Alveolar Pattern
Alveolar Pattern - The majority can be readily detected in chest radiographs, but some cases. The patterns of lung damage associated with various. If pulmonary vessels are visible but have fuzzy margins, giving the appearance of “trees in a fog”, that is an interstitial pattern. Web whenever you see an area of increased density within the lung, it must be the result of one of these four patterns. It can sometimes have a central perihilar pattern. List five broad categories of chronic ald. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage is persistent or recurrent pulmonary hemorrhage that originates from the lung parenchyma (ie, the alveoli) as opposed to the airways. We then present the typical radiological appearances alongside macroscopic and. Web interstitial and alveolar patterns essentially sit at different points on a continuum and are created by degrees of increased pulmonary opacity which partially or completely obscure the pulmonary vessels. There are 3 general patterns of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. Web female sex was a protective factor in the timing of abg in our initial univariate analysis (or = 0.44; There are numerous causes, but autoimmune disorders are most common. Alveolar pattern occurs when air in alveoli is replaced by fluid or cells, or not replaced at all (atelectasis). Difficult to diagnose and uncommon, requiring a high index of suspicion.. Difficult to diagnose and uncommon, requiring a high index of suspicion. Unique patterns of lower respiratory tract microbiota are associated with inflammation and hospital mortality in acute respiratory distress syndrome. In the pulmonary consolidation, the bronchovascular structures are obscured. List five common causes of acute respiratory distress syndrome. The majority can be readily detected in chest radiographs, but some cases. P =.018) and public insurance status (or = 3.75; Suggest a specific diagnosis of ald when supportive findings are present. For each entity, the latest findings as to its pathogenesis, aetiology and pathology are reviewed in the introductory remarks. Radiographic signs of an alveolar pattern include: P =.015).socioeconomic factors resulting in delayed presentation for abg include median income (or =. Radiographic signs of an alveolar pattern include: Alveolar pattern occurs when air in alveoli is replaced by fluid or cells, or not replaced at all (atelectasis). The patterns of lung damage associated with various. There are 3 general patterns of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. Uniform, homogeneous fluid opacity, varying from faint or fluffy, to solid, complete opacification. Web an alveolar pattern is characterized by one or more of the following radiographic features: In the pulmonary consolidation, the bronchovascular structures are obscured. The imaging studies show ground glass infiltrates or areas of consolidation (the radiologic correlate of alveolar filling). This condition is caused by collapsed alveoli or infiltration (cellular or fluid types) of the alveolar lumen, which results. For each entity, the latest findings as to its pathogenesis, aetiology and pathology are reviewed in the introductory remarks. Radiographic signs of an alveolar pattern include: A total collapse of the alveoli (atelectasis) leads to a similar appearance. List four broad categories of acute alveolar lung disease (ald). Web an alveolar pattern is characterized by one or more of the. Web an interstitial lung pattern is a regular descriptive term used when reporting a plain chest radiograph. Web an alveolar pattern is characterized by one or more of the following radiographic features: Suggest a specific diagnosis of ald when supportive findings are present. Difficult to diagnose and uncommon, requiring a high index of suspicion. Alveolar pattern occurs when air in. Radiographic signs of an alveolar pattern include: Difficult to diagnose and uncommon, requiring a high index of suspicion. (1) an air bronchogram, (2) a lobar sign, or (3) an area of relatively intense opacity that does not have the sharp margins that characterize a lung mass. Web kyo m, nishioka k, nakaya t, et al. Web 6 patterns > alveolar. Radiographic signs include border effacement with other soft tissue structures such as the pulmonary vessels, cardiac silhouette or diaphragm. Web the alveolar pattern is indicative of lack of air in the alveoli. For each entity, the latest findings as to its pathogenesis, aetiology and pathology are reviewed in the introductory remarks. Web female sex was a protective factor in the. An alveolar pattern is defined by the existence of more or less broad portions of the lung more opaque than normal due to partial or complete alveolar filling. Web interstitial vs alveolar patterns. You have selected the alveolar filling pattern! Web 6 patterns > alveolar filling. There are numerous causes, but autoimmune disorders are most common. The pattern of fibrosis depends not so much on the nature of the damage as its severity. With a few exceptions, the pulmonary architecture is overall preserved, and, if signs of interstitial involvement are present, they are not prevalent. Web interstitial vs alveolar patterns. There are 3 general patterns of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. Web the alveolar pattern is the imaging representation of a variety of diseases that tend to occupy the lung airspaces. Web whenever you see an area of increased density within the lung, it must be the result of one of these four patterns. Web an alveolar pattern is characterized by one or more of the following radiographic features: (1) an air bronchogram, (2) a lobar sign, or (3) an area of relatively intense opacity that does not have the sharp margins that characterize a lung mass. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage is persistent or recurrent pulmonary hemorrhage that originates from the lung parenchyma (ie, the alveoli) as opposed to the airways. Difficult to diagnose and uncommon, requiring a high index of suspicion. Web an alveolar pattern is the result of fluid (pus, edema, blood), or less commonly cells within the alveolar space. Web an interstitial lung pattern is a regular descriptive term used when reporting a plain chest radiograph. The majority can be readily detected in chest radiographs, but some cases. Web the alveolar pattern is indicative of lack of air in the alveoli. In the pulmonary consolidation, the bronchovascular structures are obscured. List five common causes of acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Chest radiograph showing bilateral interstitialalveolar pattern

Alveolar pattern Radiopaedia
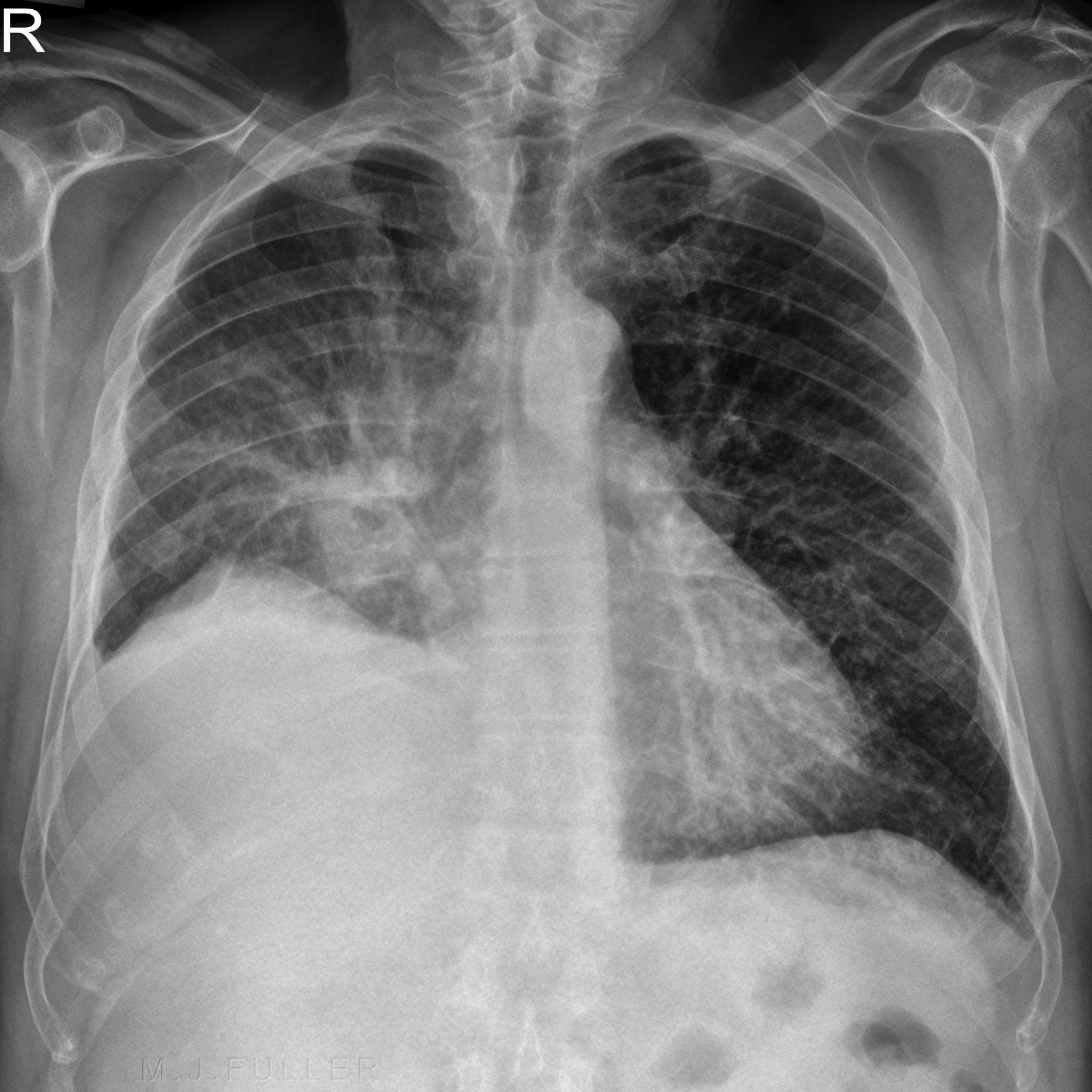
Interstitial vs Alveolar Lung Patterns wikiRadiography

The chest Xray finding of case 2. Diffuse alveolar pattern of
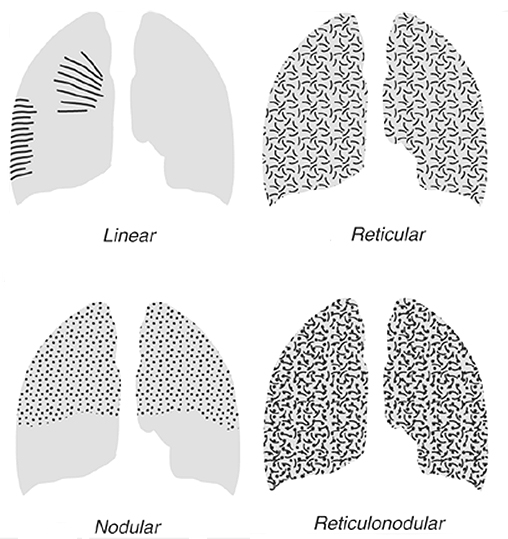
Interstitial vs Alveolar Lung Patterns wikiRadiography
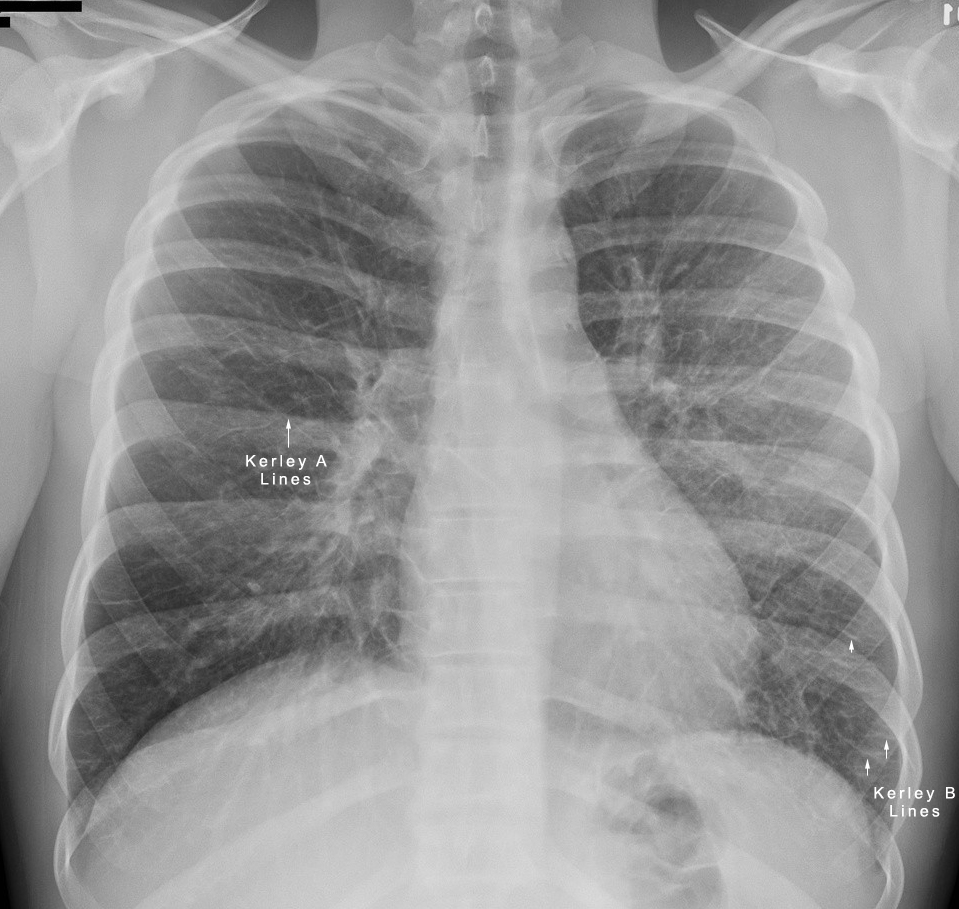
Interstitial vs Alveolar Lung Patterns wikiRadiography

Meet the Patient Radiology Rules

Thoracic radiographic image in the right lateral view showing alveolar

Chest XRay Lung disease FourPattern Approach NCLEX Quiz

Meet the Patient Radiology Rules
(Not All Signs Seen In Every Case) 1.
Radiographic Signs Include Border Effacement With Other Soft Tissue Structures Such As The Pulmonary Vessels, Cardiac Silhouette Or Diaphragm.
P =.018) And Public Insurance Status (Or = 3.75;
We Then Present The Typical Radiological Appearances Alongside Macroscopic And.
Related Post: