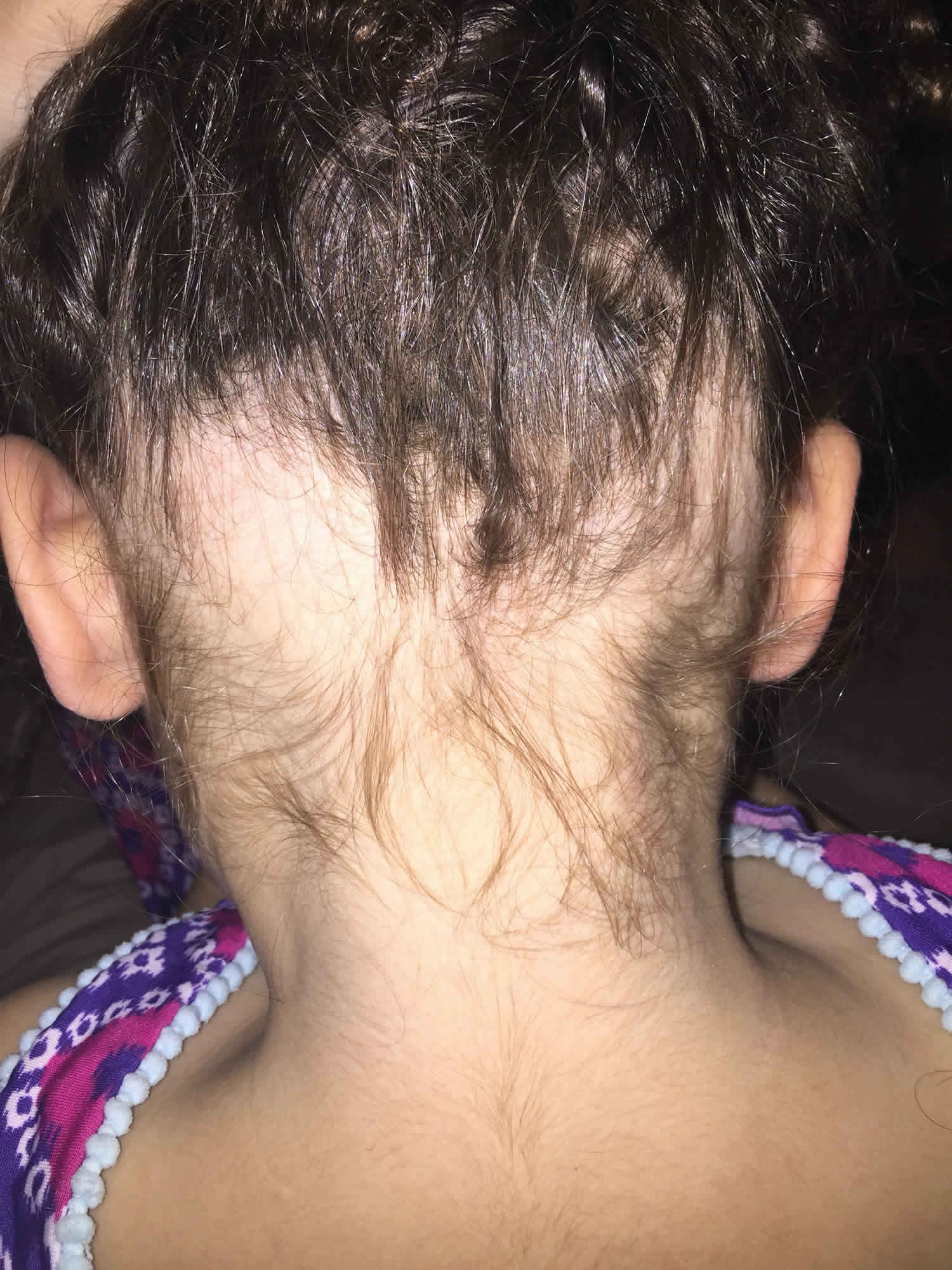
Alopecia Ophiasis Pattern
Alopecia Ophiasis Pattern - Sixty percent of cases present before 20 years of age; Extensive hair loss is experienced in coalescent patches (i.e. Ophiasis alopecia is another alopecia areata type. Web there are many clinical presentations and subtypes of alopecia areata (aa). Web alopecia areata is an autoimmune form of hair loss seen regularly in primary care. Patch subtype with multiple coalescing patches. Web since ophiasis alopecia is a form of alopecia areata, it is likely caused by an autoimmune response which attacks the hair on the back of your scalp and the area around your ears (and, in very rare cases, the hairline). 1, 2 one subtype, the ophiasis form, affects the occipital and parietal scalp and is often more resistant to treatment than aa monolocularis and aa multilocularis (ie, patchy aa). Diffuse alopecia areata (alopecia areata incognita) — rapid and widespread hair loss. Web alopecia areata most often is asymptomatic, but some patients (14%) experience a burning sensation or pruritus in the affected area. Patch subtype with solitary patch. All races and males and females are affected equally. Web alopecia areata can be classified according to its pattern, as follows: 1, 2 one subtype, the ophiasis form, affects the occipital and parietal scalp and is often more resistant to treatment than aa monolocularis and aa multilocularis (ie, patchy aa). With all types of alopecia. Patch subtype with multiple coalescing patches. The most common is patch, with circular patches recognizable on the scalp or beard areas which may coalesce with progression. Web aa can present in several patterns, which are often more therapeutically challenging: Web traction alopecia may present in an ophiasis pattern from hair care practices. With all types of alopecia areata, hair loss. Web aa can present in several patterns, which are often more therapeutically challenging: In this pattern, hair loss is localised and presents on the lower back and sides of the scalp (similar to that of an undercut). With all types of alopecia areata, hair loss and regrowth can be very unpredictable and cyclical (happen over and over). Patches that unite. Web alopecia areata is an autoimmune form of hair loss seen regularly in primary care. Family physicians are well placed to identify aa, characterize the severity of disease, and form an appropriate differential diagnosis. Patches that unite to form one mass). Patch subtype with multiple coalescing patches. Alopecia areata appears to affect both sexes equally and can occur in all. Clinical patterns of hair loss in alopecia areata are usually very distinct. Who is at risk for developing alopecia areata? Patches that unite to form one mass). Web traction alopecia may present in an ophiasis pattern from hair care practices. Family physicians are well placed to identify aa, characterize the severity of disease, and form an appropriate differential diagnosis. Web severe aa manifestations or certain clinical subtypes are rarer, with the prevalence of ophiasis type, alopecia totalis (at), alopecia universalis (au) being 0.02 %, 0.08 % and 0.03 % respectively. The hair loss occurs in a band along the sides and back of the head. The most common is patch, with circular patches recognizable on the scalp or beard. The most common is patch, with circular patches recognizable on the scalp or beard areas which may coalesce with progression. Sixty percent of cases present before 20 years of age; With all types of alopecia areata, hair loss and regrowth can be very unpredictable and cyclical (happen over and over). A person with round bald patches from alopecia areata. Web. With all types of alopecia areata, hair loss and regrowth can be very unpredictable and cyclical (happen over and over). Web traction alopecia may present in an ophiasis pattern from hair care practices. Web clinical patterns of hair loss in alopecia areata are usually very distinct. The cases of interest are presented in addition to a brief review of hairweaving. 1, 2 one subtype, the ophiasis form, affects the occipital and parietal scalp and is often more resistant to treatment than aa monolocularis and aa multilocularis (ie, patchy aa). The cases of interest are presented in addition to a brief review of hairweaving practices and hairweave removal techniques. The most common pattern is a small annular or patchy bald lesion. Web alopecia areata is an autoimmune form of hair loss seen regularly in primary care. 1 c), sisaipho (opposite of ophiasis, central hair loss resembling androgenetic alopecia) and alopecia reticularis (active, stable and resolving patches present at the same moment) [ 6 ]. Family physicians are well placed to identify aa, characterize the severity of disease, and form an appropriate. The most common pattern is a small annular or patchy bald lesion (patchy alopecia areata), usually on the scalp, that can progress to total loss of scalp hair only (alopecia totalis), and total loss of all body hair (alopecia universalis) ( box 2 ). Sixty percent of cases present before 20 years of age; Depending on its acuity and extent, hair loss is an important cause of anxiety and disability. The cases of interest are presented in addition to a brief review of hairweaving practices and hairweave removal techniques. Family physicians are well placed to identify aa, characterize the severity of disease, and form an appropriate differential diagnosis. A person with round bald patches from alopecia areata. The hair loss occurs in a band along the sides and back of the head. With all types of alopecia areata, hair loss and regrowth can be very unpredictable and cyclical (happen over and over). Web alopecia areata can be classified according to its pattern, as follows: 1, 2 one subtype, the ophiasis form, affects the occipital and parietal scalp and is often more resistant to treatment than aa monolocularis and aa multilocularis (ie, patchy aa). Ophiasis [1] is a form of alopecia areata characterized by the loss of hair in the shape of a wave at the circumference of the head. Patch subtype with solitary patch. Patch subtype with multiple coalescing patches. Web alopecia areata is an autoimmune form of hair loss seen regularly in primary care. The condition usually is localized when it first appears. Web severe aa manifestations or certain clinical subtypes are rarer, with the prevalence of ophiasis type, alopecia totalis (at), alopecia universalis (au) being 0.02 %, 0.08 % and 0.03 % respectively.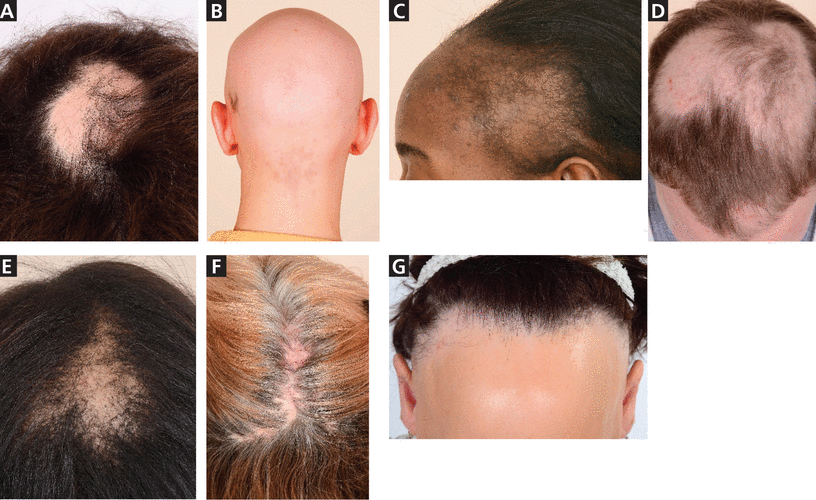
Male and female pattern hair loss Treatable and worth treating
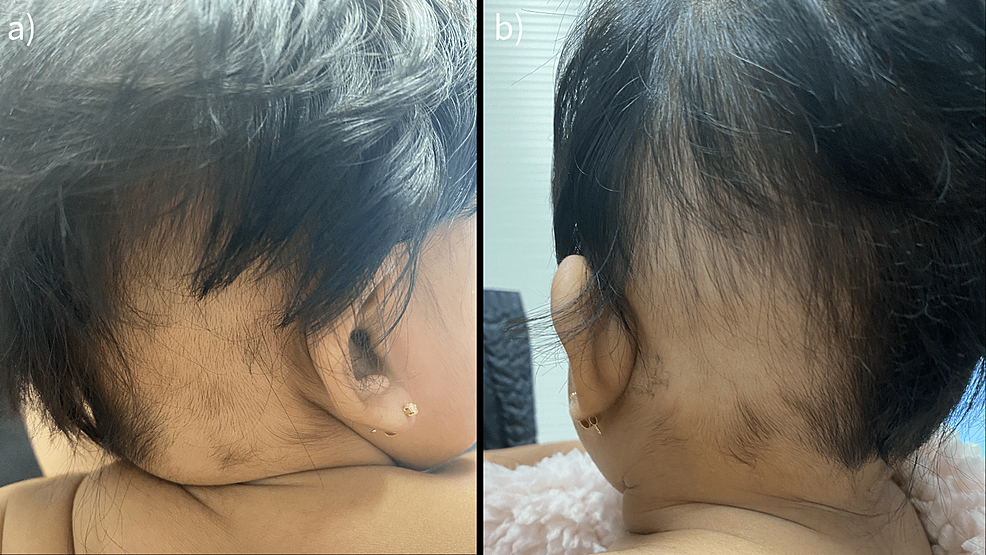
Cureus Ophiasis Pattern Alopecia Areata in an Infant
Ophiasis Alopecia Areata
Ophiasis, definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment & prognosis

Stages of Alopecia HealthGardeners

Comparing Ophiasis Alopecia Areata to Occipital Frontal Fibrosing
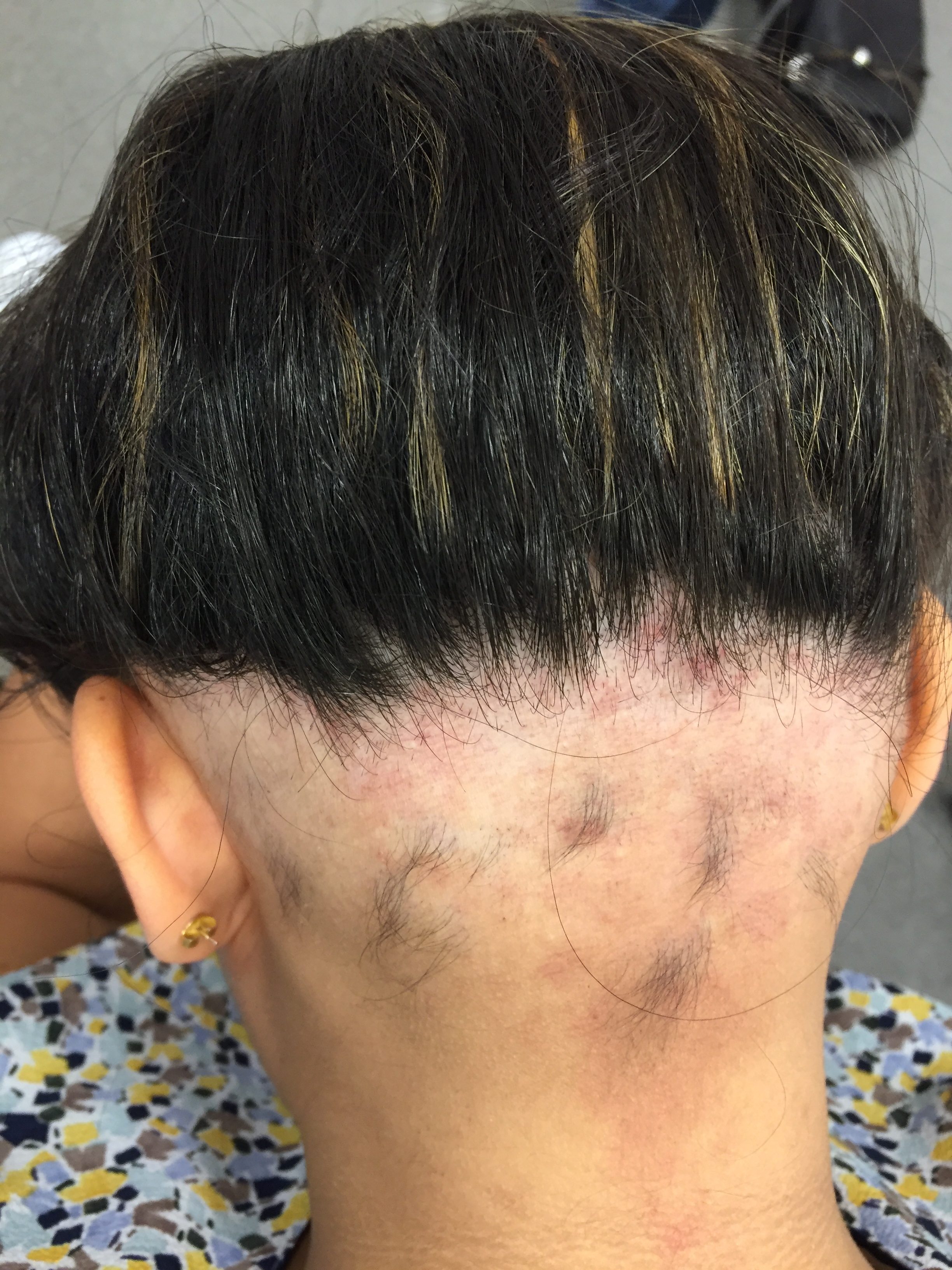
Contour Dermatology Ophiasis pattern of halo hairloss
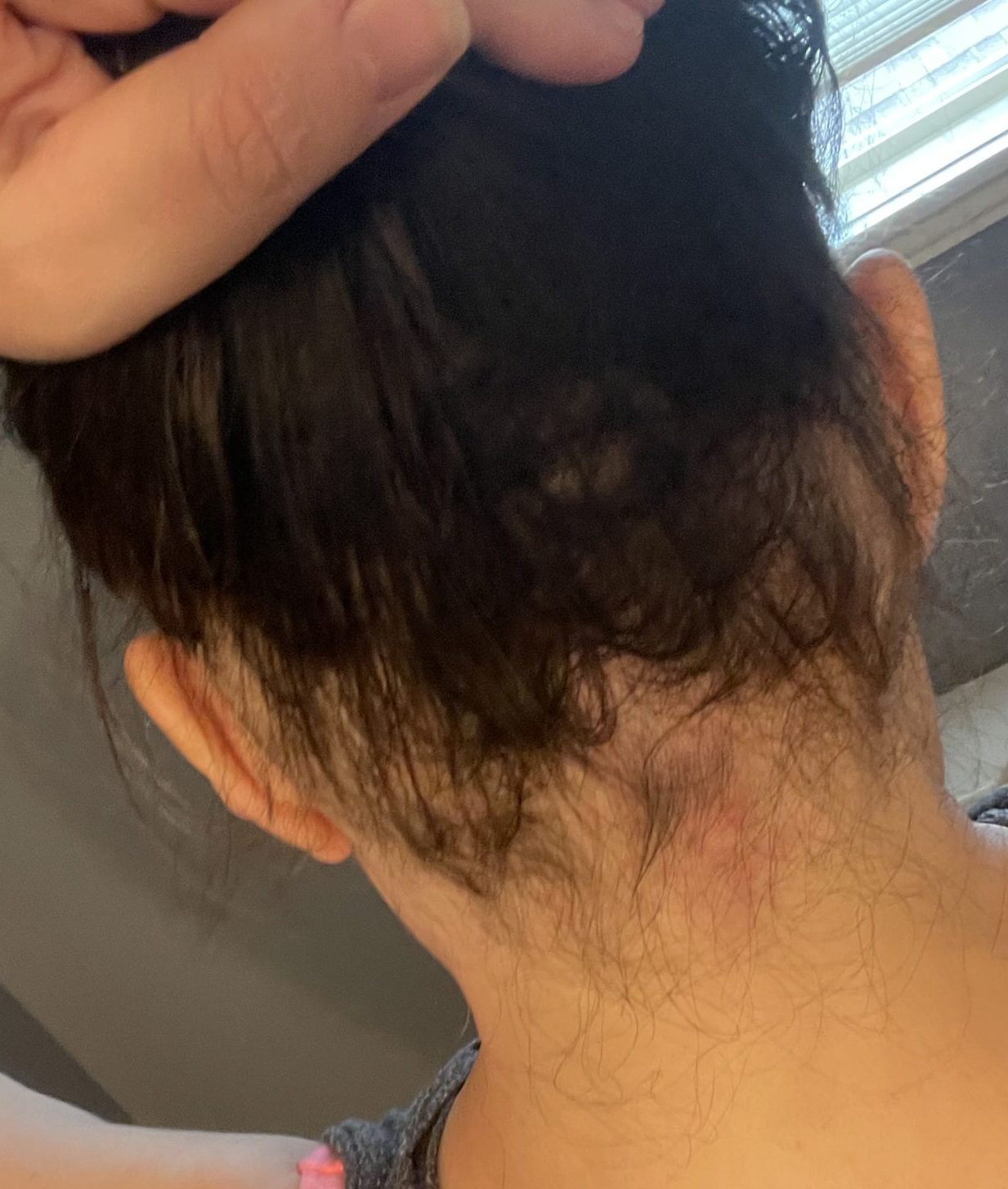
Ophiasis Alopecia Update End Of May To End Of August

Alopecia areata update Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology

What is Alopecia? Beverly Hills Hair Restoration
Ophiasis Alopecia Is Another Alopecia Areata Type.
Alopecia Areata Appears To Affect Both Sexes Equally And Can Occur In All Age Groups And Ethnic Backgrounds [ 6, 8 ].
It Is Often Refractory To Conventional Treatments And Has A Less Favorable Prognosis.
The Lifetime Risk Is 1.7%.
Related Post: