seen throughout the nucleus. Some, but not all labs will report a titre above 1:160 as positive. Autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis, graves' disease, hashimoto's thyroiditis, hepatitis c, hiv infection. Craig et al4 found an ana titer of at least 1:64 in 15% of healthy women younger than 40 years and 24% of.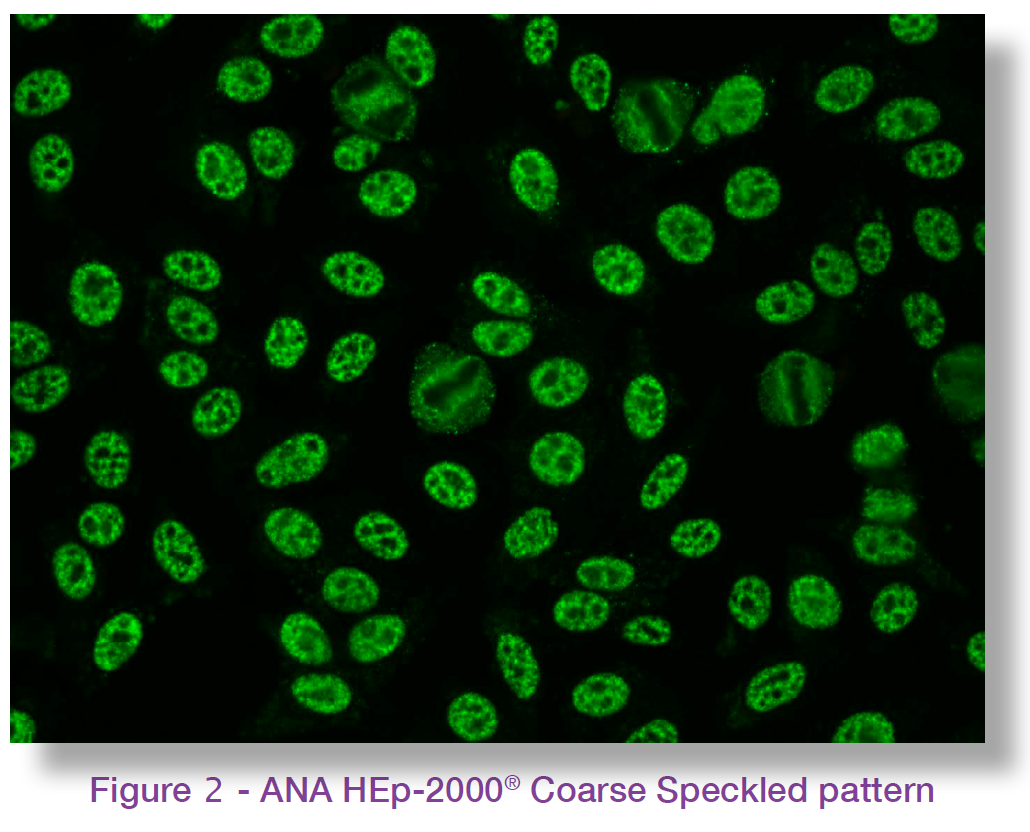
Immuno Concepts Technical Bulletin Reporting Homogeneous and Speckled

Speckled type ANA patern Download Scientific Diagram

ANA Patterns
[Solved] Based on the staining seen on these substrates identify the

ANA Patterns
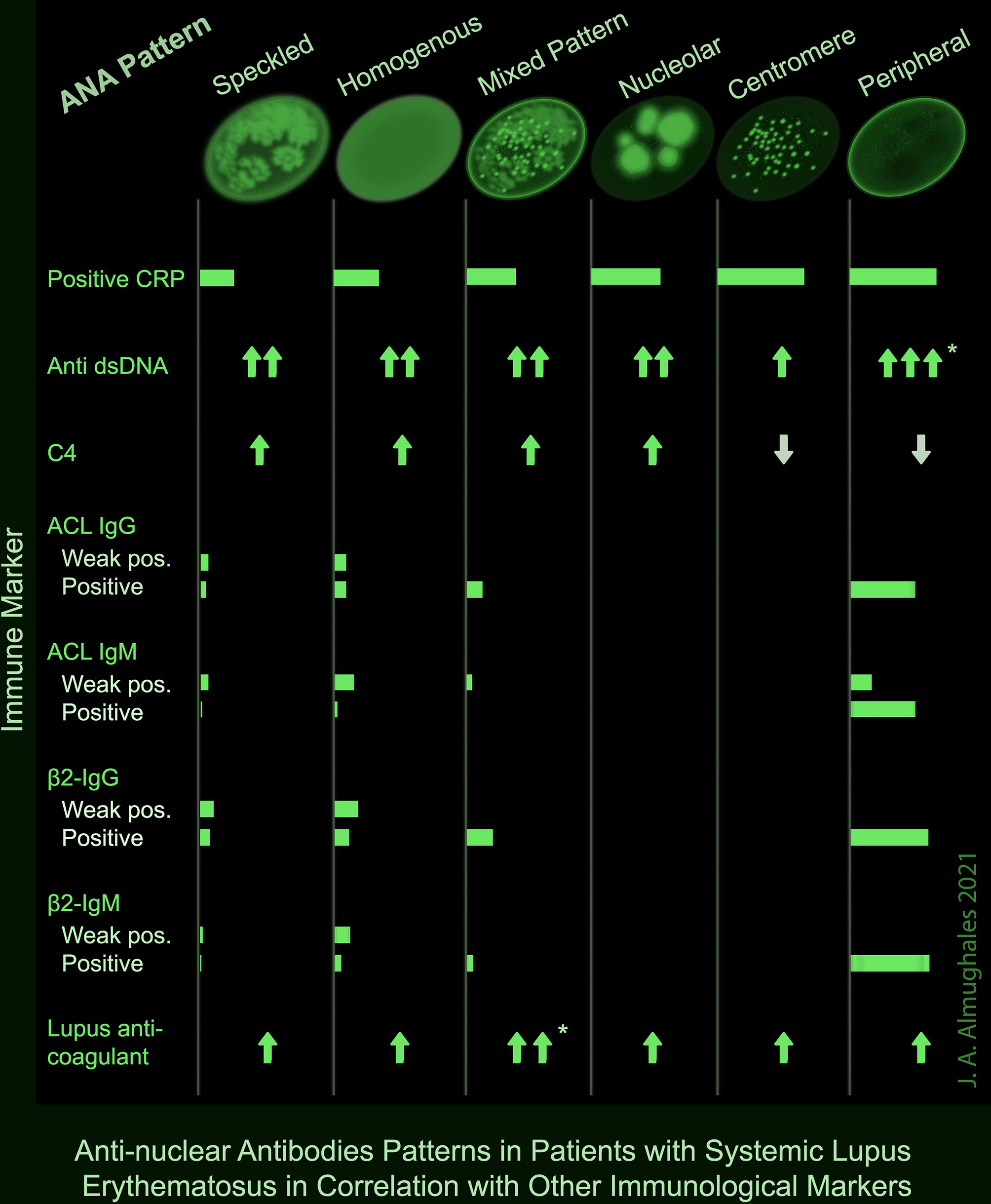
Frontiers AntiNuclear Antibodies Patterns in Patients With Systemic
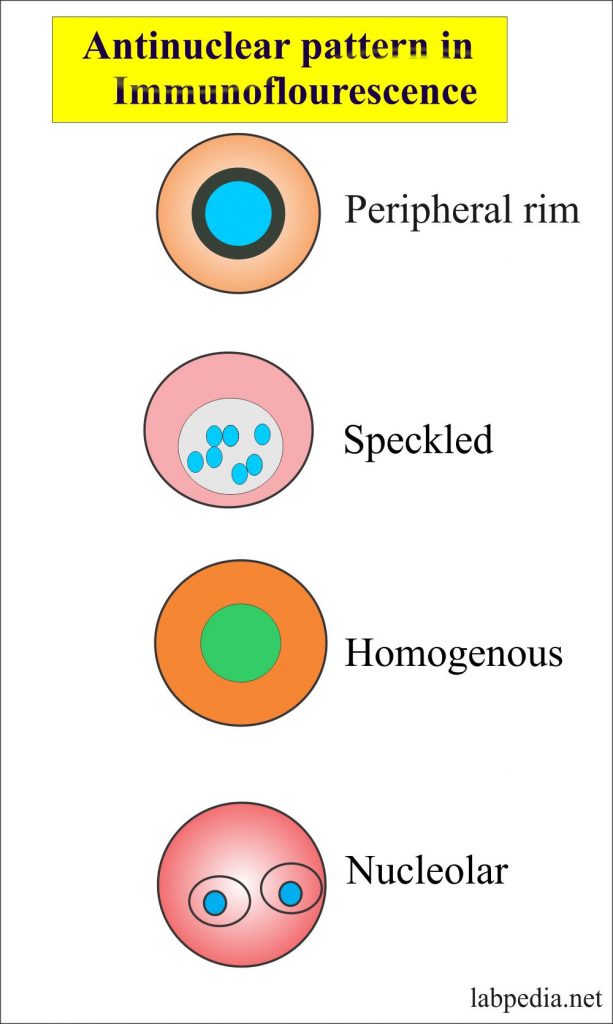
Antinuclear Factor (ANF), Antinuclear Antibody ANA)
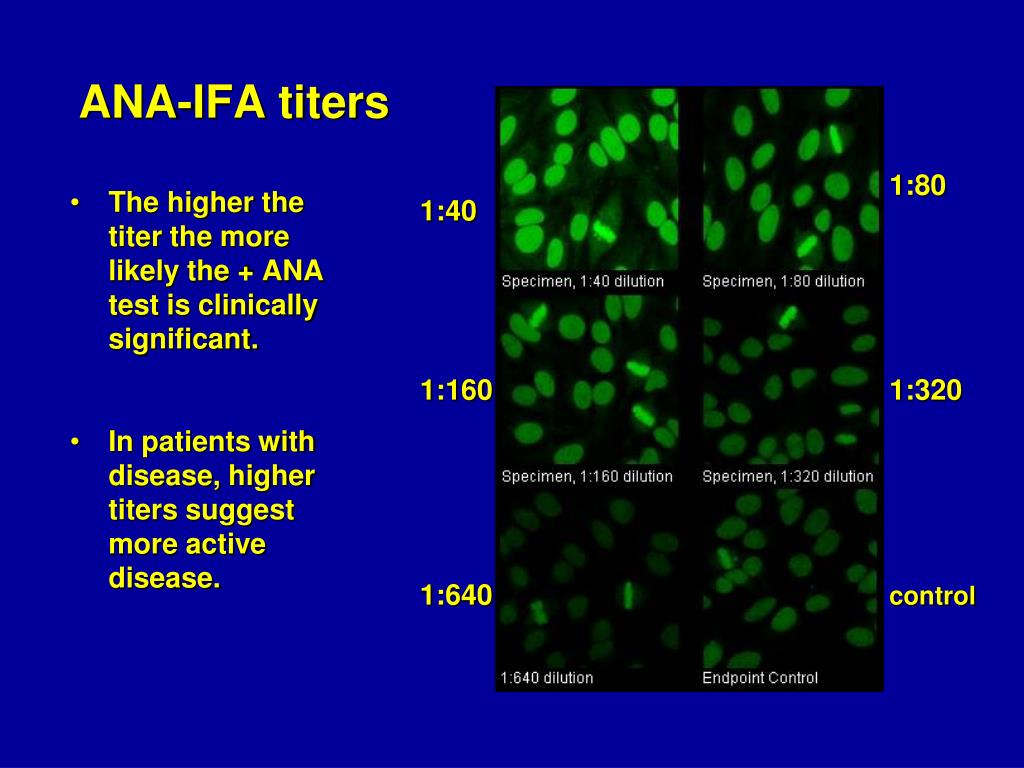
PPT Choosing the Correct ANA Technology for your Laboratory
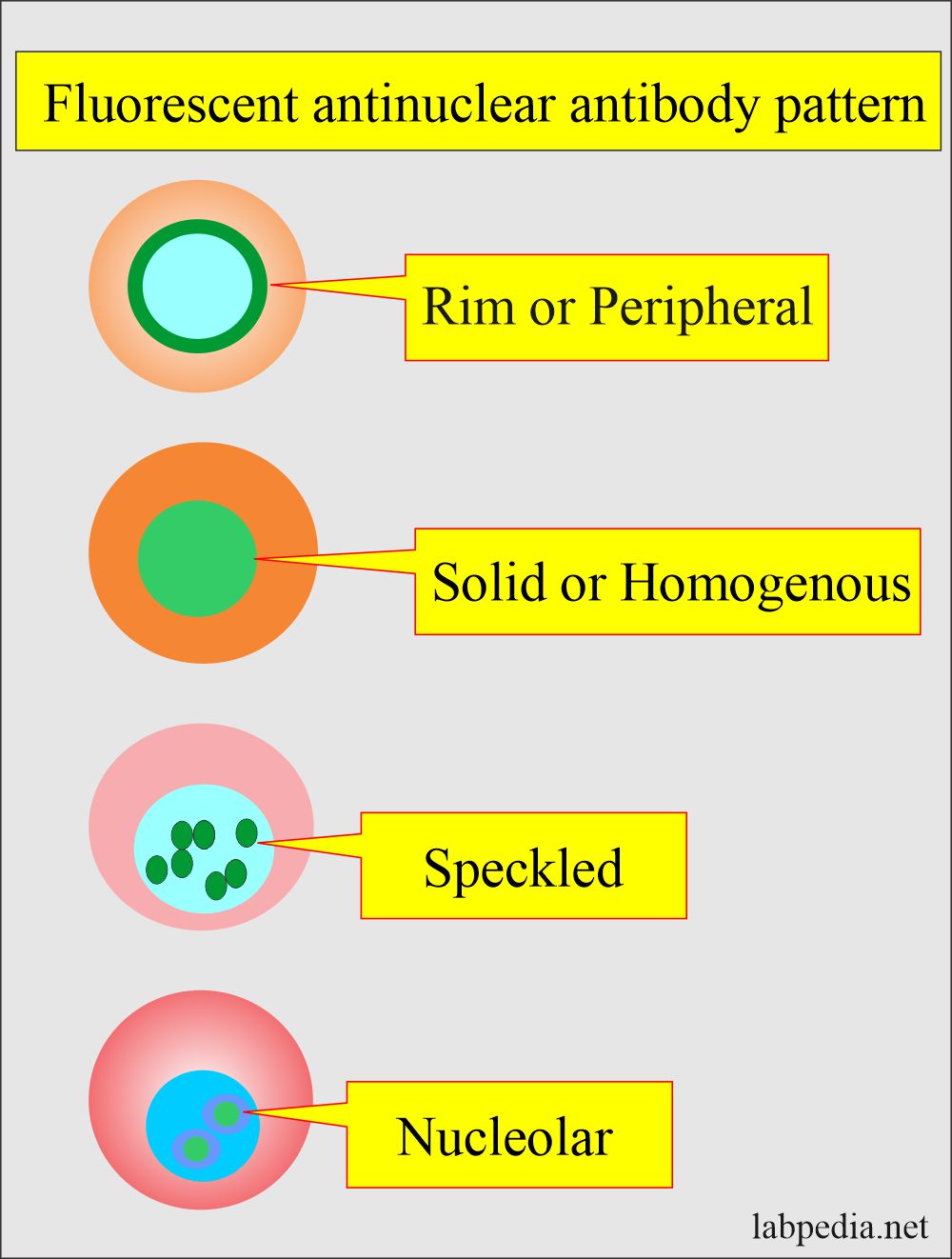
Antinuclear Factor (ANF), Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) and Its

Common ANA patterns by IIF a, negative sample; b, homogeneous; c
A Speckled Staining Pattern Means Fine, Coarse Speckles Of Ana Are Present Throughout The Nucleus.
The Titer Gives Information About How Many Times The Lab Technician Diluted The Blood Plasma To Get A.
Web Usually, The Results Of The Ana Test Are Reported In Titers And Patterns.
Web The Analysis Was Performed For The Most Prevalent Ana Patterns (Speckled, Homogeneous, Nucleolar And Centromere) And Only Monospecific Nuclear Patterns Were.
Related Post: